Abstract
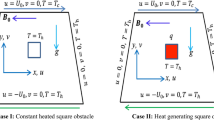
Influence of variable magnetic field on Fe3O4–H2O heat transfer in a cavity with circular hot cylinder is investigated. Innovative numerical method is chosen, namely CVFEM. The effects of radiation parameter, Rayleigh and Hartmann numbers on hydrothermal characteristics are presented. Results indicated that Lorentz forces cause the nanofluid motion to decrease and augment the thermal boundary layer thickness. Temperature gradient augments with augmentation of radiation parameter, Rayleigh number, but it reduces with augmentation of Lorentz forces.








Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- B :
-
Magnetic induction
- En:
-
Heat transfer enhancement
- Ec :
-
Eckert number
- H :
-
Magnetic field strength
- \(\mathop g\limits^{ \to }\) :
-
Gravitational acceleration vector
- Nu :
-
Nusselt number
- Ha :
-
Hartmann number
- T :
-
Fluid temperature
- Ra :
-
Rayleigh number
- V, U :
-
Vertical and horizontal dimensionless velocity
- Y, X :
-
Vertical and horizontal space coordinates
- β :
-
Thermal expansion coefficient
- μ 0 :
-
Magnetic permeability of vacuum
- α :
-
Thermal diffusivity
- Ω and Ψ :
-
Dimensionless vorticity and stream function
- Θ :
-
Dimensionless temperature
- γ :
-
Magnetic field strength at the source
- ρ :
-
Fluid density
- μ :
-
Dynamic viscosity
- σ :
-
Electrical conductivity
- nf:
-
Nanofluid
- f:
-
Base fluid
- loc:
-
Local
- c:
-
Cold
References
Zin NAM, Khan I, Shafie S (2016) The impact silver nanoparticles on MHD free convection flow of Jeffrey fluid over an oscillating vertical plate embedded in a porous medium. J Mol Liq 222:138–150
Khalid A, Khan I, Shafie S (2016) Heat transfer in ferrofluid with cylindrical shape nanoparticles past a vertical plate with ramped wall temperature embedded in a porous medium. J Mol Liq 221:1175–1183
Sheikholeslami M, Ganji DD (2016) Nanofluid convective heat transfer using semi analytical and numerical approaches: a review. J Taiwan Inst Chem Eng 65:43–77
Sheremet MA, Pop I, Roşca NC (2016) Magnetic field effect on the unsteady natural convection in a wavy-walled cavity filled with a nanofluid: Buongiorno’s mathematical model. J Taiwan Inst Chem Eng 61:211–222
Khalid A, Khan I, Shafie S (2015) Energy transfer in mixed convection MHD flow of nanofluid containing different shapes of nanoparticles in a channel filled with saturated porous medium. Nanoscale Res Lett. doi:10.1186/s11671-015-1144-4
Sheikholeslami M, Rashidi MM (2015) Effect of space dependent magnetic field on free convection of Fe3O4–water nanofluid. J Taiwan Inst Chem Eng 56:6–15
Gul A, Khan I, Shafie S, Khalid A, Khan A (2015) Heat transfer in MHD mixed convection flow of a ferrofluid along a vertical channel. PLoS ONE 11(10):1–14
Ali F, Gohara M, Khan I (2016) MHD flow of water-based Brinkman type nanofluid over a vertical plate embedded in a porous medium with variable surface velocity, temperature and concentration. J Mol Liq 223:412–419
Khalid A, Khan I, Shafie S (2015) Exact solutions for free convection flow of nanofluids with ramped wall temperature. Eur Phys J Plus 130:57
Selimefendigil F, Öztop HF (2016) Conjugate natural convection in a cavity with a conductive partition and filled with different nanofluids on different sides of the partition. J Mol Liq 216:67–77
Sheikholeslami M, Ellahi R (2015) Three dimensional mesoscopic simulation of magnetic field effect on natural convection of nanofluid. Int J Heat Mass Transf 89:799–808
Ellahi R, Hassan M, Zeeshan A (2015) Study of natural convection MHD nanofluid by means of single and multi walled carbon nanotubes suspended in a salt water solutions. IEEE Trans Nanotechnol 14(4):726–734
Zeeshan A, Majeed A, Ellahi R (2016) Effect of magnetic dipole on viscous ferro-fluid past a stretching surface with thermal radiation. J Mol Liq 215:549–554
Kandelousi MS (2014) Effect of spatially variable magnetic field on ferrofluid flow and heat transfer considering constant heat flux boundary condition. Eur Phys J Plus 129–248. doi:10.1140/epjp/i2014-14248-2
Ellahi R, Hassan M, Zeeshan A (2015) Shape effects of nanosize particles in Cu–H2O nanofluid on entropy generation. Int J Heat Mass Transf 81:449–456
Zeeshan A, Majeed A (2016) Non Darcy mixed convection flow of magnetic fluid over a permeable stretching sheet with Ohmic dissipation. J Magn 21:153–158
Sheikholeslami M, Ganji DD, Javed MY, Ellahi R (2015) Effect of thermal radiation on magnetohydrodynamics nanofluid flow and heat transfer by means of two phase model. J Magn Magn Mater 374:36–43
Sheikholeslami M, Vajravelu K, Rashidi MM (2016) Forced convection heat transfer in a semi annulus under the influence of a variable magnetic field. Int J Heat Mass Transf 92:339–348
