Abstract
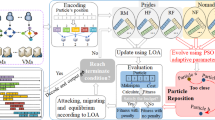
Owing to its manifold advantages in adapting cloud computing for real-world scientific workflow applications, we intend to use cloud computing for executing the scientific workflows. In the present work, we aim for scheduling the workflow in the scalable resources in the cloud. In general, security is a vital challenge in cloud and so we include security constraints into our optimization model. The main objective of our work is to find an optimized schedule having minimum makespan and cost and by satisfying security demand constraint. The users can submit their security demand to the cloud provider during negotiation. The workflow is initially scheduled with list-based heuristics, which is then optimized by Particle Swarm Optimization (PSO). Thus we device a Smart Particle Swarm Optimization (SPSO)-based secured scheduling to find the optimized schedule with minimum makespan and cost. The proposed method is capable of assigning the task in the scientific workflows to the best suitable virtual machine in the cloud. Hence, the resource allocation is addressed as well by our method. Besides, a variant of PSO algorithm called Variable Neighbourhood PSO is also experimented to overcome the local optima problem. Our experimental results show that the scheduled workflows with assured security are yielding better makespan than existing methods with minimum iterations, which is well suited for cloud environment.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abraham A, Liu H, Chang TG (2006) Variable neighborhood Particle Swarm Optimization Algorithm. In: GECCO ’06 Seattle, WA, USA Copyright ACM
Arabnejad H, Barbosa JG (2014) List scheduling algorithm for heterogeneous systems by an optimistic cost table. IEEE Trans Parallel Distrib Syst 25:682–694
Beegom ASA, Rajasree MS (2014) A Particle Swarm Optimization based pareto optimal task scheduling in cloud computing. In: Tan Y, Shi Y, Coello CAC (eds) Advances in Swarm Intelligence: 5th international conference, ICSI 2014, Hefei, China, October 17–20, 2014, Proceedings, Part II. Springer International Publishing, Cham, pp 79–86. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-11897-0_10
Berriman GB, Deelman E, et al. (2004) Montage: a grid-enabled engine for delivering custom science-grade mosaics on demand. In: SPIE conference on astronomical telescopes and instrumentation
Bilogrevic I, Jadliwala M, Kumar P, Walia SS, Hubaux JP, Aad I, Niemi V (2011) Meetings through the cloud: privacy-preserving scheduling on mobile devices. J Syst Softw 84:1910–1927
Calheiros RN, Ranjan R, Beloglazov A, DeRose CA, Buyya R (2011) CloudSim: a toolkit for modeling and simulation of cloud computing environments and evaluation of resource provisioning algorithms. Softw Pract Exp 41(1):23–50
Canon LC, Jeannot E, Sakellariou R, Zheng W (2008) Comparative evaluation of the robustness of dag scheduling heuristics. In: Gorlatch S, Fragopoulou P, Priol P (eds) Grid computing: achievements and prospects. Springer, New York, pp 73–84
Chakraborty D, Guha D, Dutta B (2016) Multi-objective optimization problem under fuzzy rule constraints using particle swarm optimization. Soft Comput 20(6):2245–2259
Chen W, Deelman E (2012) WorkflowSim: a toolkit for simulating scientific workflows in distributed environments. In: IEEE 8th International Conference on E-Science (e-Science), pp 1–8
Gens F (2008) IT cloud services user survey, pt.2: top benefits & challenges, October 2008. URL: http://blogs.idc.com/ie/?p=210
Graves R, Jordan T, Callaghan S, Deelman E, Field E et al (2010) Cybershake: a physics-based seismic hazard model for southern California. Pure Appl Geophys 168(3–4):367–381
Hansen P, Mladenovic N, Perez JM (2010) Variable neighbourhood search: methods and applications. Ann Oper Res 175(1):67–407
Juve G, Chervenak A, Deelman E, Bharathi S, Mehta G, Vahi K (2013) Characterizing and profiling scientific workflows. Future Gener Comput Syst 29(3):682–92
Kalra M, Singh S (2015) A review of metaheuristic scheduling techniques in cloud computing. Egypt Inf J 16:275–295
Kennedy J (1998) The behavior of particles. In: Porto VW, Saravana N, Waagen D, Eiben AE Proceedings of the 7th conference on evolutionary programming, pp 581–589
Kennedy J, Eberhart RC, Shi Y (2001) Swarm intelligence. Morgan Kaufmann Publishers, San Francisco
Li K, Tang X, Veeravalli B, Li K (2015) Scheduling precedence constrained stochastic tasks on heterogeneous cluster systems. IEEE Trans Comput 64(1):191–204
Liu H, Abraham A (2007) An hybrid fuzzy variable neighborhood particle swarm optimization algorithm for solving quadratic assignment problems. J Univers Comput Sci 13(9):1309–1331
