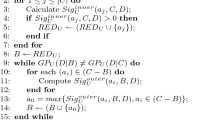Abstract
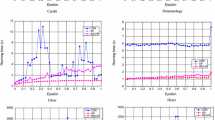
Minimal attribute reduction plays an important role in rough set. Heuristic algorithms are proposed in literature reviews to get a minimal reduction and yet an unresolved issue is that many redundancy non-empty elements involving duplicates and supersets exist in discernibility matrix. To be able to eliminate the related redundancy and pointless elements, in this paper, we propose a compactness discernibility information tree (CDI-tree). The CDI-tree has the ability to map non-empty elements into one path and allow numerous non-empty elements share the same prefix, which is recognized as a compact structure to store non-empty elements in discernibility matrix. A complete algorithm is presented to address Pawlak reduction based on CDI-tree. The experiment results reveal that the proposed algorithm is more efficient than the benchmark algorithms to find out a minimal attribute reduction.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chen D, Zhao S, Zhang L et al (2012) Sample pair selection for attribute reduction with rough set. IEEE Trans Knowl Data Eng 24(11):2080–2093
Ding W, Wang J, Guan Z (2012) Cooperative extended rough attribute reduction algorithm based on improved PSO. J Syst Eng Electron 23(1):160–166
Feng JIANG, Sha-sha WANG, Jun-wei DU et al (2015) Attribute reduction based on approximation decision entropy. Control Decis 30(1):65–70
Han JW, Pei J, Yin YW (2000) Mining frequent patterns without candidate generation. Weidong C, Jeffrey F, Proceedings of the ACM SIGMOD conference on management of data. ACM Press, Dallas, pp 1–12
Huilian FAN, Yuanchang ZHONG (2012) A rough set approach to feature selection based on wasp swarm optimization. J Comput Inf Syst 8(3):1037–1045
Jiang Yu, Wang Xie, Ye Zhen (2008) Attribute reduction algorithm of rough sets based on discernibility matrix. J Syst Simul 20(14):3717–3720, 3725
Jiang Y (2012) Minimal attribute reduction for rough set based on attribute enumeration tree. Int J Adv Comput Technol 4(19):391–399
Jian-hua ZHOU, Zhang-yan XU, Chen-guang ZHANG (2014) Quick attribute reduction algorithm based on the improved discernibility matrix. J Chin Comput Syst 35(4):831–834
Jing S-Y (2014) A hybrid genetic algorithm for feature subset selection in rough set theory. Soft Comput 18(7):1373–1382
Johnson DS (1974) Approximation algorithms for combinatorial problems. J Comput Syst Sci 9:256–278
Jue W, Ju W (2001) Reduction algorithms based on discernibility matrix: the ordered attributes method. J Comput Sci Technol 16(6):489–504
Lakshmipathi Raju NVS, Dr MN, Seetaramanath D, Srinivasa Rao P et al (2013) Rough set based privacy preserving attribute reduction on horizontally partitioned data and generation of rules. Int J Adv Res Comput Commun Eng 2(11):4343–4348
Mafarja M, Eleyan D (2013) Ant colony optimization based feature selection in rough set theory. Int J Comput Sci Electron Eng 1(2):244–247
Nguyen T-T, Nguyen P-K (2013) Reducing attributes in rough set theory with the viewpoint of mining frequent patterns. Int J Adv Comput Sci Appl 4(4):130–138
Pawlak Z (1982) Rough sets. Int J Comput Inf Sci 11(5):341–356
Pawlak Z (1991) Rough set: theoretical aspects of reasoning about data. Kluwer Academic Publishers, Boston
Pratiwi L, Choo Y-H et al (2013) Immune ant swarm optimization for optimum rough reducts generation. Int J Hybrid Intell Syst 10(3):93–105
Qian YH, Liang JY, Pedrycz W, Dang CY (2010) Positive approximation: an accelerator for attribute reduction in rough set theory. Artif Intell 174:597–618
Skowron A, Rauszer C (1992) The discernibility matrices and functions in information systems. In: Slowinski R (ed) Intelligent decision support. Handbook of Applications and Advances of the Rough Sets Theory, Kluwer, Dordrecht
Slowinski R (1992) Intelligent decision support–handbook of applications and advances of the rough sets theory. Kluwer Academic Publishers, London
Thangavel K, Pethalakshmi A (2009) Dimensionality reduction based on rough set theory: a review. Appl Soft Comput 9:1–12
Vinterbo S, Øhrn A (2000) Minimal approximate hitting sets and rule templates. Int J Approx Reason 25(2):123–143
Wang GY, Zhao J, An JJ (2005) A comparative study of algebra viewpoint and information viewpoint in attribute reduction. Fundam Inf 68(3):289–301
Wong SKM, Ziarko W (1985) On optional decision rules in decision tables. Bull Polish Acad Sci 33(11/12):693–696
Xin-min TAO, Yan WANG, Jing XU et al (2012) Minimum rough set attribute reduction algorithm based on viruscoordinative discrete particle swarm optimization. Control Decis 27(2):259–265
Yang M, Yang P (2008) A novel condensing tree structure for rough set feature selection. Neurocomputing 71(4):1092–1100
Yang M, Yang P (2011) A novel approach to improving C-Tree for feature selection. Appl Soft Comput 11(2):1924–1931
Yao YY, Zhao Y (2009) Discernibility matrix simplification for constructing attribute reducts. Inf Sci 179(5):867–882
Ye D, Chen Z (2014) A new approach to minimum attribute reduction based on discrete artificial bee colony. Soft Comput. doi:10.1007/s00500-014-1371-0
Yu JIANG, Yin-Tian LIU, Chao LI (2011) Fast algorithm for computing attribute reduction based on bucket sort. Control Decis 26(2):207–212
Zhang WenXiu W, WeiZhi LJY et al (2001) Rough set theory and method. Beijing Science Press, Beijing
Zhang Q, Shen W (2014) Research on attribute reduction algorithm with weights. J Intell Fuzzy Syst 27(2):1011–1019
Zheng J, Yan R (2012) Attribute reduction based on cross entropy in rough set theory. J Inf Comput Sci 9(3):745–750
Zhou J, Miao D, Feng Q et al. (2009) Research on complete algorithms for minimal attribute reduction. In: Proceedings of the 4th international conference on rough sets and knowledge technology. Gold Coast, Australia, pp 152–159
Zhou J, Miao D, Feng Q, Sun L (2009) Research on complete algorithms for minimal attribute reduction. Rough sets and knowledge technology, volume 5589 of lecture notes in computer science. Springer, Berlin, pp 152–159
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by V. Loia.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jiang, Y., Yu, Y. Minimal attribute reduction with rough set based on compactness discernibility information tree. Soft Comput 20, 2233–2243 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00500-015-1638-0
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00500-015-1638-0