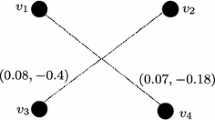
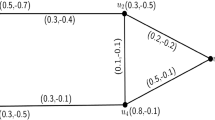
Abstract
We introduce the concepts of regular and totally regular bipolar fuzzy graphs. We prove necessary and sufficient condition under which regular bipolar fuzzy graph and totally bipolar fuzzy graph are equivalent. We introduce the notion of bipolar fuzzy line graphs and present some of their properties. We state a necessary and sufficient condition for a bipolar fuzzy graph to be isomorphic to its corresponding bipolar fuzzy line graph. We examine when an isomorphism between two bipolar fuzzy graphs follows from an isomorphism of their corresponding bipolar fuzzy line graphs.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abiyev RH (2011) Fuzzy wavelet neural network based on fuzzy clustering and gradient techniques for time series prediction. Neural Comput Appl 20(2):249–259
Akram M (2011) Interval-valued fuzzy line graphs. Neural Comput Appl. doi:10.1007/s00521-011-0733-0
Akram M (2011) Bipolar fuzzy graphs. Inf Sci 181:5548–5564
Akram M (2011) Cofuzzy graphs. J Fuzzy Math 19(4):877–888
Akram M, Dudek WA (2011) Interval-valued fuzzy graphs. Comput Math Appl 61:289–299
Akram M, Dudek WA (2008) Intuitionistic fuzzy left k-ideals of semirings. Soft Comput 12:881–890
Alaoui A (1999) On fuzzification of some concepts of graphs. Fuzzy Sets Syst 101:363–389
Atanassov KT (1999) Intuitionistic fuzzy fets: theory and applications, studies in fuzziness and soft computing. Physica-Verl, Heidelberg, New York
Atanassov KT (1994) Index matrix representation of the intuitionistic fuzzy graphs. Preprint MRL-MFAIS-10-94, Sofia, pp 36–41
Atanassov KT, Pasi G, Yager R, Atanassova V (2003) Intuitionistic fuzzy graph interpretations of multi-person multi-criteria decision making, EUSFLAT conference’, pp 177–182
Bhattacharya P (1987) remarks on fuzzy graphs. Pattern Recognit Lett 6:297–302
Bhutani KR (1989) On automorphism of fuzzy graphs. Pattern Recognit Lett 9:159–162
Bhutani KR, Rosenfeld A (2003) Strong arcs in fuzzy graphs. Inf Sci 152:319–322
Bhutani KR, Rosenfeld A (2003) Fuzzy end nodes in fuzzy graphs. Inf Sci 152:323–326
Bhutani KR, Battou A (2003) On M-strong fuzzy graphs. Inf Sci 155:103–109
Bloch I (2007) Dilation and erosion of spatial bipolar fuzzy sets. In: Proceedings of WILF, pp 385–393
Bloch I (2009) Geometry of spatial bipolar fuzzy sets based on bipolar fuzzy numbers and mathematical morphology. Fuzzy Log Appl Lect Note Comput Sci 5571:237–245
Dubois D, Kaci S, Prade H (2004) Bipolarity in reasoning and decision, an introduction. International conference on information processing and management of uncertainty IPMU’04, pp 959–966
Harary F (1972) Graph theory. 3rd edn. Addison-Wesley, Reading, MA
Huber KP, Berthold MR, Application of fuzzy graphs for metamodeling. Proceedings of the 2002 IEEE conference, pp 640–644
Kauffman A (1973) Introduction a la Theorie des Sous-emsembles Flous. Masson et Cie, vol 1
Kiss A (1991) An application of fuzzy graphs in database theory. Pure Math Appl 1(3–4):337–342
Koczy LT (1992) Fuzzy graphs in the evaluation and optimization of networks. Fuzzy Sets Syst 46:307–319
Lee K-M (2000) Bipolar-valued fuzzy sets and their basic operations. Proceedings of international conference, Bangkok, Thailand, pp 307–317
Lee K-M (2004) Comparison of bipolar fuzzy sets, intuitionistic fuzzy sets, and bipolar-valued fuzzy sets. J Fuzzy Logic Intell Syst 14:125–129
Mathew S, Sunitha MS (2009) Types of arcs in a fuzzy graph. Inf Sci 179(11):1760–1768
Mathew S, Sunitha MS (2010) Node connectivity and arc connectivity of a fuzzy graph. Inf Sci 180(4):519–531
Mordeson JN (1993) Fuzzy line graphs. Pattern Recognit Lett 14:381–384
Mordeson JN, Nair PS (1998) Fuzzy graphs and fuzzy hypergraphs, 2nd edn, 2001. Physica Verlag, Heidelberg
Nagoor Gani A, Radha K (2008) On regular fuzzy graphs. J Phys Sci 12:33–40
Perchant A, Bloch I (2002) morphisms between graphs. Fuzzy Sets Syst 128:149–168
Parvathi R, Karunambigai MG, Atanassov KT (2009) Operations on intuitionistic fuzzy graphs. Fuzzy Systems, FUZZ-IEEE 2009. IEEE international conference, pp 1396–1401
Pasi G, Yager R, Atanassov KT (2004) Intuitionistic fuzzy graph interpretations of multi-person multi-criteria decision making: generalized net approach. Intelligent systems, proceedings, 2004 2nd international IEEE conference 2:434–439
Rosenfeld A (1975) Fuzzy graphs. In: Zadeh LA, Fu KS, Shimura M (eds) Fuzzy sets and their applications, Academic Press, New York, pp 77–95
Shannon A, Atanassov KT (1994) A first step to a theory of the intuitionistic fuzzy graphs. In: Lakov D (ed) Proceeding of FUBEST, Sofia, Sept 28–30, pp 59–61
Shannon A, Atanassov KT (1995) Intuitionistic fuzzy graphs from α−, β−, and (α, b)- levels. Note Intuitionistic Fuzzy Sets 1(1):32–35
Riff M, Zún¨iga M, Montero E (2010) A graph-based immune-inspired constraint satisfaction search. Neural Comput Appl 19(8):1133–1142
Yin Y, Zhan J, Corsini P (2011) Fuzzy roughness of n-ary hypergroups based on a complete residuated lattice. Neural Comput Appl 20(1):41–57
Zadeh LA (1965) Fuzzy sets. Inf Control 8:338–353
Zadeh LA (1971) Similarity relations and fuzzy orderings. Inf Sci 3(2):177–200
Zadeh LA (2005) Toward a generalized theory of uncertainty (GTU)—an outline. Inf Sci 172:1–40
Zadeh LA (2005) From imprecise to granular probabilities. Fuzzy Sets Syst 154:370–374
Zhang W-R (1994) Bipolar fuzzy sets and relations: a computational framework forcognitive modeling and multiagent decision analysis, Proceedings of IEEE conference, pp 305–309
Zhang W-R (1998) Bipolar fuzzy sets. Proceedings of FUZZ-IEEE, pp 835–840
Zhang J, Yang X (2010) Some properties of fuzzy reasoning in propositional fuzzy logic systems. Inf Sci 180:4661–4671
Acknowledgments
The authors are thankful to the referees for their valuable comments and suggestions for improving the paper.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Akram, M., Dudek, W.A. Regular bipolar fuzzy graphs. Neural Comput & Applic 21 (Suppl 1), 197–205 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-011-0772-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-011-0772-6