Abstract
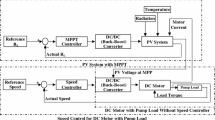
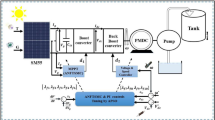
Maximum power point tracking (MPPT) is used in photovoltaic (PV) systems to maximize its output power. A new MPPT system has been suggested for PV–DC motor pump system by designing two PI controllers. The first one is used to reach MPPT by monitoring the voltage and current of the PV array and adjusting the duty cycle of the DC/DC converter. The second PI controller is designed for speed control of DC series motor by setting the voltage fed to the DC series motor through another DC/DC converter. The suggested design problem of MPPT and speed controller is formulated as an optimization task which is solved by artificial bee colony (ABC) to search for optimal parameters of PI controllers. Simulation results have shown the validity of the developed technique in delivering MPPT to DC series motor pump system under atmospheric conditions and tracking the reference speed of motor. Moreover, the performance of the ABC algorithm is compared with genetic algorithm for various disturbances to prove its robustness.

















Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- i a :
-
The armature current
- V t :
-
The motor terminal voltage
- R a and L a :
-
The armature resistance and inductance
- R f and L f :
-
The field resistance and inductance
- ω r :
-
The motor angular speed
- J m :
-
The moment of inertia
- T L :
-
The load torque
- f :
-
The friction coefficient
- M af :
-
The mutual inductance between the armature and field
- I and V :
-
Module output current and voltage
- I c and V c :
-
Cell output current and voltage
- I ph and V ph :
-
The light generation current and voltage
- I s :
-
Cell reverse saturation current
- I sc :
-
The short circuit current
- I o :
-
The reverse saturation current
- R s :
-
The module series resistance
- T :
-
Cell temperature
- K :
-
Boltzmann’s constant
- q o :
-
Electronic charge
- KT:
-
(0.0017 A/°C) short circuit current temperature coefficient
- G :
-
Solar illumination in W/m2
- E g :
-
Band gap energy for silicon
- A :
-
Ideality factor
- T r :
-
Reference temperature
- I or :
-
Cell rating saturation current at T r
- n s :
-
Series connected solar cells
- k i :
-
Cell temperature coefficient
- V B and I B :
-
The output converter voltage and current respectively
- k :
-
The duty cycle of the pulse width modulation (PWM)
- e 1 :
-
The error in the MPPT control loop
- e 2 :
-
The error in the speed control loop
- J :
-
The objective function
- K P1 and K I1 :
-
The parameters of first PI controller for MPPT control loop
- K P2 and K I2 :
-
The parameters of second PI controller for speed control loop
- t sim :
-
The time of simulation
References
Masters GM (2004) Renewable and efficient electric power systems. Wiley, Hoboken
Ahin AE (2012) Modeling and optimization of renewable energy systems. InTech, India
Patel MR (2006) Wind and solar power systems: design, analysis, and operation, 2nd edn. CRC Press, Taylor & Francis Group, USA
Veerachary M, Seniyu T, Uezato K (2001) Maximum power point tracking control of IDB converter supplied PV system. IEE Proc Electron Power Appl 148(6):494–502
Armstrong S, Hurley W (2004) Self regulating maximum power point tracking for solar energy systems. In: 39th international universities power engineering conference, UPEC, Bristol, UK, pp 604–609
Piegari L, Rizzo R (2010) Adaptive perturb and observe algorithm for photovoltaic maximum power point tracking. IET Renew Power Gener 4(4):317–328
Eltawil MA, Zhao Z (2013) MPPT techniques for photovoltaic applications. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 25:793–813
Brambilla A, Gambarara M, Garutti A, Ronchi F (1999) New approach to photovoltaic arrays maximum power point tracking. In: 30th annual IEEE power electronics specialists conference 1999 (PESC 99), vol 2, pp 632–637
Hohm DP, Ropp ME (2000) Comparative study of maximum power point tracking algorithm using an experimental programmable, maximum power point tracking test bed. In: Proceedings of 28th IEEE photovoltaic specialist conference, pp 1699–1702
Swiegers W, Enslin J (1998) An integrated maximum power point tracker for photovoltaic panels. In: Proceedings IEEE international symposium on industrial electronics, vol 1, pp 40–44
Oshiro M, Tanaka K, Senjyu T, Toma S, Atsushi Y, Saber A, Funabashi T, Kim C (2011) Optimal voltage control in distribution systems using PV generators. Int J Electr Power Energy Syst 33(3):485–492