Sheikholeslami M, Chamkha AJ (2016) Electrohydrodynamic free convection heat transfer of a nanofluid in a semi-annulus enclosure with a sinusoidal wall. Numer Heat Transf Part A 69(7):781–793. doi:10.1080/10407782.2015.1090819
Majeed A, Zeeshan A, Ellahi R (2016) Unsteady ferromagnetic liquid flow and heat transfer analysis over a stretching sheet with the effect of dipole and prescribed heat flux. J Mol Liq 223:528–533
Sheikholeslami M (2016) Influence of Coulomb forces on Fe3O4–H2O nanofluid thermal improvement. Int J Hydrog Energy. doi:10.1016/j.ijhydene.2016.09.185
Sheikholeslami M, Chamkha AJ (2016) Flow and convective heat transfer of a ferro-nanofluid in a double-sided lid-driven cavity with a wavy wall in the presence of a variable magnetic field. Numer Heat Transf Part A 69(10):1186–1200. doi:10.1080/10407782.2015.1125709
Sheikholeslami M, Hayat T, Alsaedi A (2016) Numerical study for external magnetic source influence on water based nanofluid convective heat transfer. Int J Heat Mass Transf. doi:10.1016/j.ijheatmasstransfer.2016.09.077
Sheikholeslami M, Ganji DD (2016) Influence of magnetic field on CuO–H2O nanofluid flow considering Marangoni boundary layer. Int J Hydrog Energy. doi:10.1016/j.ijhydene.2016.09.121
Sheikholeslami M, Hayat T, Alsaedi A (2016) MHD free convection of Al2O3–water nanofluid considering thermal radiation: a numerical study. Int J Heat Mass Transf 96:513–524
Anwar MI, Khan I, Hussanan A, Salleh MZ, Sharidan S (2013) Stagnation-point flow of a nanofluid over a nonlinear stretching sheet. World Appl Sci J 23(8):998–1006
Sheikholeslami M (2016) Influence of Lorentz forces on nanofluid flow in a porous cylinder considering Darcy model. J Mol Liq doi:10.1016/j.molliq.2016.11.022
Ellahi R, Zeeshan A, Hassan M (2015) Particle shape effects on Marangoni convection boundary layer flow of a nanofluid. Int J Numer Methods Heat Fluid Flow 26:2160–2174
Sheikholeslami M, Ashorynejad HR, Rana P (2016) Lattice Boltzmann simulation of nanofluid heat transfer enhancement and entropy generation. J Mol Liq 214:86–95
Sheikholeslami M, Rashidi MM (2015) Ferrofluid heat transfer treatment in the presence of variable magnetic field. Eur Phys J Plus 130:115
Sheikholeslami M, Abelman S (2015) Two phase simulation of nanofluid flow and heat transfer in an annulus in the presence of an axial magnetic field. IEEE Trans Nanotechnol 14(3):561–569
Sheikholeslami M, Ellahi R (2015) Simulation of ferrofluid flow for magnetic drug targeting using lattice Boltzmann method. J Z Naturforschung A 70(2):115–124
Sheikholeslami M, Rokni HB (2017) Nanofluid two phase model analysis in existence of induced magnetic field. Int J Heat Mass Transf 107:288–299
Sheikholeslami M, Shehzad SA (2016) Magnetohydrodynamic nanofluid convection in a porous enclosure considering heat flux boundary condition. Int J Heat Mass Transf. doi:10.1016/j.ijheatmasstransfer.2016.10.107
Hayat T, Hussain Z, Muhammad T, Alsaedi A (2016) Effects of homogeneous and heterogeneous reactions in flow of nanofluids over a nonlinear stretching surface with variable surface thickness. J Mol Liq 221:1121–1127
Sheikholeslami M, Ellahi R, Hassan M, Soleimani S (2014) A study of natural convection heat transfer in a nanofluid filled enclosure with elliptic inner cylinder. Int J Numer Methods Heat Fluid Flow 24(8):1906–1927
Kandelousi MS (2014) KKL correlation for simulation of nanofluid flow and heat transfer in a permeable channel. Phys Lett A 378(45):3331–3339
Sheikholeslami M (2015) Effect of uniform suction on nanofluid flow and heat transfer over a cylinder. J Braz Soc Mech Sci Eng 37:1623–1633
Sheikholeslami M, Ganji DD (2014) Ferrohydrodynamic and Magnetohydrodynamic effects on ferrofluid flow and convective heat transfer. Energy 75:400–410
Sheikholeslami M, Ganji DD (2016) External magnetic field effects on hydrothermal treatment of nanofluid. William Andrew, Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 1–354. ISBN: 9780323431385
Khanafer K, Vafai K, Lightstone M (2003) Buoyancy-driven heat transfer enhancement in a two-dimensional enclosure utilizing nanofluids. Int J Heat Mass Transfr 46:3639–3653
Rudraiah N, Barron RM, Venkatachalappa M, Subbaraya CK (1995) Effect of a magnetic field on free convection in a rectangular enclosure. Int J Eng Sci 33:1075–1084
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sheikholeslami, M. Magnetic source impact on nanofluid heat transfer using CVFEM. Neural Comput & Applic 30, 1055–1064 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-016-2740-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-016-2740-7