Abstract
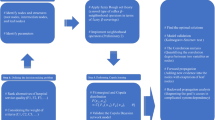
This paper proposes fuzzy integral-based decision methods to identify the core factors and their relationships for smart homes product improvement. The dominance-based rough set approach was used to retrieve core attributes and obtain rough knowledge-based rules. The decision-making trial and evaluation laboratory (DEMATEL) technique was used to build an influential network relationship map, and influential weights were determined through the DEMATEL-based analytic network process. Subsequently, the inter-relationships among criteria were calculated. Finally, the fuzzy integral method was used to measure the plausible synergy effects among the criteria, evaluate/rank alternatives for smart homes, and then provide suggestions for product improvement. The main innovation is the use of rough knowledge-based rule retrieval procedures and fuzzy measures for exploring the synergy effects on smart home improvement. Three smart home products/systems were examined to illustrate their performance on each criterion for improvement planning. This study contributes knowledge to research on consumer adoption of smart homes and presents improvement strategies.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahvar E, Lee GM, Han SN, Crespi N, Khan I (2016) Sensor network-based and user-friendly user location discovery for future smart homes. Sensors 16(7):969
Alaiad A, Zhou LN (2015) Patients’ behavioral intentions toward using WSN based smart home healthcare systems: an empirical investigation. Hawaii Int Conf Syst Sci 30(3):824–833
Al-Suqri MN, Al-Aufi AS (2015) Information seeking behavior and technology adoption: theories and trends. IGI Global, Hershey
Atanassov KT (2014) Index matrices: towards an augmented matrix calculus. Springer, Cham, p 573
Atanassov K, Pasi G, Yager R (2005) Intuitionistic fuzzy interpretations of multi-criteria multi-person and multi-measurement tool decision making. Int J Syst Sci 36(14):859–868
Balta-Ozkan N, Davidson R, Bicket M, Whitmarsh L (2013a) Social barriers to the adoption of smart homes. Energy Policy 63(3):363–374
Balta-Ozkan N, Davidson R, Bicket M, Whitmarsh L (2013b) The development of smart homes market in the UK. Energy 60(7):361–372
Bao H, Chong YL, Ooi KB, Lin B (2014) Are Chinese consumers ready to adopt mobile smart home? An empirical analysis. Int J Mob Commun 12(5):496–511
Błaszczyński J, Greco S, Słowiński R (2007) Multi-criteria classification—a new scheme for application of dominance-based decision rules. Eur J Oper Res 181(3):1030–1044
Bouwer J (2016) Evaluating eWALL: assessing and enhancing older adults’ acceptance of a prototype smart home technology. University of Twente, Enschede
Cesta A, Cortellessa G, Rasconi R, Pecora F, Scopelliti M, Tiberio L (2011) Monitoring elderly people with the robocare domestic environment: interaction synthesis and user evaluation. Comput Intell 27(1):60–82
Chan M, Esteve D, Escriba C, Campo E (2008) A review of smart homes—present state and future challenges. Comput Methods Programs Biomed 91:55–81
Chen YC, Lien HP, Tzeng GH (2010) Measures and evaluation for environment watershed alternatives using a novel hybrid MCDM model. Expert Syst Appl 37(2):926–938
Chiu YJ, Chen HC, Tzeng GH, Shyu JZ (2006) Marketing strategy based on customer behaviour for the LCD-TV. Int J Manag Decis Mak 7(2–3):143–165
Chiu WY, Tzeng GH, Li HL (2013) A new hybrid MCDM model combining DANP with VIKOR to improve e-store business. Knowl Based Syst 37:48–61
Coughlin JF, D’Ambrosio LA, Reimer B, Pratt MR (2007) Older adult perceptions of smart home technologies: implications for research, policy & market innovations in healthcare. In: International conference of the IEEE engineering in medicine and biology society, pp 1810–1815
Courtney KL, Demiris G, Rantz M, Skubic M (2008) Needing smart home technologies: the perspectives of older adults in continuing care retirement communities. Inform Primary Care 16(3):195–201
Davidovic B, Labus A (2015) A smart home system based on sensor technology. Facta Univ Ser Electron Energ 29(3):451–460
De Leaniz PMG, Del Bosque Rodríguez IR (2016) Corporate image and reputation as drivers of customer loyalty. Corp Reput Rev 19(2):166–178
Dinh DL, Kim JT, Kim TS (2014) Hand gesture recognition and interface via a depth imaging sensor for smart home appliances. Energy Procedia 6:576–582
