Abstract
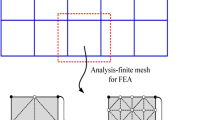
This paper investigates the use of a genetic algorithm (GA) to perform the large-scale triangular mesh optimization process. This optimization process consists of a combination of mesh reduction and mesh smoothing that will not only improve the speed for the computation of a 3D graphical or finite element model, but also improve the quality of its mesh. The GA is developed and implemented to replace the original mesh with a re-triangulation process. The GA features optimized initial population, constrained crossover operator, constrained mutation operator and multi-objective fitness evaluation function. While retaining features is important to both visualization models and finite element models, this algorithm also optimizes the shape of the triangular elements, improves the smoothness of the mesh and performs mesh reduction based on the needs of the user.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Caponetto R, Fortuna L, Graziani S, Xibilia MG (1993) Genetic algorithms and applications in system engineering: a survey. Trans Inst Meas Control 15(3):143–156
Rudolph G (1994) Convergency analysis of canonical genetic algorithms. IEEE Trans Neural Netw 5(1):96–101
Michalewicz Z (1998) Genetic algorithms + data structures = evolution programs, 3rd edn. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York, ISBN 3-540-60676-9
Goldberg DE (1989) Genetic algorithms in search, optimization, and machine learning. Addison-Wesley, Reading
Holland JH (1975) Adaptation in natural and artificial system. The University of Michigan Press, Ann Arbor
Dorsey RE, Mayer WJ (1995) Genetic algorithms for estimation problems with multiple optima, non-differentiability, and other irregular features. J Bus Econ Stat 13(1):53–66
Liu X, Begg DW, Fishwick RJ (1998) Genetic approach to optimal topology/controller design of adaptive structures. Int J Numer Methods Eng 41(5):815–830
Absaloms H, Tomikawa T (1996) Surface reconstruction by triangulation using GA. In: Proceedings of the 20th international conference on computers and industrial engineering, Kyongju, Korea, 6–9 October 1996, pp 441–444
Qin KH, Wang WP, Gong ML (1997) A genetic algorithm for the minimum weight triangulation. In: Proceedings of the IEEE conference on evolutionary computation, Indianapolis, IN, USA, 13–16 April 1997, pp 541–546
Hamann B (1994) A data reduction scheme for triangulated surfaces. Comput Aided Geom Des 11(2):197–214
Hoppe H, DeRose T, Duchamp T, McDonald J, Stuetzle W (1993) Mesh optimization. In: ACM SIGGRAPHICS Proceedings, vol 1, pp 19–26
Ronfard R, Rossignace J (1996) Full-range approximations of triangulated polyhedra. Proceedings of EUROGRAPHIVS’96. Comput Graph Forum 15(3):67–76
Gieng TS, Joy KI, Schussman GL, Trotts IJ (1998) Constructing hierarchies for triangle meshes. IEEE Trans Vis Comput Graph 4(2):145–161
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chong, C.S., Lee, H.P. & Senthil Kumar, A. Genetic algorithms in mesh optimization for visualization and finite element models. Neural Comput & Applic 15, 366–372 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-006-0041-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-006-0041-2