Abstract
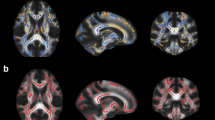
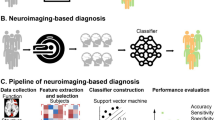
Schizo-obsessive disorder is characterized by the clinical syndrome in which comorbid obsessive–compulsive disorder accompanies schizophrenia. A substantial number of studies have investigated the neuropsychological and clinical differences between schizophrenia and schizo-obsessive disorder. However, the neurostructural differences between these two groups have not been adequately investigated. The aim of this study was to explore gray matter differences between schizophrenia and schizo-obsessive patients using voxel-based morphometry and support vector machines combined with feature selection algorithm. Twenty-three schizophrenia and 23 schizo-obsessive patients matched by age, gender and handedness were recruited. Clinical assessments were completed in addition to high-resolution structural MRI scanning. Group differences were investigated using contrast maps, and significant regions were subjected to a feature selection and support vector machine hybrid model. In addition, voxel-of-interest values for the commonly shared brain areas between schizophrenia and OCD reported in previous meta-analyses were also used as inputs in this step. The results showed that schizo-obsessive patients had greater gray matter densities in paracentral areas (including supplementary motor area) and middle cingulate gyrus than schizophrenia patients. These brain areas together with the fronto-subcortical areas could successfully discriminate two groups with an accuracy of 78.26 %. Our results provide the first neuroanatomical evidence that schizo-obsessive disorder and schizophrenia may be two distinct clinical entities. Based on these findings, considering schizo-obsessive disorder as a subtype of schizophrenia is discernible.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Poyurovsky M, Hramenkov S, Isakov V, Rauchverger B, Modai I, Schneidman M, Fuchs C, Weizman A (2001) Obsessive–compulsive disorder in hospitalized patients with chronic schizophrenia. Psychiatry Res 102:49–57
Bottas A, Cooke RG, Richter MA (2005) Comorbidity and pathophysiology of obsessive–compulsive disorder in schizophrenia: Is there evidence for a schizo-obsessive subtype of schizophrenia? J Psychiatry Neurosci 30:187–193
Braff DL, Ryan J, Rissling AJ, Carpenter WT (2013) Lack of use in the literature from the last 20 years supports dropping traditional schizophrenia subtypes from DSM-5 and ICD-11. Schizophr Bull 39:751–753
Berman I, Sapers BL, Chang HH, Losonczy MF, Schmildler J, Green AI (1995) Treatment of obsessive–compulsive symptoms in schizophrenic patients with clomipramine. J Clin Psychopharmacol 15:206–210
Sevincok L, Akoglu A, Topaloglu B, Aslantas H (2004) Neurological soft signs in schizophrenic patients with obsessive–compulsive disorder. Psychiatry Clin Neurosci 58:274–279
Nechmad A, Ratzoni G, Poyurovsk M, Meged S, Avidan G, Fuchs C, Bloch Y, Weizman R (2003) Obsessive–compulsive disorder in adolescent schizophrenia patients. Am J Psychiatry 160:1002–1004
Michalopoulou PG, Konstantakopoulos G, Typaldou M, Papageorgiou C, Christodoulou GN, Lykouras L, Oulis P (2014) Can cognitive deficits differentiate between schizophrenia with and without obsessive–compulsive symptoms? Compr Psychiatry 55:1015–1021
Cunill R, Huerta Ramos E, Castells X (2013) The effect of obsessive–compulsive symptomatology on executive functions in schizophrenia: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Psychiatry Res 210:21–28
