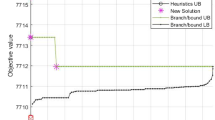
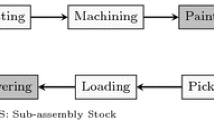
Abstract
Big data (BD) approach has significantly impacted on the development and expansion of supply chain network management and design. The available problems in the supply chain network (SCN) include production, distribution, transportation, ordering, and inventory holding problems. These problems under the BD environment are challenging and considerably affect the efficiency of the SCN. The drastic environmental and regulatory changes around the world and the rising concerns about carbon emissions have increased the awareness of customers regarding the carbon footprint of the products they are consuming. This has enforced supply chain managers to change strategies to reframe carbon emissions.. The decisions such as an optimization of the suitable network of the proper lot sizes can play a crucial role in minimizing the whole carbon emissions in the SCN. In this paper, a new integrated production–transportation–ordering–inventory holding problem for SCN is developed. In this regard, a mixed-integer nonlinear programming (MINLP) model in the multi-product, multi-level, and multi-period SCN is formulated based on the minimization of the total costs and the related cost of carbon emissions. The research also uses a chance-constrained programming approach. The proposed model needs a range of real-time parameters from capacities, carbon caps, and costs. These parameters along with the various sizes of BD, namely velocity, variety, and volume, have been illustrated. A lot-sizing policy along with carbon emissions is also provided in the proposed model. One of the important contributions of this paper is the three various carbon regulation policies that include carbon capacity-and-trade, the strict capacity on emission, and the carbon tax on emissions in order to assess the carbon emissions. As there is no benchmark available in the literature, this study contributes toward this aspect by proposing two hybrid novel meta-heuristics (H-1) and (H-2) to optimize the large-scale problems with the complex structure containing BD. Hence, a generated random dataset possessing the necessary parameters of BD, namely velocity, variety, and volume, is provided to validate and solve the suggested model. The parameters of the proposed algorithms are calibrated and controlled using the Taguchi approach. In order to evaluate hybrid algorithms and find optimal solutions, the study uses 15 randomly generated data examples having necessary features of BD and T test significance. Finally, the effectiveness and performance of the presented model are analyzed by a set of sensitivity analyses. The outcome of our study shows that H-2 is of higher efficiency.


















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Addo-Tenkorang R, Helo PT (2016) BD applications in operations/supply-chain management: a literature review. Comput Ind Eng 101:528–543
Afrouzy ZA, Paydar MM, Nasseri SH, Mahdavi I (2017) A meta-heuristic approach supported by NSGA-II for the design and plan of supply chain networks considering new product development. J Ind Eng Int 14(1):95–109
Akter S, Wamba SF (2019) BD and disaster management: a systematic review and agenda for future research. Ann Oper Res 283(1–2):939–959
Alavidoost MH, Tarimoradi M, Zarandi MF (2018) Bi-objective mixed-integer nonlinear programming for multi-commodity tri-echelon supply chain networks. J Intell Manuf 29(4):809–826
Amiri SAHS, Zahedi A, Kazemi M, Soroor J, Hajiaghaei-Keshteli M (2020) Determination of the optimal sales level of perishable goods in a two-echelon supply chain network. Comput Ind Eng 139:106156
Bank M, Mazdeh M, Heydari M (2020) Applying meta-heuristic algorithms for an integrated production–distribution problem in a two level supply chain. Uncertain Supply Chain Manag 8(1):77–92
Baryannis G, Validi S, Dani S, Antoniou G (2019) Supply chain risk management and artificial intelligence: state of the art and future research directions. Int J Prod Res 57(7):2179–2202
Ben-Daya M, Hassini E, Bahroun Z (2019) Internet of things and supply chain management: a literature review. Int J Prod Res 57(15–16):4719–4742
Cheng S, Zhang Q, Qin Q (2016) BD analytics with swarm intelligence. Ind Manag Data Syst 116(4):646–666
Choi TM, Wallace SW, Wang Y (2018) BD analytics in operations management. Prod Oper Manag 27(10):1868–1883
Chung SH, Tse YK, Choi TM (2015) Managing disruption risk in express logistics via proactive planning. Ind Manag Data Syst 115(8):1481–1509
Cui Y, Kara S, Chan KC (2020) Manufacturing BD ecosystem: a systematic literature review. Robot Comput Integr Manuf 62:101861