Youesf A, Oshaba A (2012) Efficient fuzzy logic speed control for various types of DC motors supplied by photovoltaic system under maximum power point tracking. J Eng Sci Assiut Univ 40(5):1455–1474
Hui J, Sun X (2010) MPPT strategy of PV system based on adaptive fuzzy PID algorithm. In: International conference on life system modeling and intelligent computing, vol 97, pp 220–228
Ouada M, Meridjet M, Saoud M, Talbi N (2013) Increase efficiency of photovoltaic pumping system based BLDC motor using fuzzy logic MPPT control. WSEAS Trans Power Syst 8(3):104–113
AI-Amoudi A, Zhang L (2000) Application of radial basis function networks for solar-array modeling and maximum power-point prediction. In: IEE proceeding-generation, transmission and distribution, vol 147, no. 5, pp 310–316
Bahgat ABG, Helwa NH, Ahmad GE, El Shenawy ET (2005) Maximum power point tracking controller for PV systems using neural networks. Renew Energy 30(8):1257–1268
Zhang H, Cheng S (2011) A new MPPT algorithm based on ANN in solar PV systems. Adv Comput Commun Control Autom LNEE 121:77–84
Baek J, Ko J, Choi J, Kang S, Chung D (2010) Maximum power point tracking control of photovoltaic system using neural network. In: International of conference on electrical machines and systems (ICEMS), pp 638–643
Kassem AM (2012) MPPT control design and performance improvements of a PV generator powered DC motor-pump system based on artificial neural networks. Int J Electr Power Energy Syst 43:90–98
Younis MA, Khatib T, Najeeb M, Ariffin AM (2012) An improved maximum power point tracking controller for PV systems using artificial neural network. Prz Elektrotech 88(3b):116–121
Ishaque K, Salam Z (2011) An improved modeling method to determine the model parameters of photovoltaic (PV) modules using differential evolution (DE). Sol Energy 85:2349–2359
Ishaque K, Salam Z, Taheri H, Shamsudin A (2011) A critical evaluation of EA computational methods for photovoltaic cell parameter extraction Based on two diode model. Sol Energy 85:1768–1779
Ramaprabha R, Gothandaraman V, Kanimozhi K, Divya R, Mathur BL (2011) Maximum power point tracking using GA optimized artificial neural network for solar PV system. In: IEEE international conference on electrical energy systems, pp 264–268
Ishaque K, Salam Z, Amjad M, Mekhilef S (2012) An improved particle swarm optimization (PSO)-based MPPT for PV with reduced steady-state oscillation. IEEE Trans Power Electron 27(8):3627–3638
Zhao Y, Zhao X, Zhang Y (2014) MPPT for photovoltaic system using multi-objective improved particle swarm optimization algorithm. Teklanika Indones J Electr Eng 12(1):261–268
Gokmen N, Karatepe E, Ugranli F, Silvestre S (2013) Voltage band based global MPPT controller for photovoltaic systems. Sol Energy 98(3):322–334
Oshaba AS, Ali ES (2013) Speed control of induction motor fed from wind turbine via particle swarm optimization based PI controller. Res J Appl Sci Eng Technol 5(18):4594–4606
Oshaba AS, Ali ES (2013) Swarming speed control for DC permanent magnet motor drive via pulse width modulation technique and DC/DC converter. Res J Appl Sci Eng Technol 5(18):4576–4583
Pooja B, Dub SS, Singh JB, Lehana P (2013) Solar power optimization using BFO algorithm. Int J Adv Res Comput Sci Softw Eng 3(12):238–241
Ali ES, Abd-Elazim SM (2013) Power system stability enhancement via bacteria foraging optimization algorithm. Int Arab J Sci Eng (AJSE) 38(3):599–611
Abd-Elazim SM, Ali ES (2013) Synergy of particle swarm optimization and bacterial foraging for TCSC damping controller design. Int J WSEAS Trans Power Syst 8(2):74–84
Abd-Elazim SM, Ali ES (2013) A hybrid particle swarm optimization and bacterial foraging for optimal power system stabilizers design. Int J Electr Power Energy Syst 46:334–341
Oshaba AS, Ali ES (2014) Bacteria foraging: A new technique for speed control of DC series motor supplied by photovoltaic system. Int J WSEAS Trans Power Syst 9:185–195
Ali ES, Abd-Elazim SM (2014) Power system stability enhancement via new coordinated design of PSSs and SVC. Int J WSEAS Trans Power Syst 9:428–438
Karaboga D (2005) An idea based on honey bee swarm for numerical optimization. In: Technical report-TR06, Erciyes University, Engineering Faculty, Computer Engineering Department
Karaboga D, Basturk B (2007) A powerful and efficient algorithm for numerical function optimization: artificial bee colony algorithm. J Glob Optim 39(3):459–471
Abedinia O, Wyns B, Ghasemi A (2011) Robust fuzzy PSS design using ABC. In: 10th environment and electrical energy international conference (EEEIC) Rome, Italy, pp 100–103