Tibbo P, Kroetsch M, Chue P, Warneke L (2000) Obsessive–compulsive disorder in schizophrenia. J Psychiatr Res 34:139–146
Cunill R, Castells X, Simeon D (2009) Relationships between obsessive–compulsive symptomatology and severity of psychosis in schizophrenia: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Clin Psychiatry 70:70–82
Üçok A, Ceylan ME, Tihan AK, Lapçin S, Ger C, Tükel R (2010) Obsessive compulsive disorder and symptoms may have different effects on schizophrenia. Prog Neuro-Psychopharmacol 35:429–433
Patel DD, Laws KR, Padhi A, Farrow JM, Mukhopadhaya K, Krishnaiah R, Fineberg NA (2010) The neuropsychology of the schizo-obsessive subtype of schizophrenia: a new analysis. Psychol Med 40:921–933
Iida J, Matumura K, Aoyama F, Iwasaka H, Hirao F, Sakiyama S (1998) Cerebral MRI findings in childhood-onset schizophrenia, comparison of patients with prodromal obsessive–compulsive symptoms and those without symptoms. Recent Prog Child Adolesc Psychiatry 2:75–83
Aoyama F, Iida J, Inoue M, Iwasaka H, Sakiyam S, Hata K, Kishimoto T (2000) Brain imaging in childhood- and adolescence-onset schizophrenia associated with obsessive–compulsive symptoms. Acta Psychiatr Scand 102:32–37
Gross Isseroff R, Hermesh H, Zohar J, Weizman A (2003) Neuroimaging communality between schizophrenia and obsessive compulsive disorder: A putative basis for schizo-obsessive disorder? World J Biol 4:129–134
Menzies L, Chamberlain SR, Laird AR, Thelen SM, Sahakian BJ, Bullmore ET (2008) Integrating evidence from neuroimaging and neuropsychological studies of obsessive–compulsive disorder: the orbitofronto-striatal model revisited. Neurosci Biobehav R 32:525–549
Rotge JY, Guehl D, Dilharreguy B, Tignol J, Bioulac B, Allard M, Burbaud P, Aouizerate B (2009) Meta-analysis of brain volume changes in obsessive–compulsive disorder. Biol Psychiatry 65:75–83
Rotge JY, Langbour N, Guehl D, Bioulac B, Jaafar N, Allard M, Aouizerate B, Burbaud P (2010) Gray matter alterations in obsessive–compulsive disorder: an anatomic likelihood estimation meta-analysis. Neuropsychopharmacology 35:686–691
Bor E, Fornito A, Radu J, Walterfang M, Seal M, Wood SJ, Yücel M, Velakoulis D, Pantelis C (2011) Neuroanatomical abnormalities in schizophrenia: a multimodal voxelwise meta-analysis and meta-regression analysis. Schizophr Res 127:46–57
Fusar-Poli P, Radua J, McGuire P, Borgwardt S (2011) Neuroanatomical maps ofpsychosis onset: voxel-wise meta-analysis of antipsychotic-naive VBM studies. Schizophr Bull 38:1297–1307
Glahn DC, Laird AR, Ellison-Wright I, Thelen SM, Robinson JL, Lancaster JL, Bullmore E, Fox PT (2008) Meta-analysis of gray matter anomalies in schizophrenia: application of anatomic likelihood estimation and network analysis. Biol Psychiatry 64:774–781
McIntosh AM, Job DE, Moorhead TW, Harrison LK, Forrester K, Lawrie SM, Johnstone EC (2004) Voxel-based morphometry of patients with schizophrenia or bipolar disorder and their unaffected relatives. Biol Psychiatry 56:544–552
Orrù G, Pettersson-Yeo W, Marquand AF, Sartori G, Mechelli A (2012) Using support vector machine to identify imaging biomarkers of neurological and psychiatric disease: a critical review. Neurosci Biobehav R 36:1140–1152
Lemm S, Blankertz B, Dickhaus T, Müller KR (2011) Introduction to machine learning for brain imaging. Neuroimage 56:387–399