Dai HN, Wang H, Xu G, Wan J, Imran M (2020) Big data analytics for manufacturing internet of things: opportunities, challenges and enabling technologies. Enterp Inf Syst 14(9-10):1279–1303
Del Giudice M, Chierici R, Mazzucchelli A, Fiano F (2020) Supply chain management in the era of circular economy: the moderating effect of big data. Int J Logist Manag. https://doi.org/10.1108/IJLM-03-2020-0119
Dev NK, Shankar R, Gupta R, Dong J (2019) Multi-criteria evaluation of real-time key performance indicators of supply chain with consideration of BD architecture. Comput Ind Eng 128:1076–1087
Duan Y, Edwards JS, Dwivedi YK (2019) Artificial intelligence for decision making in the era of BD—evolution, challenges and research agenda. Int J Inf Manag 48:63–71
Eberhart R, Kennedy J (1995) A new optimizer using particle swarm theory. In: MHS'95. Proceedings of the sixth international symposium on micro machine and human science. IEEE, pp 39–43
Fakhrzad MB, Goodarzian F (2019) A fuzzy multi-objective programming approach to develop a green closed-loop supply chain network design problem under uncertainty: modifications of imperialist competitive algorithm. RAIRO Oper Res 53(3):963–990
Fakhrzad MB, Goodarzian F (2020) A new multi-objective mathematical model for a citrus supply chain network design: metaheuristic algorithms. J Optim Ind Eng 14(2):127–144
Fakhrzad MB, Goodarzian F, Golmohammadi AM (2019) Addressing a fixed charge transportation problem with multi-route and different capacities by novel hybrid meta-heuristics. J Ind Syst Eng 12(1):167–184
Fakhrzad MB, Talebzadeh P, Goodarzian F (2018) Mathematical formulation and solving of green closed-loop supply chain planning problem with production, distribution and transportation reliability. Int J Eng 31(12):2059–2067
Fang Y, Ming H, Li M, Liu Q, Pham DT (2020) Multi-objective evolutionary simulated annealing optimization for mixed-model multi-robotic disassembly line balancing with interval processing time. Int J Prod Res 58(3):846–862
Fathollahi-Fard AM, Ahmadi A, Goodarzian F, Cheikhrouhou N (2020) A bi-objective home healthcare routing and scheduling problem considering patients’ satisfaction in a fuzzy environment. Appl Soft Comput 93:106385
Fattahi M, Mahootchi M, Govindan K, Husseini SMM (2015) Dynamic supply chain network design with capacity planning and multi-period pricing. Transp Res Part E Logist Transp Rev 81:169–202
Fonseca GB, Nogueira TH, Ravetti MG (2019) A hybrid Lagrangian metaheuristic for the cross-docking flow shop scheduling problem. Eur J Oper Res 275(1):139–154
Gandomi A, Haider M (2015) Beyond the hype: BD concepts, methods, and analytics. Int J Inf Manag 35(2):137–144
Ghasemiyeh R, Moghdani R, Sana SS (2017) A hybrid artificial neural network with metaheuristic algorithms for predicting stock price. Cybern Syst 48(4):365–392
Gholizadeh H, Fazlollahtabar H (2020) Robust optimization and modified genetic algorithm for a closed loop green supply chain under uncertainty: case study in melting industry. Comput Ind Eng 147:106653
Gholizadeh H, Fazlollahtabar H, Khalilzadeh M (2020a) A robust fuzzy stochastic programming for sustainable procurement and logistics under hybrid uncertainty using big data. J Clean Prod 258:120640
Gholizadeh H, Tajdin A, Javadian N (2020b) A closed-loop supply chain robust optimization for disposable appliances. Neural Comput Appl 32(8):3967–3985
Gholizadeh H, Javadian N, Fazlollahtabar H (2020c) An integrated fuzzy-genetic failure mode and effect analysis for aircraft wing reliability. Soft Comput 1–12
Goldberg DE, Korb B, Deb K (1989) Messy genetic algorithms: motivation, analysis, and first results. Complex Syst 3(5):493–530
Goodarzian F, Hosseini-Nasab H, Muñuzuri J, Fakhrzad MB (2020a) A multi-objective pharmaceutical supply chain network based on a robust fuzzy model: A comparison of meta-heuristics. Applied soft computing 92:106331
Goodarzian F, Hosseini-Nasab H, Fakhrzad MB (2020b) A multi-objective sustainable medicine supply chain network design using a novel hybrid multi-objective metaheuristic algorithm. Int J Eng 33(10):1986–1995
Goodarzian F, Abraham A, Fathollahi-Fard AM (2021) A biobjective home health care logistics considering the working time and route balancing: a self-adaptive social engineering optimizer. J Comput Design Eng 8(1):452–474
Goodarzian F, Hosseini-Nasab H (2019) Applying a fuzzy multi-objective model for a production–distribution network design problem by using a novel self-adoptive evolutionary algorithm. Int J Syst Sci Oper Logist 1–22
