Abstract
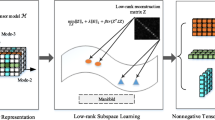
We contribute, through this paper, to design a novel algorithm called maximum margin projection with tensor representation (MMPTR). This algorithm is able to recognize gait and micro-expression represented as third-order tensors. Through maximizing the inter-class Laplacian scatter and minimizing the intra-class Laplacian scatter, MMPTR can seek a tensor-to-tensor projection that directly extracts discriminative and geometry-preserving features from the original tensorial data. We show the validity of MMPTR through extensive experiments on the CASIA(B) gait database, TUM GAID gait database, and CASME micro-expression database. The proposed MMPTR generally obtains higher accuracy than MPCA, GTDA as well as state-of-the-art DTSA algorithm. Experimental results included in this paper suggest that MMPTR is especially effective in such tensorial object recognition tasks.























Similar content being viewed by others
References
Daniel E, Lars H, Bernd H (2011) A survey of dimension reduction methods for high-dimensional data analysis and visualization. In: Visualization of large and unstructured data sets, pp 135–149
Andrew RW (1995) Multidimensional scaling by iterative majorization using radial basis functions. Pattern Recogn 28:753–759
Tenenbaum JB, Silva V, Langford JC (2000) A global geometric framework for nonlinear dimensionality reduction. Science 290(5500):2319–2323
Roweis ST, Lawrence KS (2000) Nonlinear dimensionality reduction by locally linear embedding. Science 290:2323–2326
Kim M, Pavlovic V (2011) Central subspace dimensionality reduction using covariance operators. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 33:657–670
Yang W, Wang Z, Sun C (2015) A collaborative representation based projections method for feature extraction. Pattern Recogn 48:20–27
Wang R, Shan S, Chen X, Chen J, Gao W (2011) Maximal linear embedding for dimensionality reduction. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 33:1776–1792
He XF, Cai D, Niyogi P (2005) Tensor subspace analysis. In: Advances in neural information proceeding systems 18, Vancouver, Canada
Vasilescu MAO, Terzopoulos D (2005) Multilinear independent components analysis. IEEE Comput Soc Conf Comput Vision Pattern Recogn 1:547–553
Raj RG, Bovik AC (2010) A fast multilinear ICA algorithm. In: 17th IEEE international conference on image processing (ICIP), pp 1889–1892
Lu H, Plataniotis KN, Venetsanopoulos AN (2008) MPCA: multilinear principal component analysis of tensor objects. IEEE Trans Neural Netw 19:18–39
Panagakis Y, Kotropoulos C, Arce GR (2010) Non-negative multilinear principal component analysis of auditory temporal modulations for music genre classification. IEEE Trans Audio Speech Lang Process 18:576–588
Yan S, Xu D, Yang Q, Zhang L, Tang X, Zhang HJ (2007) Multilinear discriminant analysis for face recognition. IEEE Trans Image Process 16:212–220
Yan S, Xu D, Yang Q, Zhang L, Tang X, Zhang HJ (2005) Discriminant analysis with tensor representation. IEEE Comput Soc Conf Comput Vision Pattern Recogn 1:526–532
Tao D, Li X, Wu X, Maybank SJ (2007) General tensor discriminant analysis and gabor features for gait recognition. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 29:1700–1715
Chang X, Nie F, Wang S, Yang Y, Zhou X, Zhang C (2015) Compound Rank-k Projections for Bilinear Analysis. IEEE Trans Neural Netw Learn Syst. doi:10.1109/TNNLS.2015.2441735
Zhang L, Zhang L, Tao D, Huang X (2013) Tensor discriminative locality alignment for hyperspectral image spectral-spatial feature extraction. IEEE Trans Geosci Remote Sens 51:242–256
Lu H, Plataniotis KN, Venetsanopoulos AN (2009) Uncorrelated multilinear principal component analysis for unsupervised multilinear subspace learning. IEEE Trans Neural Netw 20:1820–1836
Ben XY, Jiang MY, Yan R et al (2015) Orthogonal multilinear discriminant analysis and its subblock tensor analysis version. Optik Int J Light Electron Opt 126:361–367
Lu J, Tan YP (2009) Uncorrelated multilinear geometry preserving projections for multimodal biometrics recognition. In: IEEE international symposium on circuits and systems, pp 2601–2604
Li X, Lin S, Yan S, Xu D (2008) Discriminant locally linear embedding with high-order tensor data. IEEE Trans Syst Man Cybern B Cybern 38:342–352
Zheng D, Du X, Cui L (2010) Tensor locality preserving projections for face recognition. In: 2010 IEEE international conference on systems man and cybernetics (SMC), pp 2347–2350
Lu J, Tan YP (2008) Enhanced face recognition using tensor neighborhood preserving discriminant projections. In: 15th IEEE international conference on image processing, pp 1916–1919
Lu J, Wang G, Tan YP (2011) Multilinear locality preserving canonical correlation analysis for face recognition, information. In: 8th international conference on communications and signal processing (ICICS), pp 1–5
Wang SJ, Chen HL, Yan WJ, Chen YH, Fu XL (2014) Face recognition and micro-expression recognition based on discriminant tensor subspace analysis plus extreme learning machine. Neural Process Lett 39(1):25–43
Han XH, Chen YW, Ruan X (2012) Multilinear supervised neighborhood embedding of a local descriptor tensor for scene/object recognition. IEEE Trans Image Process 21:1314–1326
Liu Y, Liu Y, Chan KCC (2010) Tensor distance based multilinear locality-preserved maximum Information embedding. IEEE Trans Neural Netw 21:1848–1854
Liu Y, Liu Y, Chan KCC (2009) Multilinear isometric embedding for visual pattern analysis. In: IEEE 12th international conference on computer vision workshops (ICCV Workshops), pp 212–218