Liu Y, Teverovskiy L, Carmichael O, Kikinis R, Shenton M, Carter CS, Stenger VA, Davis S, Aizenstein H, Becker J, Lopez O, Meltzer C (2004) Discriminative MR image feature analysis for automatic schizophrenia and Alzheimer’s disease classification. In: Barillot C, David H, Hellier R, Pierre (eds) Medical image computing and computer-assisted intervention—MICCAI2004 7th international conference. Springer, Saint-Malo, pp 393–401
Ecker C, Rocha-Rego V, Johnston P, Mourao-Miranda J, Marquand A, Daly EM, Brammer MJ, Murphy C, Murphy DG (2010) Investigating the predictive value of whole-brain structural MR scans in autism: a pattern classification approach. NeuroImage 49:44–56
Magnin B, Mesrob L, Kinkingnéhun S, Pélégrini-Issac M, Colliot O, Sarazin M, Dubois B, Lehéricy S, Benali H (2009) Support vector machine-based classification of Alzheimer’s disease from whole-brain anatomical MRI. Neuroradiology 51:73–83
Erguzel TT, Ozekes S, Tan O, Gultekin S (2014) Feature selection and classification of electroencephalographic signals an artificial neural network and genetic algorithm based approach. Clin EEG Neurosci. doi:10.1177/1550059414523764
Huang CL (2009) ACO-based hybrid classification system with feature subset selection and model parameters optimization. Neurocomputing 73:438–448
Oldfield RC (1971) The assessment and analysis of handedness: the Edinburgh inventory. Neuropsychologia 9:97–113
Rijcken CA, Monster TB, Brouwers JR (2003) Chlorpromazine equivalents versus defined daily doses: How to compare antipsychotic drug doses? J Clin Psychopharmacol 23:657–659
Kroken RA, Johnsen E, Ruud T, Wentzel-Larsen T, Jørgensen HA (2009) Treatment of schizophrenia with antipsychotics in Norwegian emergency wards, a cross-sectional national study. BMC Psychiatry 9:24
Doyle M, Chorcorain AN, Griffith E, Trimble T, O’Callaghan E (2014) Obsessive compulsive symptoms in patients with Schizophrenia on clozapine and with obsessive compulsive disorder: a comparison study. Compr Psychiatry 55:130–136
Overall JE, Gorham DR (1962) The brief psychiatric rating scale. Psychol Rep 10:799–812
Kay SR, Flszbein A, Opfer LA (1987) The positive and negative syndrome scale (PANSS) for schizophrenia. Schizophr Bull 13:261
Goodman WK, Price LH, Rasmussen SA, Mazure C, Fleischmann RL, Hill CL, Heninger GR, Charney DS (1989) The Yale-Brown obsessive compulsive scale: I. Development, use, and reliability. Arch Gen Psychiatry 46:1006–1011
Ashburner J, Friston KJ (2000) Voxel-based morphometry—the methods. NeuroImage 11:805–821
Ashburner J (2007) A fast diffeomorphic image registration algorithm. NeuroImage 38:95–113
Lao Z, Shen D, Xue Z, Karacali B, Resnick SM, Davatzikos C (2004) Morphological classification of brains via high-dimensional shape transformations and machine learning methods. Neuroimage 21:46–57
Fung G, Stoeckel J (2007) SVM feature selection for classification of SPECT images of Alzheimer’s disease using spatial information. Knowl Inf Syst 11:243–258
Maldjian JA, Laurienti PJ, Kraft RA, Burdette JH (2003) An automated method for neuroanatomic and cytoarchitectonic atlas-based interrogation of fMRI data sets. NeuroImage 19:1233–1239
Kohavi R, John GH (1997) Wrappers for feature subset selection. Artif Intell 97:273–324
Li Y, Wang G, Chen H, Shi L, Qin L (2013) An ant colony optimization based dimension reduction method for high-dimensional datasets. J Bionic Eng 10:231–241
Dorigo M, Gambardella LM (1997) Ant colony system: a cooperative learning approach to the traveling salesman problem. IEEE Trans Evol Comput 1:53–66
Song S, Zhan Z, Long Z, Zhang J, Yao L (2011) Comparative study of SVM methods combined with voxel selection for object category classification on fMRI data. PLoS One 6(2):e17191