Gupta S, Altay N, Luo Z (2019) BD in humanitarian supply chain management: a review and further research directions. Ann Oper Res 283(1):1153–1173
Günther WA, Mehrizi MHR, Huysman M, Feldberg F (2017) Debating BD: a literature review on realizing value from BD. J Strateg Inf Syst 26(3):191–209
Hilbert M (2016) BD for development: a review of promises and challenges. Dev Policy Rev 34(1):135–174
Jamili N, Ranjbar M, Salari M (2016) A bi-objective model for integrated scheduling of production and distribution in a supply chain with order release date restrictions. J Manuf Syst 40:105–118
Jiang J, Wu D, Chen Y, Li K (2019b) Complex network oriented artificial bee colony algorithm for global bi-objective optimization in three-echelon supply chain. Appl Soft Comput 76:193–204
Jiang J, Wu D, Chen Y, Yu D, Wang L, Li K (2019a) Fast artificial bee colony algorithm with complex network and naive bayes classifier for supply chain network management. Soft Comput 23(24):13321–13337
Jin X, Wah BW, Cheng X, Wang Y (2015) Significance and challenges of BD research. BD Res 2(2):59–64
Kamble SS, Gunasekaran A (2020) BD-driven supply chain performance measurement system: a review and framework for implementation. Int J Prod Res 58(1):65–86
Kaur H, Singh SP (2018) Heuristic modeling for sustainable procurement and logistics in a supply chain using BD. Comput Oper Res 98:301–321
Kazemi A, Khezrian V, Javad MOM, Alinezhad A (2015) Presenting a bi-objective integrated model for production–distribution problem in a multi-level supply chain network. Int J Supply Oper Manag 1(4):507
Khalifehzadeh S, Seifbarghy M, Naderi B (2015) A four-echelon supply chain network design with shortage: mathematical modeling and solution methods. J Manuf Syst 35:164–175
Khalifehzadeh S, Seifbarghy M, Naderi B (2017) Solving a fuzzy multi objective model of a production–distribution system using meta-heuristic based approaches. J Intell Manuf 28(1):95–109
Kirkpatrick S, Gelatt CD, Vecchi MP (1983) Optimization by simulated annealing. Science 220(4598):671–680
Ko T, Lee JH, Cho H, Cho S, Lee W, Lee M (2017) Machine learning-based anomaly detection via integration of manufacturing, inspection and after-sales service data. Ind Manag Data Syst 117(5):927–945
Koç Ç (2017) An evolutionary algorithm for supply chain network design with assembly line balancing. Neural Comput Appl 28(11):3183–3195
Lamba K, Singh SP (2018) Modeling BD enablers for operations and supply chain management. Int J Logist Manag. https://doi.org/10.1108/IJLM-07-2017-0183
Lee I (2017) BD: dimensions, evolution, impacts, and challenges. Bus Horiz 60(3):293–303
Lee JG, Kang M (2015) Geospatial BD: challenges and opportunities. BD Res 2(2):74–81
Liu P (2019) Pricing policies and coordination of low-carbon supply chain considering targeted advertisement and carbon emission reduction costs in the big data environment. J Clean Prod 210:343–357
Liu M, Yao X, Li Y (2020) Hybrid whale optimization algorithm enhanced with Lévy flight and differential evolution for job shop scheduling problems. Appl Soft Comput 87:105954
Lv Z, Song H, Basanta-Val P, Steed A, Jo M (2017) Next-generation BD analytics: state of the art, challenges, and future research topics. IEEE Trans Ind Inf 13(4):1891–1899
Maghsoudlou H, Kahag MR, Niaki STA, Pourvaziri H (2016) Bi-objective optimization of a three-echelon multi-server supply-chain problem in congested systems: modeling and solution. Comput Ind Eng 99:41–62
Mahmoodirad A, Sanei M (2016) Solving a multi-stage multi-product solid supply chain network design problem by meta-heuristics. Sci Iran 23(3):1428–1440
Memari A, Ahmad R, Akbari Jokar MR, Rahim A, Rahman A (2019) A new modified firefly algorithm for optimizing a supply chain network problem. Appl Sci 9(1):7
Mikalef P, Pappas IO, Krogstie J, Giannakos M (2018) BD analytics capabilities: a systematic literature review and research agenda. IseB 16(3):547–578
Mohamed A, Najafabadi MK, Wah YB, Zaman EAK, Maskat R (2020) The state of the art and taxonomy of BD analytics: view from new BD framework. Artif Intell Rev 53(2):989–1037
Mohammed AM, Duffuaa SO (2020) A tabu search based algorithm for the optimal design of multi-objective multi-product supply chain networks. Expert Syst Appl 140:112808
Mousavi SM, Alikar N, Niaki STA, Bahreininejad A (2015) Optimizing a location allocation-inventory problem in a two-echelon supply chain network: a modified fruit fly optimization algorithm. Comput Ind Eng 87:543–560
Mousavi SM, Bahreininejad A, Musa SN, Yusof F (2017) A modified particle swarm optimization for solving the integrated location and inventory control problems in a two-echelon supply chain network. J Intell Manuf 28(1):191–206