Gitizadeh M, Khalilnezhad H, Hedayatzadeh R (2013) TCSC allocation in power systems considering switching loss using MOABC algorithm. Electr Eng 95(2):73–85
Tiacharoen S, Chatchanayuenyong T (2012) Design and development of an intelligent control by using bee colony optimization technique. Am J Appl Sci 9(9):1464–1471
Awan SM, Aslam M, Khan ZA, Saeed H (2014) An efficient model based on artificial bee colony optimization algorithm with neural networks for electric load forecasting. Neural Comput Appl 25(7–8):1967–1978
Abedinia O, Naslian MD, Bekravi M (2014) A new stochastic search algorithm bundled honeybee mating for solving optimization problems. Neural Comput Appl 25(7–8):1921–1939
Mostofi F, Safavi M (2013) Application of ABC algorithm for grid-independent hybrid hydro/photovoltaic/wind/fuel cell power generation system considering cost and reliability. Int J Renew Energy Res 3(4):928–940
Oliva D, Cuevas E, Pajares G (2014) Parameter identification of solar cells using artificial bee colony optimization. Energy 72(1):93–102
Babar B, Crăciunescu A (2014) Comparison of artificial bee colony Algorithm with other algorithms used for tracking of maximum power point of photovoltaic arrays. Renew Energy Power Q J 12:1–4
Benyoucef AS, Chouder A, Kara K, Silvestre S, Sahed OA (2015) Artificial bee colony based algorithm for maximum power point tracking (MPPT) for PV systems operating under partial shaded conditions. Appl Soft Comput 32:38–48
Yeadon WH, Yeadon AW (2001) Handbook of small electric motors. McGraw-Hill, New York
Mehta R, Mehta VK (2013) Principles of electrical machines, 2nd edn. S. Chand Publishing, New Delhi, India
Erickson RW, Maksimovic D (2001) Fundamentals of power electronics, 2nd edn. Springer, New York
Mohan N, Undeland TM, Robbins WP (2003) Power electronics converters, applications, and design, 3rd edn. Wiley, Amsterdam
Osheba DS (2011) Photovoltaic system fed DC motor controlled by converters. In: M.Sc. Thesis, March 2011, Menoufiya University, Egypt
Salam Z, Ahmed J, Merugu BS (2013) The application of soft computing methods for MPPT of PV system: a technological and status review. Appl Energy 107:135–148
Oshaba AS, Ali ES, Abd-Elazim SM (2015) MPPT control design of PV system supplied SRM using BAT search algorithm. Sustain Energy Grids Netw 2C:51–60
Hua C, Shen C (1997) Control of DC/DC converters for solar energy system with maximum power tracking. In: 23rd international conference on industrial electronics, control and instrumentation. IECON’97, vol 2, pp 827–832
Liu X, Lopes LAC (2004) An improvement perturbation and observation maximum power point tracking algorithm for PV arrays. In: Power electronics specialists conference, PESC’04, vol 3, pp 2005–2010
Nafeh AA, Fahmy FH, Mahgoub OA, El-Zahab EM (1998) Developed algorithm of maximum power tracking for stand-alone photovoltaic system. Energy Sour 20:45–53
Yu GJ, Jung YS, Choi JY, Kim GS (2004) A novel two-mode MPPT control algorithm based on comparative study of existing algorithms. Sol Energy 76(4):445–463
Cheikh MSA, Larbes C, Kebir GFT, Zerguerras A (2007) Maximum power point tracking using fuzzy logic control scheme. Rev Energ Renouv 10(3):387–395
Amrouche B, Belhamel M, Guessoum A (2007) Artificial intelligence based P&O MPPT method for photovoltaic systems. Revue des Energies Renouvelables ICRESD-07 Tlemcen 11–16
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Appendix
Appendix
The system data are as shown below:
-
(a)
DC series motor parameters are shown below
DC motor parameters | Value |
|---|---|
Motor rating | 3.5 HP |
Motor rated voltage | 240 V |
Motor rated current | 12 A |
Inertia constant J m | 0.0027 kg m2 |
Damping constant B | 0.0019 N m s/rad |
Armature resistance R a | 1.63 Ω |
Armature inductance L a | 0.0204 H |
Motor speed | 2000 rpm |
Full load torque | 19 N m |
-
(b)
The parameters of ABC are as follows: The number of colony size = 50; the number of food sources equals to the half of the colony size; the number of cycles = 100; the limit = 100.
-
(c)
The parameters of GA are as follows: max generation = 100; population size = 50; crossover probabilities = 0.75; mutation probabilities = 0.1.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Oshaba, A.S., Ali, E.S. & Abd Elazim, S.M. PI controller design using ABC algorithm for MPPT of PV system supplying DC motor pump load. Neural Comput & Applic 28, 353–364 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-015-2067-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-015-2067-9