Abstract
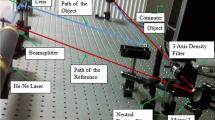
Recent developments in architectures, devices, and protocols have dramatically increased the traffic capacity of telecommunication networks. New control and management techniques are needed for the potential, by this progress promising, to be achieved. Soft computing (SC) is the approach that gives an attractive way to this goal. From the hardware point of view, the main problem is SC based methods are computationally expensive. Optics gives a reasonable alternative for purely electronic hardware. Our main interest in this paper is to establish connections between optics as a physical reality and fuzzy set theory as an abstract construction and develop a model of Fourier-holography set-up as a neuro-fuzzy system. We formulate an algebraic description of both geometrical and Fourier-approximations of optics by using t-norms based approach to take into consideration non-linearity of real optical devices and recording media. We design logic for both approximations. We consider Fourier-holography set-up as a neuro-fuzzy system. We present experimental realisation of General Modus Ponens rule and develop model of partial associations.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pavlov, A. An algebraic model for application of optical neuro-fuzzy systems to networking problems. Soft Computing 5, 318–324 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1007/s005000100105
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s005000100105