Ehrenhard M, Kijl B, Nieuwenhuis L (2014) Market adoption barriers of multi-stakeholder technology: smart homes for the aging population. Technol Forecast Soc Change 89:306–315
Gabus A, Fontela E (1972) World problems, an invitation to further thought within the framework of DEMATEL. Battelle Geneva Research Centre, Geneva
Gaul S, Ziefle M (2009) Smart home technologies: insights into generation-specific acceptance motives. In: Hci & Usability for E-inclusion, vol 5889, pp 312–332
González García C, Meana-Llorián D, Cueva Lovelle JM (2017) A review about smart objects, sensors, and actuators. Int J Interact Multimed Artif Intell 4(3):7–10
González García C, Núñez-Valdez ER, García-Díaz V (2019) A review of artificial intelligence in the internet of things. Int J Interact Multimed Artif Intell 5(4):9–20
Greco S, Matarazzo B, Slowinski R(1998) A new rough set approach to evaluation of bankruptcy risk. In: Operational tools in the management of financial risks, pp 121–136
Greco S, Matarazzo B, Slowinski R (1999) Rough approximation of a preference relation by dominance relations. Eur J Oper Res 117(1):63–83
Greco S, Matarazzo B, Slowinski R (2002) Rough sets methodology for sorting problems in presence of multiple attributes and criteria. Eur J Oper Res 138(2):247–259
He F, Chen R (2007) Advertising and promotion expenditures on business performance: comparison between Chinese and Japanese household appliance industry. In: 2007 International conference on service systems and service management. IEEE, pp 1–5
Hu SK, Lu MT, Tzeng GH (2014) Exploring smart phone improvements based on a hybrid MCDM model. Expert Syst Appl 41(9):4401–4413
Huang CY, Shyu JZ, Tzeng GH (2007) Reconfiguring the innovation policy portfolios for Taiwan’s SIP mall industry. Technovation 27(12):744–765
Kang WM, Moon SY, Park JH (2017) An enhanced security framework for home appliances in smart home. Hum Centric Comput Inf Sci 7(1):6
Keeney RL, Raiffa H (1993) Decisions with multiple objectives: preferences and value trade-offs. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Lago P, Roncancio C, Jimenez-Guarin C (2018) Learning and managing context enriched behavior patterns in smart homes. Future Gener Comput Syst Int J Esci 91:191–205
Li YY, Wang JQ, Wang TL (2019) A linguistic neutrosophic multi-criteria group decision-making approach with EDAS method. Arab J Sci Eng 44(3):2737–2749
Lim SE, Seungho P (2016) A study on functional priority of smart home service for single-person household-focusing on perceived attributes of innovation. Des Converg Study 15(2):37–52
Lin CL, Hsieh MS, Tzeng GH (2010) Evaluating vehicle telematics system by using a novel MCDM techniques with dependence and feedback. Expert Syst Appl 37(10):6723–6736
Lin H, Ji K, Wang J, Zou G (2015) Promote the industry standard of smart home in China by intelligent router technology. Sci Inf Conf 2(3):1113–1117
Liou JJJ, Tzeng GH (2012) Comments on “Multiple criteria decision making (MCDM) methods in economics: an overview”. Technol Econ Dev Econ 18(4):672–695
Liu CH, Tzeng GH, Lee MH, Lee PY (2013) Improving metro-airport connection service for tourism development: using hybrid MCDM models. Tour Manag Perspect 6:95–107
Liu Y, Chen Y, Tzeng G-H (2017) Identification of key factors in consumers’ adoption behavior of intelligent medical terminals based on a hybrid modified MADM model for product improvement. Int J Med Inform 105:68–82
Lu MT, Lin SW, Tzeng GH (2013) Improving RFID adoption in Taiwan’s healthcare industry based on a DEMATEL technique with a hybrid MCDM model. Decis Support Syst 56:259–269
Lu IY, Kuo T, Lin TS, Tzeng GH, Huang SL (2016) Multicriteria decision analysis to develop effective sustainable development strategies for enhancing competitive advantages: case of the TFT-LCD industry in Taiwan. Sustainability 8(7):646
Marikyan D, Papagiannidis S, Alamanos E (2018) A systematic review of the smart home literature: A user perspective. Technol Forecast Soc Change138:139–154
Molano JIR, Lovelle JMC, Montenegro CE, Granados JJR, Crespo RG (2018) Metamodel for integration of internet of things, social networks, the cloud and industry 4.0. J Ambient Intell Humaniz Comput 9(3):709–723
Morente-Molinera JA, Kou G, Pérez IJ, Samuylov K, Selamat A, Herrera-Viedma E (2018) A group decision making support system for the Web: how to work in environments with a high number of participants and alternatives. Appl Soft Comput 68:191–201
