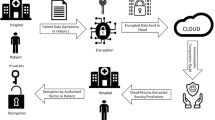
Abstract
Face recognition is one of the most important biometrics pattern recognitions, which has been widely applied in a variety of enterprise, civilian and law enforcement. The privacy of biometrics data raises important concerns, in particular if computations over biometric data is performed at untrusted servers. In previous work of privacy-preserving face recognition, in order to protect individuals’ privacy, face recognition is performed over encrypted face images. However, these results increase the computation cost of the client and the face database owners, which may enable face recognition not to be executed. Consequently, it would be desirable to reduce computation cost over sensitive biometric data in such environments. Currently, no secure techniques for outsourcing face biometric recognition are readily available. In this paper, we propose a privacy-preserving face recognition protocol with outsourced computation for the first time, which efficiently protects individuals’ privacy. Our protocol substantially improves the previous works in terms of the online computation cost by outsourcing large computation task to a cloud server who has large computing power. In particular, the overall online computation cost of the client and the database owner in our protocol is at most 1/2 of the corresponding protocol in the state-of-the-art algorithms. In addition, the client requires the decryption operations with only O(1) independent of M, where M is the size of the face database. Furthermore, the client can verify the correctness of the recognition result.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Avidan S, Butman M (2006) Efficient methods for privacy preserving face detection. In: Advances in neural information processing systems (NIPS’06), pp 57–64
Bhattacharjee D, Basu DK, Nasipuri M, Kundu M (2010) Human face recognition using fuzzy multilayer perceptron. Soft Comput 14(6):559–570
Blanton M, Aliasgari M (2012) Secure outsourced computation of Iris matching. J Comput Security 20(2):259–305
Boyen X (2004) Reusable cryptographic fuzzy extractors. In: Proceedings of the 11th ACM conference on Computer and communications security, pp 82–91
Castiglione A, Pizzolante R, De-Santis A, Carpentieri B, Castiglione A, Palmieri F (2015) Cloud-based adaptive compression and secure management services for 3D healthcare data. Futur Gener Comput Syst 1(43):120–134
Chang EC, Li Q (2006) Hiding secret points amidst chaff. In: Advances in Cryptology-EUROCRYPT, vol. LNCS 4004, pp 59–72
Chen XF, Li J, Ma J, Tang Q, Lou W (2014) New algorithms for secure outsourcing of modular exponentiations. IEEE Trans Parallel Distrib Syst 9(25):2386–2396
Damgard IB, Jurik MJ (2001) A generalisation, a simplification and some applications of paillier’s probabilistic public-key system. In: Public-Key Cryptography (PKC’01), vol LNCS 1992, pp 119–136
Damgard I, Geisler M, Kroigard M (2008) Homomorphic encryption and secure comparison. J Appl Cryptol 1(1):22–31
Damgard I, Geisler M, Kroigard M (2007) Efficient and secure comparison for online auctions. In: Australasian Conference on Information Security and Privacy (ACISP’07), vol LNCS 4586, pp 416–430
Dijk MV, Gentry C, Halevi S, Vaikuntanathan V (2010) Fully homomorphic encryption over the integers. In: Advances in Cryptology—ASIACRYPT 2010, vol LNCS 6110, pp 24–43
Dodis Y, Ostrovsky R, Reyzin L, Smith A (2008) Fuzzy extractors: how to generate strong keys from biometrics and other noisy data. SIAM J Comput 38(1):97–139
Dodis Y, Reyzin L, Smith A (2004) Fuzzy extractors: How to generate strong keys from biometrics and other noisy data. In: Advances in cryptology-Eurocrypt, vol LNCS 3027, pp 523–540
Dufaux F, Ebrahimi T (2006) Scrambling for video surveillance with privacy. In: Computer vision and pattern recognition workshop, New York, pp 160–160
Erkin Z, Franz M, Guajardo J, Katzenbeisser S, Lagendijk I, Toft T (2009) Privacy-preserving face recognition. In: Privacy Enhancing Technologies (PET’09), vol LNCS 5672, pp 235–253
Esposito C, Ficco M, Palmieri F, Castiglione A (2013) Interconnecting federated clouds by using publish-subscribe service. Clust Comput 16(4):887–903
Esposito C, Ficco M, Palmieri F, Castiglione A (2015) Smart cloud storage service selection based on fuzzy logic. IEEE Trans Comput, Theory Evid Game Theory (99). doi:10.1109/TC.2015.2389952
Juels A, Sudan M (2006) A fuzzy vault scheme. Des Codes Cryptogr 38(2):237–257
Kevenaar T (2007) Protection of Biometric Information. In: Security with Noisy Data, pp 169–193