Liu H, Abraham A, Snasel V, McLoone S (2012) Swarm scheduling approaches for work-flow applications with security constraints in distributed data-intensive computing environments. Inf Sci 192:228–243
Liu G, Zeng Y, Li D, Chen Y (2015) Schedule length and reliability-oriented multi-objective scheduling for distributed computing. Soft Comput 19(6):1727–1737
Marinakis Y, Marinaki M (2013) Particle swarm optimization with expanding neighborhood topology for the permutation flowshop scheduling problem. Soft Comput 17(7):1159–1173
Mell P, Grance T (2011) The NIST definition of cloud computing. Special Publication, pp 800–145
Montage: an astronomical image mosaic engine (2015) http://montage.ipac.caltech.edu/
Pandey S, Wu L, Guru SM, Buyya R (2010) A Particle Swarm Optimization-based Heuristic for scheduling workflow applications in cloud computing environments. In: 24th IEEE international conference on advanced information networking and applications, pp 400–407. https://doi.org/10.1109/AINA.2010.31
Pegasus Workflow Management System (2015) https://pegasus.isi.edu/projects/pegasus/
Pritzker P (2013) NIST cloud computing standards roadmap Working Group NIST Cloud Computing Standards Roadmap. National Institute of Standards and Technology Special Publication, pp 500–291, 108 pages
Rodriguez MA, Buyya R (2014) Deadline based resource provisioning and scheduling algorithm for scientific workflows on clouds. IEEE Trans Cloud Comput 2(2):222–235
Schema of workflow in XML format (2015) http://pegasus.isi.edu/wms/docs/schemas/dax-3.4/dax-3.4.html
Selvi T, Govindarajan K (2014) CLOUDRB: a framework for scheduling and managing high-performance computing (HPC) applications in science cloud. Future Gener Comput Syst 34:47–65
Sih GC, Lee EA (1993) A compile-time scheduling heuristic for interconnection-constrained heterogeneous processor architecture. IEEE Trans Parallel Distrib Syst 4(2):175–187
Song S, Hwang K, Kwok Y-K (2006) Risk-resilient heuristics and genetic algorithms for security-assured grid job scheduling. IEEE Trans Comput 55(6):703–719
Sujana JAJ, Revathi T, Malarvizhili M (2015) Scheduling of scientific workflows in cloud with replication. Appl Math Sci 9(46):2273–2280
Tan WA, Sun Y, Li LX, Lu GZ, Wang T (2014) A trust service-oriented scheduling model for workflow applications in cloud computing. IEEE Syst J 8(3):868–878
Tang X, Li K, Liao G, Li R (2010) List scheduling with duplication for heterogeneous computing systems. J Parallel Distrib Comput 70:323–329
Tang X, Li K, Zeng Z, Veeravalli B (2011) A novel security-driven scheduling algorithm for precedence-constrained tasks in heterogeneous distributed systems. IEEE Trans Comput 60(7):1017–1029
Topcuoglu H, Hariri S, Wu MY (2002) Performance-effective and low complexity task scheduling for heterogeneous computing. IEEE Trans Parallel Distrib Syst 13(3):260–274
USC Epigenome Center (2015) http://epigenome.usc.edu
Wang W, Zeng G, Tang D, Yao J (2012) Cloud-DLS: dynamic trusted scheduling for cloud computing. Expert Syst Appl 39:2321–2329
Workflow Generator (2015) http://vtcpc.isi.edu/pegasus/index.php/WorkflowGenerator
Wu Z, Ni Z, Gu L, Liu X (2010) A revised discrete particle swarm optimization for cloud workflow scheduling. In: Proceedings of IEEE international conference on computational intelligence and security (CIS), pp 184–188
Xie T, Qin X (2006) Scheduling security-critical real-time applications on clusters. IEEE Trans Comput 55(7):864–879
Xie T, Qin X (2008) Security-aware resource allocation for real-time parallel jobs on homogeneous and heterogeneous clusters. IEEE Trans Parallel Distrib Syst 19(5):682–697
Xue S, Wu W (2012) Scheduling workflow in cloud computing based on hybrid Particle Swarm Algorithm. TELKOMNIKA 10(7):1560–1566
Zeng L, Veeravalli B, Li X (2015) SABA: a security-aware and budget-aware workflow scheduling strategy in clouds. J Parallel Distrib Comput 75:141–151
Zhang Q, Cheng L, Boutaba R (2010) Cloud computing: state-of-the-art and research challenges. J Internet Serv Appl 1:7–18
Zuo X, Zhang G, Tan W (2014) Self-adaptive learning PSO-based deadline constrained task scheduling for hybrid IaaS cloud. IEEE Trans Autom Sci Eng 11(2):564–573
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Our research work doesn’t have any conflict of interest. The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Human and animal rights
This research work doesn’t involve human participants and/or animals.
Additional information
Communicated by V. Loia.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sujana, J.A.J., Revathi, T., Priya, T.S.S. et al. Smart PSO-based secured scheduling approaches for scientific workflows in cloud computing. Soft Comput 23, 1745–1765 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00500-017-2897-8
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00500-017-2897-8