Morente-Molinera JA, Wu X, Morfeq A, Al-Hmouz R, Herrera-Viedma E (2020) A novel multi-criteria group decision-making method for heterogeneous and dynamic contexts using multi-granular fuzzy linguistic modelling and consensus measures. Inf Fusion 53:240–250
Murali S, Pugazhendhi S, Muralidharan C (2016) Modelling and Investigating the relationship of after sales service quality with customer satisfaction, retention and loyalty—a case study of home appliances business. J Retail Consum Serv 30(1):67–83
Opricovic S, Tzeng G-H (2003) Defuzzification within a multicriteria decision model. Int J Uncertain Fuzziness Knowl Based Syst 11:635–652
Opricovic S, Tzeng G-H (2004) Compromise solution by MCDM methods: a comparative analysis of VIKOR and TOPSIS. Eur J Oper Res 156:445–455
Opricovic S, Tzeng G-H (2007) Extended VIKOR method in comparison with outranking methods. Eur J Oper Res 178:514–529
Pal D, Funilkul S, Vanijja V, Papasratorn B (2018) Analyzing the elderly users’ adoption of smart-home services. IEEE Access 6:51238–51252
Pawlak Z (1982) Rough sets. Int J Parallel Program 11(5):341–356
Peng KH, Tzeng GH (2013) A hybrid dynamic MADM model for problems improvement in economics and business. Technol Econ Dev Econ 19(4):638–660
Saaty TL (1980) The analytic hierarchy process. Mcgraw-hill, New York
Saaty TL (1996) Decision making with dependence and feedback: the analytic network process. RWS Publications, Pittsburgh
Shen K-Y, Tzeng G-H (2015) Combined soft computing model for value stock selection based on fundamental analysis. Appl Soft Comput 37:142–155
Shen J, Wang C, Li T, Chen X, Huang X, Zhan Z-H (2018) Secure data uploading scheme for a smart home system. Inf Sci 453:186–197
Shii K, Sugeno M (1985) A model of human evaluation process using fuzzy measure. Int J Man Mach Stud 22(1):19–38
Shin J, Park Y, Lee D (2018) Who will be smart home users? An analysis of adoption and diffusion of smart homes. Technol Forecast Soc Change 134:246–253
Silva B, Khan M, Han K (2018) Load balancing integrated least slack time-based appliance scheduling for smart home energy management. Sensors 18(3):685
Słowiński R, Greco S, Matarazzo B (2014) Rough-set-based decision support. In: Search methodologies. Springer, pp 557–609
Sugeno M (1974) Theory of fuzzy integrals and its applications. Doctorial Thesis
Toshiba KK (2007) Customer relationship management provision method for domestic electrical appliance manufacturing company, involves deriving appliance market strategy by analyzing stored appliance purchasing information and customer information. JP2004213483-A
Tzeng GH, Lin CW, Opricovic S (2005) Multi-criteria analysis of alternative-fuel buses for public transportation. Energy Policy 33(11):1373–1383
Tzeng GH, Cheng HJ, Huang TD (2007a) Multi-objective optimal planning for designing relief delivery systems. Transp Res Part E Logist Transp Rev 43(6):673–686
Tzeng GH, Chiang CH, Li CW (2007b) Evaluating intertwined effects in elearning programs: a novel hybrid MCDM model based on factor analysis and DEMATEL. Expert Syst Appl 32(4):1028–1044
Wang JQ, Peng JJ, Zhang HY, Chen XH (2019) Outranking approach for multi-criteria decision-making problems with hesitant interval-valued fuzzy sets. Soft Comput 23(2):419–430
Wickramasinghe V, Mathusinghe K (2016) After-sales services of home appliances: evidence from Sri Lanka. Int J Consum Stud 40(1):115–124
Wilson C, Hargreaves T, Hauxwell-Baldwin R (2015) Smart homes and their users: a systematic analysis and key challenges. Pers Ubiquitous Comput 19(2):463–476
Zia Uddin M, Kim TS, Kim JT (2011) Video-based indoor human gait recognition using depth imaging and hidden Markov model: a smart system for smart home. Indoor Built Environ 20(1):120–128
Acknowledgements
Special thanks are extended to all the tutors for checking this paper and giving direct or indirect help. This paper was sponsored by The National Natural Science Foundation of China, Grant 71402040. This study was also supported by Chinese Postdoctoral Science Foundation, Grant 2015M571310.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Communicated by V. Loia.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, Y., Li, M., Chen, Y. et al. Evaluation of and improvement planning for smart homes using rough knowledge-based rules on a hybrid multiple attribute decision-making model. Soft Comput 24, 7781–7800 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00500-019-04396-3
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00500-019-04396-3