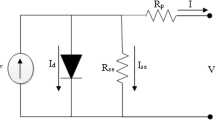
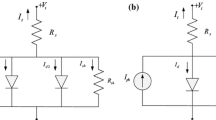
Abstract
The efficiency of a photovoltaic system may be increased with the use of effective solar PV cell modelling. Solar cell characteristics with flaws, on the other hand, have an unfavorable impact on PV cell modelling. In most cases, manufacturers do not provide all of the information required for accurate PV cell modelling. As a result, it is vital to accurately anticipate the characteristics of the PV cell. Although the literature describes different optimization techniques, most of them provide unsatisfactory results owing to their convergence toward local minima. This research presents a new stochastic optimization approach for estimating the parameters of solar PV cells. As a result, this work introduces the Chaotic Dragonfly Algorithm, a new chaotic algorithm for evaluating solar cells. The suggested technique has the major benefit of employing chaotic maps to calculate and automatically change the internal parameters of the optimization algorithm. This circumstance is advantageous in difficult situations since the suggested method enhances their ability to seek for the optimal solution throughout the iterative phase. Complex and multimodal objective functions can be optimised using the modified technique. In order to show the potential of the proposed algorithm in the solar cell architecture, it is contrasted with other methods of optimization over two different datasets. The chaotic variants for R.T.C France model (CDA1 1.1543, CDA2 2.1896, CDA3 2.1994, CDA4 2.2011, and CDA5 2.2015) have a faster computation time than the other compared algorithms (particle swarm optimization (PSO) 10.1458, Sine Cosine Algorithm (SCA) 7.9980, Multi Verse optimization (MVO) 4.8450, Grey Wolf optimizer (GWO) 3.9042, and Dragonfly Algorithm (DA) .8056). Similarly, the chaotic variants for Photo-Watt model (CDA1-1.1441, CDA2-1.1864, CTSA3-2.1989, CTSA4-2.2014, and CTSA5-2.2022) had a faster calculation time than the other examined algorithms for the triple-diode model (PSO-10.2045, SCA-7.9999, MVO-4.8544, GWO-3.9057, and DA-3.8110). Nonparametric test, statistical error analysis, and sensitivity temperature variation are all used to prove the suggested algorithm’s superiority.














Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Enquiries about data availability should be directed to the authors.
References
Abbassi R, Abbassi A, Heidari AA, Mirjalili S (2019) An efficient salp swarm-inspired algorithm for parameters identification of photovoltaic cell models. Energy Convers Manag 179:362–372
Abd Elaziz M, Oliva D (2018) Parameter estimation of solar cells diode models by an improved opposition-based whale optimization algorithm. Energy Convers Manag 171:1843–1859
Abualigah L, Yousri D, Abd Elaziz M, Ewees AA, Al-Qaness MA, Gandomi AH (2021a) Aquila optimizer: a novel meta-heuristic optimization algorithm. Comput Ind Eng 157:107250
Abualigah L, Diabat A, Sumari P, Gandomi AH (2021b) A novel evolutionary arithmetic optimization algorithm for multilevel thresholding segmentation of covid-19 ct images. Processes 9(7):1155
Allam D, Yousri DA, Eteiba MB (2016) Parameters extraction of the three diode model for the multi-crystalline solar cell/module using moth-flame optimization algorithm. Energy Convers Manag 123:535–548
Amroune M, Bouktir T, Musirin I (2018) Power system voltage stability assessment using a hybrid approach combining dragonfly optimization algorithm and support vector regression. Arab J Sci Eng 43(6):3023–3036
Askarzadeh A, dos Santos Coelho L (2015) Determination of photovoltaic modules parameters at different operating conditions using a novel bird mating optimizer approach. Energy Convers Manag 89:608–614
Askarzadeh A, Rezazadeh A (2012) Parameter identification for solar cell models using harmony search-based algorithms. Sol Energy 86(11):3241–3249
Babayigit B (2018) Synthesis of concentric circular antenna arrays using dragonfly algorithm. Int J Electron 105(5):784–793