Li ZZ, Lai TH (2012) Deterministic fully homomorphic encryptions for privacy preserving cloud computing. http://web.cse.ohio-state.edu/-lizh/
Li J, Huang X, Li JW, Chen XF, Xiang Y (2014) Securely outsourcing attribute-based encryption with checkability. IEEE Trans Parallel Distrib Syst 25(8):2201–2210
Li J, Chen XF, Li MQ, Li JW, Lee P, Lou WJ (2014a) Secure deduplication with efficient and reliable convergent key management. IEEE Trans Parallel Distrib Syst 25(6):1615–1625
Li J, Chen XF, Li JW, Jia CF, Ma JF, Lou WJ (2013) Fine-grained access control based on outsourced attribute-based encryption. In: Proceeding of The European Symposium on Research in Computer Security (ESORICS), vol LNCS 3184, pp 592–609
Lindell Y, Pinkas B (2004) A proof of Yao’s protocol for secure two-party computation. In: Cryptology ePrint Archive, Report 2004/175
Linnartz J, Tuyls P (2003) New shielding functions to enhance privacy and prevent misuse of biometric templates. In: International Conference on Audio and Video Based Biometric Person Authentication, pp 393–402
Liu XZ, Ye HW (2014) Dual-kernel based 2D linear discriminant analysis for face recognition. J Ambient Intell Hum Comput (4). doi:10.1007/s12652-014-0230-2
Li J, Wang Q, Wang C, Cao N, Ren K, Lou W (2010) Fuzzy keyword search over encrypted data in cloud computing. In: proceeding of the 29th IEEE International Conference on Computer Communications(INFOCOM 2010), pp 441–445
Naumann I, Hogben G (2008) Privacy features of European aid card specifications. In: Network Security, European Network and Information Security Agency (ENISA), vol 8, pp 9–13
Newton EM, Sweeney L, Malin B (2005) Preserving privacy by de-identifying face images. IEEE Trans Knowl Data Eng 17(2):232–243
Paillier P (1999) Public-key cryptosystems based on composite degree residuosity classes. In Advances in Cryptology-EUROCRYPT’99, vol LNCS 1592, pp 223–238
Ratha NK, Connell JH, Bolle RM (2001) Enhancing security and privacy in biometrics-based authentication systems. IBM Syst J 40(3):614–634
Ratha N, Connell J, Bolle R, Chikkerur S (2006) Cancelable biometrics: A case study in fingerprints. In: Proceedings of the 18th International Conference on Pattern Recognition (ICPR), vol IV, pp 370–373
Sadeghi AR, Schneider T, Wehrenberg I (2010) Efficient Privacy-Preserving Face Recognition. In: Information, Security and Cryptology-ICISC 2009, vol LNCS 5984, pp 229–244
Tang CM, Chen YN (2014) Efficient non-interactive verifiable outsourced computation for arbitrary functions. http://eprint.iacr.org/2014/439
Turk MA, Pentland AP (1991) Face recognition using eigenfaces. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Computer vision and pattern recognition (CVPR’91), pp 586–591
Tuyls P, Akkermans AH, Kevenaar TA, Schrijen GJ, Bazen AM, Veldhuis RN (2005) Practical biometric authentication with template protection. In: Audio- and video-based biometric person authentication (AVBPA), vol LNCS 3546, 436–446
Wang YJ, Wu QH, Wong DS, Qin B, Chow SSM, Liu Z, Tan X (2014) Securely outsourcing exponentiations with single untrusted program for cloud storage. Comput Secur-ESORICS 2014:326–343
Yao AC (1986) How to generate and exchange secrets. In: Foundations of Computer Science, 1986, 27th Annual Symposium, pp 162–167
Yu X, Chinomi K, Koshimizu T, Nitta N, Ito Y, Babaguchi N (2008) Privacy protecting visual processing for secure video surveillance. In: Proceedings of the International Conference on Image Processing (ICIP’08), pp 1672–1675
Acknowledgments
This work is supported in part by the National Natural Science Foundation of China under Grant No. 11271003, the National Research Foundation for the Doctoral Program of Higher Education of China under Grant No. 20134410110003, High Level Talents Project of Guangdong, Guangdong Provincial Natural Science Foundation under Grant No. S2012010009950, the Project of Department of Education of Guangdong Province under Grant No. 2013KJ-CX0146, the Natural Science Foundation of Bureau of Education of Guangzhou under Grant No. 2012A004, the basic research major projects of Department of Education of Guangdong Province under Grant No. 2004KZDXM044, and the Guangzhou Zhujiang Science and Technology Future Fellow Fund under Grant No. 2012J2200094.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by V. Loia.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xiang, C., Tang, C., Cai, Y. et al. Privacy-preserving face recognition with outsourced computation. Soft Comput 20, 3735–3744 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00500-015-1759-5
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00500-015-1759-5