Abstract
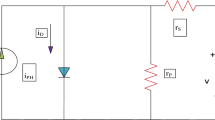
Ann-level multilevel inverter for PV connected systems is proposed in this paper. The proposed inverter is the combination of a buck–boost converter and an H-bridge inverter (B2H multilevel inverter). This system produces a constant AC output voltage with multilevels for a PV connected system with few number of switches. With the proposed inverter, the constant output voltage level is obtained from the PV system irrespective of the variable irradiance. Any number of levels is achieved by varying the duty cycle of the buck–boost converter over a wide range using an n-level generation algorithm. Thus, many numbers of levels can be attained in the output voltage which reduces the THD significantly. The voltage regulation process is performed by designing an optimized fractional-order proportional integral and derivative (FOPID) controller. The FOPID controller provides improved voltage regulation characteristics through the optimization of parameters of controller with the use of modified flower pollination algorithm. The proposed configuration is designed and implemented in MATLAB Simulink. The quality of output, their harmonics and the output resolution time are evaluated for various input voltages and for various numbers of output levels.

























Similar content being viewed by others
References
Babaei E, Kangarlu MF, Hosseinzadeh MA (2013) Asymmetrical multilevel converter topology with reduced number of components. IET Power Electron 6(6):1188–1196
Balamurugan CR, Natarajan SP, Arumugam M (2015) A review on various multilevel inverter topologies. Global J Adv Res 2(1):11
Banaei MR, Khounjahan H, Salary E (2012) Single-source cascaded transformers multilevel inverter with reduced number of switches. IET Power Electron 5(9):1748–1753
Capel A, Jalade J, Valentin M, Marpinard JC (1982) Large signal dynamic stability analysis of synchronised current controlled modulators, application to sine wave high power inverters. In: IEEE PESC conference record, pp 101–110
Chang E-C (2018) Improving performance for full-bridge inverter of wind energy conversion system using a fast and efficient control technique. Energies 11(2):262
Floricau D, Gateau G, Leredde A (2010) New active stacked NPC multilevel converter: operation and features. IEEE Trans Ind Electron 57(7):2272–2278
Han B, Lai J-S, Kim M (2017) Dynamic modeling and controller design of dual-mode Cuk inverter in grid-connected PV/TE applications. IEEE Trans Power Electron 33(10):8887–8904
Hinago Y, Koizumi H (2010) A single phase multilevel inverter using switched series/parallel DC voltage sources. IEEE Trans Ind Electron 58(8):2643–2650
Kangarlu MF, Babaei E (2013) Cross-switched multilevel inverter: an innovative topology. IET Power Electron 6(4):642–651
Kangarlu MF, Babaei E, Laali S (2012) Symmetric multilevel inverter with reduced components based on non-insulated DC voltage sources. IET Power Electron 5(5):571–581
Mantegna RN (1994) Fast, accurate algorithm for numerical simulation of Levy stable stochastic processes. Phys Rev E 49(5):4677
Miao S, Wang F, Ma X (2016) A new transformer less buck-boost converter with positive output voltage. IEEE Trans Ind Electron 63(5):2965–2975
Najafi E, Yatim AHM (2012) Design and implementation of a new multilevel inverter topology. IEEE Trans Ind Electron 59(11):4148–4154
Pavlyukevich I (2007) Lévy flights, non-local search and simulated annealing. J Comput Phys 226(2):1830–1844
Peng FZ, Lai JS, McKeever JW, VanCoevering J (1996) A multilevel voltage-source inverter with separate DC sources for static var generation. IEEE Trans Ind Appl 32:1130–1138
Prabaharan N, Palanisamy K (2017) A comprehensive review on reduced switch multilevel inverter topologies, modulation techniques and applications. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 76:1248–1282
Reddy BD, Anish NK, Selvan MP, Moorthi S (2015) Embedded control of n-level DC–DC–AC inverter. IEEE Trans Power Electron 30(7):3703–3711
Rodriguez J, Bernet S, Steimer PK, Lizama IE (2009) A survey on neutral-point-clamped inverters. IEEE Trans Industr Electron 57(7):2219–2230
Sajedi S, Farrell M, Basu M (2019) DC side and AC side cascaded multilevel inverter topologies: a comparative study due to variation in design features. Int J Electr Power Energy Syst 113:56–70
Sarowar G, Choudhury MA, Hoque MA (2015) A novel control scheme for buck-boost DC to AC converter for variable frequency applications. Procedia-Soc Behav Sci 195:2511–2519
Trzynadlowski AM (2015) Introduction to modern power electronics. Wiley, Hoboken
Waltrich G, Hendrix MA, Duarte JL (2015) Three-phase bidirectional DC/DC converter with six inverter legs in parallel for EV applications. IEEE Trans Ind Electron 63(3):1372–1384
Wang J et al (2018) Bidirectional three-phase DC–AC converter with embedded DC–DC converter and carrier-based PWM strategy for wide voltage range applications. IEEE Trans Ind Electron 66(6):4144–4155
Yang XS, Karamanoglu M, He X (2014) Flower pollination algorithm: a novel approach for multiobjective optimization. Eng Optim 46(9):1222–1237
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All authors state that there is no conflict of interest.
Human and animal rights statement
Humans/animals are not involved in this work.
Additional information
Communicated by V. Loia.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rajeswari, C., Santhi, M. Modified flower pollination algorithm for optimizing FOPID controller and its application with the programmable n-level inverter using fuzzy logic. Soft Comput 25, 2615–2633 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00500-020-05305-9
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00500-020-05305-9