Baiche K, Meraihi Y, Hina MD, Ramdane-Cherif A, Mahseur M (2019) Solving graph coloring problem using an enhanced binary dragonfly algorithm. Int J Swarm Intell Res (IJSIR) 10(3):23–45
Brano VL, Orioli A, Ciulla G, Di Gangi A (2010) An improved five-parameter model for photovoltaic modules. Sol Energy Mater Sol Cells 94(8):1358–1370
Chegaar M, Ouennoughi Z, Guechi F, Langueur H (2003) Determination of solar cells parameters under illuminated conditions. J Electron Device 2(2003):17–21
Chen X, Yu K (2019) Hybridizing cuckoo search algorithm with biogeography-based optimization for estimating photovoltaic model parameters. Sol Energy 180:192–206
Chen Z, Wu L, Lin P, Wu Y, Cheng S (2016) Parameters identification of photovoltaic models using hybrid adaptive nelder-mead simplex algorithm based on eagle strategy. Appl Energy 182:47–57
Easwarakhanthan T, Bottin J, Bouhouch I, Boutrit C (1986) Nonlinear minimization algorithm for determining the solar cell parameters with microcomputers. Int J Sol Energy 4(1):1–12
El-Shafeiy E, Sallam KM, Chakrabortty RK, Abohany AA (2021) A clustering based swarm intelligence optimization technique for the internet of medical things. Expert Syst Appl 173:114648
Gnetchejo PJ, Essiane SN, Ele P, Wamkeue R, Wapet DM, Ngoffe SP (2019) Important notes on parameter estimation of solar photovoltaic cell. Energy Convers Manag 197:111870
Gupta J, Nijhawan P, Ganguli S (2021b) Parameter extraction of solar PV cell models using novel metaheuristic chaotic tunicate swarm algorithm. Int Trans Electr Energy Syst 31(12):e13244
Gupta J, Nijhawan P, Ganguli S (2021) Parameter estimation of different solar cells using a novel swarm intelligence technique. Soft Comput 1–31:5833–5863
Han L, Koide N, Chiba Y, Islam A, Mitate T (2006) Modeling of an equivalent circuit for dye-sensitized solar cells: improvement of efficiency of dye-sensitized solar cells by reducing internal resistance. C R Chim 9(5–6):645–651
Huld T, Gottschalg R, Beyer HG, Topič M (2010) Mapping the performance of PV modules, effects of module type and data averaging. Sol Energy 84(2):324–338
Ishaque K, Salam Z, Mekhilef S, Shamsudin A (2012) Parameter extraction of solar photovoltaic modules using penalty-based differential evolution. Appl Energy 99:297–308
Jafari M, Chaleshtari MHB (2017) Using dragonfly algorithm for optimization of orthotropic infinite plates with a quasi-triangular cut-out. Eur J Mech A Solid 66:1–14
Jun-hua L, Ming L (2013) An analysis on convergence and convergence rate estimate of elitist genetic algorithms in noisy environments. Optik 124(24):6780–6785
Lin P, Cheng S, Yeh W, Chen Z, Wu L (2017) Parameters extraction of solar cell models using a modified simplified swarm optimization algorithm. Sol Energy 144:594–603
Ma T, Yang H, Lu L (2014) Solar photovoltaic system modeling and performance prediction. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 36:304–315
Mahseur M, Boukra A, Meraihi Y (2018) QoS multicast routing based on a quantum chaotic dragonfly algorithm. International symposium on modelling and implementation of complex systems. Springer, Cham, pp 47–59
Mirjalili S (2016) Dragonfly algorithm: a new meta-heuristic optimization technique for solving single-objective, discrete, and multi-objective problems. Neural Comput Appl 27(4):1053–1073
Navabi R, Abedi S, Hosseinian SH, Pal R (2015) On the fast convergence modeling and accurate calculation of PV output energy for operation and planning studies. Energy Convers Manag 89:497–506
Niu Q, Zhang L, Li K (2014) A biogeography-based optimization algorithm with mutation strategies for model parameter estimation of solar and fuel cells. Energy Convers Manag 86:1173–1185
Oliva D, Abd Elaziz M, Elsheikh AH, Ewees AA (2019) A review on meta-heuristics methods for estimating parameters of solar cells. J Power Source 435:126683
Pan H, Wang L, Liu B (2006) Particle swarm optimization for function optimization in noisy environment. Appl Math Comput 181(2):908–919