Norman KA, Polyn SM, Detre GJ, Haxby JV (2006) Beyond mind-reading: multi-voxel pattern analysis of fMRI data. Trends Cognit Sci 10:424–430
Misaki M, Kim Y, Bandettini P, Kriegeskorte N (2010) Comparison of multivariate classifiers and response normalizations for pattern-information fMRI. NeuroImage 53:103–118
Douglas PK, Lau E, Anderson A, Head A, Kerr W, Wollner M, Cohen MS (2013) Single trial decoding of belief decision making from EEG and fMRI data using independent components features. Front Hum Neurosci 7:392
Krstajic D, Buturovic LJ, Leahy DE, Thomas S (2014) Cross-validation pitfalls when selecting and assessing regression and classification models. J Cheminform 6:1–15
Japkowicz N, Shah M (2011) Evaluating learning algorithms: a classification perspective. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Varma S, Simon R (2006) Bias in error estimation when using cross-validation for model selection. BMC Bioinform 7:91
Exner C, Weniger G, Schmidt-Samoa C, Irle E (2006) Reduced size of the pre-supplementary motor cortex and impaired motor sequence learning in first-episode schizophrenia. Schizophr Res 84:386–396
Voets NL, Hough MG, Douaud G, Matthews PM, James A, Winmill L, Webster P, Smith S (2008) Evidence for abnormalities of cortical development in adolescent-onset schizophrenia. NeuroImage 43:665–675
Stegmayer K, Horn H, Federspiel A, Razav N, Bracht T, Laimböck K, Strik W, Dierks T, Wiest R, Müller TJ (2014) Supplementary motor area (SMA) volume is associated with psychotic aberrant motor behaviour of patients with schizophrenia. Psychiatry Res Neuroimaging 223:49–51
Goldberg G (1985) Supplementary motor area structure and function: review and hypotheses. Behav Brain Sci 8:567–588
Jürgens U (1984) The efferent and afferent connections of the supplementary motor area. Brain Res 300:63–81
Hoffstaedter F, Grefkes C, Caspers S, Roski C, Palomero-Gallagher N, Laird AN, Fox PT, Eickhoff SB (2013) The role of anterior midcingulate cortex in cognitive motor control. Hum Brain Mapp 35:2741–2753
Vogt BA, Berger GR, Derbyshire SW (2003) Structural and functional dichotomy of human midcingulate cortex. Eur J Neurosci 18:3134–3144
Iacoboni M, Molnar-Szakacs I, Gallese V, Buccino G, Mazziotta JC, Rizzolatti G (2005) Grasping the intentions of others with one’s own mirror neuron system. PLoS Biol 3:79
Gould IC, Shepherd AM, Laurens KR, Cairns MJ, Carr VJ, Green MJ (2014) Multivariate neuroanatomical classification of cognitive subtypes in schizophrenia: a support vector machine learning approach. Neuroimage Clin 18:229–236
Riffkin J, Yücel M, Maruff P, Wood SJ, Soulsby B, Olver J, Pantelis C (2005) A manual and automated MRI study of anterior cingulate and orbito-frontal cortices, and caudate nucleus in obsessive–compulsive disorder: comparison with healthy controls and patients with schizophrenia. Psychiatry Res Neuroimaging 138:99–113
Rajkumar RP, Reddy Y, Kandavel T (2008) Clinical profile of “schizo-obsessive” disorder: a comparative study. Compr Psychiatry 49:262–268
Acknowledgments
Uskudar University Research Council and NPIstanbul Neuropsychiatry Hospital funded the sample collection and MRI scans (No. NPI-120814).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tas, C., Mogulkoc, H., Eryilmaz, G. et al. Discriminating schizophrenia and schizo-obsessive disorder: a structural MRI study combining VBM and machine learning methods. Neural Comput & Applic 29, 377–387 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-016-2451-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-016-2451-0