Abstract
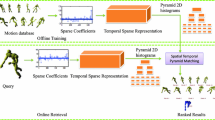
A novel motion retrieval method which combines semantic analysis with graph model is proposed. The method includes 2 main stages: (1) in stage of learning, firstly, we can get the Motion Semantic Dictionary (MSD) and the Motion Code Table (MCT) by clustering and handmade based on motion training data learning. Next, the MSD and the MCT are used to calculate system parameters, and the Hidden Markov Model (HMM) is built. For each motion in testing data, aligned cluster analysis (ACA) is used to get key frames, and semantic code is got based on HMM inference. All semantic codes of testing data are combined to construct the Semantic Code Book (SCB). (2) In stage of motion retrieval, according to the above steps, query motion code is got, and the query motion is recognized based on motion code matching. Our method has lesser time and cost than existing algorithms. The experimental results show that the proposed method is effectiveness.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baak A, Müller M, Seidel HP (2008) An efficient algorithm for keyframe-based motion retrieval in the presence of temporal deformations. ACM Conf Multimed Inf Retr:451–458
Chakrabarti K, Keogh E, Mehrotra S, Pazzani M (2002) Locally adaptive dimensionality reduction for indexing large time series databases. ACM Trans Database Syst 27(2):188–228
Chen C, Yang Y, Nie F, Odobez JM (2011) 3D human pose recovery from image by efficient visual feature selection. Comput Vis Image Underst 115(3):290–299
Chen C, Zhuang Y, Nie F (2011) Learning a 3D human pose distance metric from geometric pose descriptor. IEEE Trans Vis Comput Graph 17(11):1676–1689
Graphics Lab “Motion Capture Database”. Carnegie Mellon University. http://mocap.cs.cmu.edu/
Gross JL, Yellen J (2011) Graph theory and its applications, 2nd edn. Chapman and Hall/CRC, Boca Raton
Hachaj T, Ogiela MR (2012) Semantic description and recognition of human body poses and movement sequences with Gesture Description Language. In: Kim TH et al. (eds) Computer applications for bio-technology, multimedia and ubiquitous city, CCIS 353. Springer, Heidelberg, pp 1–8
Hachaj T, Ogiela MR (2014) Rule-based approach to recognizing human body poses and gestures in real time. Multimed Syst 20:81–99
Keogh E, Palpanas T, Zordan V, Gunopulos D, Cardle M (2004) Indexing large human-motion databases. Proc VLDB:780–791
Kovar L, Gleicher M (2004) Automated extraction and parameterization of motions in large data sets. ACM Trans Graph 23(3):559–568
Kovar L, Gleicher M (2004) Automated extraction and parameterization of motions in large data sets. ACM Trans Graph 23(3):559–568
Kovar L, Gleicher M, Pighin F (2002) Motion graphs. Proc ACM SIGGRAPH:473–482
Krüger B, Tautges J, Weber A, Zinke A (2010) Fast local and global similarity searches in large motion capture databases. Eurogr ACM SIGGRAPH Symp Comput Anim
Lin Y (2006) Efficient human motion retrieval in large databases. Proc ACM Graph:31–37
Ma Z, Nie F, Yang Y, Uijlings J, Sebe N, Hauptmann AG (2012) Discriminating joint feature analysis for multimedia data understanding. IEEE Trans Multimed 14(6):1662–1672
Müller M, Röder T, Clausen M (2005) Efficient content-based retrieval of motion capture data. ACM Trans Graph 24(3):677–685
Müller M, Röder T (2006) Motion templates for automatic classification and retrieval of motion capture data. Eurogr ACM SIGGRAPH Symp Comput Anim
Ogiela L, Ogiela MR (2011) Semantic analysis processes in advanced pattern understanding systems. In: Kim TH et al. (eds) AST 2011, CCIS 195. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg, pp 26–30
Salton G, McGill MJ (1983) Introduction to modern information retrieval. McGraw-Hill, New York
Tian JW, Qi WH, Liu XX (2011) Retrieving deep web data through multi-attributes interfaces with structured queries. Int J Softw Eng Knowl Eng 21(4):523–542
Yang Y, Zhuang Y, Pan Y (2008) Harmonizing hierarchical manifolds for multimedia document semantics understanding and cross-media retrieval. IEEE Trans Multimed 10(3):437–446
Yang Y, Nie F, Xu D, Luo J, Zhuang Y, Pan Y (2012) A multimedia retrieval framework based on semi-supervised ranking and relevance feedback. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 34(4):723–742
Zhang Z, Tao D (2012) Slow feature analysis for human action recognition. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 34(3):436–450
Zhou F, De la Torre F, Hodgins JK (2013) Hierarchical aligned cluster analysis for temporal clustering of human motion. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 35(3):582–596
Zhou F, De La Torre F (2012) Factorized graph matching. IEEE Comput Soc Conf Comput Vis Pattern Recogn:127–134
Zhou F, De La Torre F (2013) Deformable graph matching. IEEE Comput Soc Conf Comput Vis Pattern Recogn:2922–2929
Acknowledgments
This work is partly supported by the National Science Foundation of China (Nos. 60972095, 61271362).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Communicated by V. Loia.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xiao, Q., Song, R. Motion retrieval based on Motion Semantic Dictionary and HMM inference. Soft Comput 21, 255–265 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00500-016-2059-4
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00500-016-2059-4