Mousavi SM, Foroozesh N, Zavadskas EK, Antucheviciene J (2020) A new soft computing approach for green supplier selection problem with interval type-2 trapezoidal fuzzy statistical group decision and avoidance of information loss. Soft Computing 24(16)
Nguyen T, Li ZHOU, Spiegler V, Ieromonachou P, Lin Y (2018) BD analytics in supply chain management: a state-of-the-art literature review. Comput Oper Res 98:254–264
Oussous A, Benjelloun FZ, Lahcen AA, Belfkih S (2018) BD technologies: a survey. J King Saud Univ Comput Inf Sci 30(4):431–448
Rao PD, Kiran CU, Prasad KE (2020) Modeling elastic constants of keratin-based hair fiber composite using response surface method and optimization using grey Taguchi method. In: Advanced engineering optimization through intelligent techniques. Springer, Singapore, pp 275–289
Saghaeeian A, Ramezanian R (2018) An efficient hybrid genetic algorithm for multi-product competitive supply chain network design with price-dependent demand. Appl Soft Comput 71:872–893
Sahebjamnia N, Goodarzian F, Hajiaghaei-Keshteli M (2020) Optimization of multi-period three-echelon citrus supply chain problem. J Optim Ind Eng 13(1):39–53
Sangaiah AK, Tirkolaee EB, Goli A, Dehnavi-Arani S (2020) Robust optimization and mixed-integer linear programming model for LNG supply chain planning problem. Soft Comput 24(11):7885–7905
Sarrafha K, Rahmati SHA, Niaki STA, Zaretalab A (2015) A bi-objective integrated procurement, production, and distribution problem of a multi-echelon supply chain network design: a new tuned MOEA. Comput Oper Res 54:35–51
Shaw K, Irfan M, Shankar R, Yadav SS (2016) Low carbon chance constrained supply chain network design problem: a Benders decomposition based approach. Comput Ind Eng 98:483–497
Shoja A, Molla-Alizadeh-Zavardehi S, Niroomand S (2019) Adaptive meta-heuristic algorithms for flexible supply chain network design problem with different delivery modes. Comput Ind Eng 138:106107
Singh D, Reddy CK (2015) A survey on platforms for BD analytics. J BD 2(1):8
Sitek P, Wikarek J, Nielsen P (2017) A constraint-driven approach to food supply chain management. Ind Manag Data Syst 117(9):2115–2138
Sivarajah U, Kamal MM, Irani Z, Weerakkody V (2017) Critical analysis of BD challenges and analytical methods. J Bus Res 70:263–286
Tamannaei M, Rasti-Barzoki M (2019) Mathematical programming and solution approaches for minimizing tardiness and transportation costs in the supply chain scheduling problem. Comput Ind Eng 127:643–656
Tavana M, Santos-Arteaga FJ, Mahmoodirad A, Niroomand S, Sanei M (2018) Multi-stage supply chain network solution methods: hybrid metaheuristics and performance measurement. Int J Syst Sci Oper Logist 5(4):356–373
Tiwari S, Wee HM, Daryanto Y (2018) BD analytics in supply chain management between 2010 and 2016: insights to industries. Comput Ind Eng 115:319–330
Tsai CW, Lai CF, Chao HC, Vasilakos AV (2015) BD analytics: a survey. J BD 2(1):21
Wang G, Gunasekaran A, Ngai EW, Papadopoulos T (2016) BD analytics in logistics and supply chain management: certain investigations for research and applications. Int J Prod Econ 176:98–110
Wang X, White L, Chen X (2015) BD research for the knowledge economy: past, present, and future. Ind Manag Data Syst 115(9). https://doi.org/10.1108/IMDS-09-2015-0388
Woo YB, Kim BS (2019) A genetic algorithm-based matheuristic for hydrogen supply chain network problem with two transportation modes and replenishment cycles. Comput Ind Eng 127:981–997
Yan R (2017) Optimization approach for increasing revenue of perishable product supply chain with the Internet of Things. Ind Manag Data Syst 117(4):729–741
Yaqoob I, Hashem IAT, Gani A, Mokhtar S, Ahmed E, Anuar NB, Vasilakos AV (2016) BD: from beginning to future. Int J Inf Manag 36(6):1231–1247
Zhan Y, Tan KH (2020) An analytic infrastructure for harvesting BD to enhance supply chain performance. Eur J Oper Res 281(3):559–574
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Human and animal rights
This article does not contain any studies with human or animal subjects performed by any of the authors.
Informed consent
Informed consent was not required as no human or animals were involved.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Goodarzian, F., Kumar, V. & Abraham, A. Hybrid meta-heuristic algorithms for a supply chain network considering different carbon emission regulations using big data characteristics. Soft Comput 25, 7527–7557 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00500-021-05711-7
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00500-021-05711-7