Liu M, Chowdhury AKR (2010) Multilinear feature extraction and classification of multi-focal images, with applications in nematode taxonomy, 2010. In: IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (CVPR), pp 2823–2830
Feng ZH, Kittler J, Christmas W, Wu XJ, Pfeiffer S (2012) Automatic face annotation by multilinear AAM with missing values. In: 2012 21st international conference on pattern recognition (ICPR), pp 2586–2589
Hu H (2013) Enhanced gabor feature based classification using a regularized locally tensor discriminant model for multiview gait recognition. IEEE Trans Circuits Syst Video Technol 23:1274–1286
Ben XY, Xu S, Wang KJ (2012) Review on pedestrian gait feature expression and recognition. Pattern Recog Artif Intell 25:71–81
Yu S, Wang L, Huang K et al. (2004) Gait analysis for human identification in frequency domain. In: Proceedings of the 3rd international conference on image and graphics, pp 282–285
Boulgouris NV, Plataniotis KN, Hatzinakos D (2006) Gait recognition using linear time normalization. Pattern Recogn 39:969–979
Chen C, Liang J, Zhu X (2011) Gait recognition based on improved dynamic bayesian networks. Pattern Recogn 44:988–995
Wang L, Hu WM, Tan TN (2003) Gait-Based human identification. Chin J Comput 26:353–360
Goffredo M, Carter JN, Nixon MS (2008) Front view gait recognition. In: Proceedings of the 2nd IEEE international conference on biometrics: theory, applications and systems, pp 1–6
Urtasun R, Fua P (2004) 3D tracking for ait characterization and recognition. In: Proceedings of the sixth IEEE international conference on automatic face and gesture recognition, pp 17–22
Ben XY, Xu S, Wang KJ (2012) Research on gait recognition based on trace transform. J Jilin Univ (Engineering and Technology Edition) 42:1–5
Toby HWL, Cheung KH, James NKL (2011) Gait flow image: a silhouette-based gait representation for human identification. Pattern Recogn 44:973–987
Wang KJ, Ben XY, Liu LL et al (2009) Gait recognition using information fusion of energy. J Huazhong Univ Sci Technol 37:14–17
Owayjan M, Kashour A, Haddad NA, Fadel M, Souki GA (2012) The design and development of a lie detection system using facial micro-expressions. In: 2012 2nd international conference on advances in computational tools for engineering applications (ACTEA), pp 33–38
Pfister T, Li X, Zhao G, Pietikainen M (2011) Recognising spontaneous facial micro-expressions. In: 2011 IEEE international conference on computer vision (ICCV), pp 1449–1456
Yang W, Wang J, Ren M, Yang J (2009) Feature extraction based on laplacian bidirectional maximum margin criterion. Pattern Recogn 42:2327–2334
Yu S, Tan D, Tan T (2006) A framework for evaluating the effect of view angle, clothing and carrying condition on gait recognition. In: Proceedings of the 18th international conference on pattern recognition, Hong Kong, China, pp 441–444
Ben XY, Meng WX, Yan R (2012) Dual-ellipse fitting approach for robust gait periodicity detection. Neurocomputing 79:173–178
Hofmann M, Geiger J, Bachmann S, Schuller B, Rigoll G (2013) The TUM gait from audio, image and depth (GAID) database: multimodal recognition of subjects and traits. In: Journal of visual communication and image representation, special issue on visual understanding and applications with rgb-d cameras, Elsevier
Hofmann M, Bachmann S, Rigoll G (2012) 2.5D gait biometrics using the depth gradient histogram energy image. In: IEEE fifth international conference on biometrics: theory, applications and systems (BTAS 2012), Washington, DC, USA, pp 23–26
Zhang HL, Ben XY, Zhang P, Liu TJ (2014) Gait period detection based on layered coding of depth information. In: The 2014 international conference on mechanical engineering and intelligent systems, Qingdao, China
Yan WJ, Wu Q, Liu YJ, Wang SJ, Fu XL (2013) CASME database: A dataset of spontaneous micro-expressions collected from neutralized faces. In: 2013 10th IEEE international conference and workshops on automatic face and gesture recognition (FG), pp 1–7
Shen X, Wu Q, Fu X (2012) Effects of the duration of expressions on the recognition of micro-expressions. J Zhejiang Univ Sci B 13:221–230
Acknowledgments
We sincerely thank the Institute of Automation Chinese Academy of Sciences for granting us permission to use the CASIA(B) gait database, and thank the Institute for Human–Machine Communication, Technische Universität München for granting us permission to use the TUM GAID database, and also thank the Institute of Psychology, Chinese Academy of Sciences for granting us permission to use the CASME database. This project is supported by the Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 61201370, 61571275, and 61571274), the Specialized Research Fund for the Doctoral Program of Higher Education of China (Grant No. 20120131120030), the Independent Innovation Foundation for Post-doctoral Scientists of Shandong Province (Grant No. 201303100), the Special Financial Program of China Post-doctoral Science Foundation (Grant No. 2014T70636), the Key Laboratory of Intelligent Perception and Systems for High-Dimensional Information, Ministry of Education (Grant No. 30920140122006), the Shandong Provincial Natural Science Foundation, China (Grant Nos. ZR2014FM030 and ZR2013FM32), and the Young Scholars Program of Shandong University (Grant No. 2015WLJH39).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ben, X., Zhang, P., Yan, R. et al. Gait recognition and micro-expression recognition based on maximum margin projection with tensor representation. Neural Comput & Applic 27, 2629–2646 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-015-2031-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-015-2031-8