Rekioua D, Matagne E (2012) Optimization of photovoltaic power systems: modelization, simulation and control. Springer
Sayed GI, Tharwat A, Hassanien AE (2019) Chaotic dragonfly algorithm: an improved metaheuristic algorithm for feature selection. Appl Intell 49(1):188–205
Schranz M, Di Caro GA, Schmickl T, Elmenreich W, Arvin F, Şekercioğlu A, Sende M (2021) Swarm intelligence and cyber-physical systems: concepts, challenges and future trends. Swarm Evol Comput 60:100762
Sharma M, Singh G, Singh R (2019) A review of different cost-based distributed query optimizers. Prog Artif Intell 8(1):45–62
Sharma S, Singh G, Sharma M (2021) A comprehensive review and analysis of supervised-learning and soft computing techniques for stress diagnosis in humans. Comput Biol Med 134:104450
Sharma M, Sharma S, Singh G (2020) Remote monitoring of physical and mental state of 2019-nCoV victims using social internet of things, fog and soft computing techniques. Comput Method Program Biomed 196:105609–105609
Singla MK, Nijhawan P, Oberoi AS (2021) Parameter estimation of proton exchange membrane fuel cell using a novel meta-heuristic algorithm. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28(26):34511–34526
Singla MK, Nijhawan P (2021) Triple diode parameter estimation of solar PV cell using hybrid algorithm. Int J Environ Sci Technol 1–24:4265–4288
Singla MK, Nijhawan P, Oberoi AS (2022) A novel hybrid particle swarm optimization rat search algorithm for parameter estimation of solar PV and fuel cell model. COMPEL-Int J Comput Math Electr Electron Eng. https://doi.org/10.1108/COMPEL-07-2021-0257
Subudhi B, Pradhan R (2017) Bacterial foraging optimization approach to parameter extraction of a photovoltaic module. IEEE Trans Sustain Energy 9(1):381–389
Villalva MG, Gazoli JR, Ruppert Filho E (2009) Comprehensive approach to modeling and simulation of photovoltaic arrays. IEEE Trans Power Electron 24(5):1198–1208
Xiao W, Lind MG, Dunford WG, Capel A (2006) Real-time identification of optimal operating points in photovoltaic power systems. IEEE Trans Industr Electron 53(4):1017–1026
Xu S, Wang Y (2017) Parameter estimation of photovoltaic modules using a hybrid flower pollination algorithm. Energy Convers Manag 144:53–68
Yang D, Li G, Cheng G (2007) On the efficiency of chaos optimization algorithms for global optimization. Chaos Solitons Fractal 34(4):1366–1375
Ye M, Wang X, Xu Y (2009) Parameter extraction of solar cells using particle swarm optimization. J Appl Phys 105(9):094502
Yousri D, Allam D, Eteiba MB, Suganthan PN (2019) Static and dynamic photovoltaic models’ parameters identification using chaotic heterogeneous comprehensive learning particle swarm optimizer variants. Energy Convers Manag 182:546–563
Yu K, Liang JJ, Qu BY, Chen X, Wang H (2017a) Parameters identification of photovoltaic models using an improved JAYA optimization algorithm. Energy Convers Manag 150:742–753
Yu K, Chen X, Wang X, Wang Z (2017b) Parameters identification of photovoltaic models using self-adaptive teaching-learning-based optimization. Energy Convers Manag 145:233–246
Yu K, Liang JJ, Qu BY, Cheng Z, Wang H (2018) Multiple learning backtracking search algorithm for estimating parameters of photovoltaic models. Appl Energy 226:408–422
Zemmal N, Azizi N, Sellami M, Cheriguene S, Ziani A, AlDwairi M, Dendani N (2020) Particle swarm optimization based swarm intelligence for active learning improvement: application on medical data classification. Cogn Comput 12(5):991–1010
Funding
The authors have not disclosed any funding.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have declared no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Singla, M.K., Nijhawan, P. & Oberoi, A.S. Parameter estimation of three diode solar PV cell using chaotic dragonfly algorithm. Soft Comput 26, 11567–11598 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00500-022-07425-w
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00500-022-07425-w