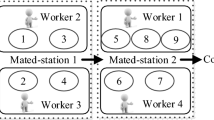
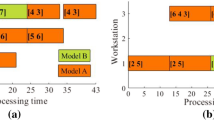
Abstract
U-shaped assembly lines have been popularly adopted in electronics and appliances to improve their flexibility and efficiency. However, most past studies assumed that the processing time of each task is fixed and hence just considered the task allocation but ignored worker assignment. In this paper, the processing time of each task depends on the workers and then the cooperative optimization of task allocation and workers assignment is considered in U-shaped assembly line balancing problems to optimize the cycle time. Later, an enhanced migrating birds optimization algorithm (EMBO) is proposed to solve it. In the EMBO algorithm, since this new problem has two subproblems: task allocation and worker assignment, the prevent work designs two neighborhood structures to improve the leader and following birds. Furthermore, the temperature acceptance criteria, to judge whether the neighbor replaces current following bird, are developed to ensure the diversity of population and avoid being trapped in the local optimum. And a competitive mechanism is introduced to increase the probability of the promising birds locating in the front of the line. The proposed algorithm is compared with other well-known algorithms in the literature, and the numerical results demonstrate that the proposed algorithm outperforms other algorithms.














Similar content being viewed by others
References
Avikal S, Jain R, Mishra PK et al (2013) A heuristic approach for U-shaped assembly line balancing to improve labor productivity. Comput Ind Eng 64:895–901
Baykasoğlu A, Özbakır L (2006) Stochastic U-line balancing using genetic algorithms. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 32:139–147
Blum C, Miralles C (2011) On solving the assembly line worker assignment and balancing problem via beam search. Comput Oper Res 38:328–339
Borba L, Ritt M (2014) A heuristic and a branch-and-bound algorithm for the assembly line worker assignment and balancing problem. Comput Oper Res 45:87–96
Buyukozkan K, Kucukkoc I, Satoglu SI et al (2016) Lexicographic bottleneck mixed-model assembly line balancing problem: artificial bee colony and tabu search approaches with optimised parameters. Expert Syst Appl 50:151–166
Chaves AA, Lorena LA, Miralles C (2009) Hybrid metaheuristic for the assembly line worker assignment and balancing problem. In: Hybrid metaheuristics, international workshop, Hm 2009, Udine, Italy, 16–17 October 2009. Proceedings. pp 1–14
Chaves AA, Miralles C, Lorena LaN (2007) Clustering search approach for the assembly line worker assignment and balancing problem. In: Proceedings of the 37th international conference on computers and industrial engineering, Alexandria, Egypt, pp 1469–1478
Delice Y, Aydoğan EK, Özcan U et al (2016) Balancing two-sided U-type assembly lines using modified particle swarm optimization algorithm. 4OR 15:37–66
Dou J, Li J, Zhao X (2017) A novel discrete particle swarm algorithm for assembly line balancing problems. Assem Autom 37:452–463
Duman E, Uysal M, Alkaya AF (2012) Migrating birds optimization: a new metaheuristic approach and its performance on quadratic assignment problem. Inf Sci 217:65–77
Gökçen H, Ağpak K, Gencer C et al (2005) A shortest route formulation of simple U-type assembly line balancing problem. Appl Math Model 29:373–380
García-Villoria A, Corominas A, Pastor R (2015) Heuristics and simulated annealing procedures for the accessibility windows assembly line problem level 1 (AWALBP-L1). Comput Oper Res 62:1–11
Hamta N, Fatemi Ghomi SMT, Jolai F et al (2013) A hybrid PSO algorithm for a multi-objective assembly line balancing problem with flexible operation times, sequence-dependent setup times and learning effect. Int J Prod Econ 141:99–111
Hazır DA (2015) A decomposition based solution algorithm for U-type assembly line balancing with interval data. Comput Oper Res 59:126–131
Jayaswal S, Agarwal P (2014) Balancing U-shaped assembly lines with resource dependent task times: a Simulated Annealing approach. J Manuf Syst 33:522–534
Kellegöz T, Toklu B (2012) An efficient branch and bound algorithm for assembly line balancing problems with parallel multi-manned workstations. Comput Oper Res 39:3344–3360
Li M, Tang Q, Zheng Q et al (2017) A rules–based heuristic approach for the U-shaped assembly line balancing problem. Appl Math Model 48:423–439
Li Z, Dey N, Ashour AS et al (2017) Discrete cuckoo search algorithms for two-sided robotic assembly line balancing problem. Neural Comput Appl. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-017-2855-5
Li Z, Tang Q, Zhang L (2016) Minimizing energy consumption and cycle time in two-sided robotic assembly line systems using restarted simulated annealing algorithm. J Clean Prod 135:508–522
Lin D-Y, Chu Y-M (2014) A Lagrangian relaxation approach to the mixed-product assembly line sequencing problem: a case study of a door-lock company in Taiwan. Appl Math Model 38:4493–4511
Liu SB, Ng KM, Ong HL (2006) Branch-and-bound algorithms for simple assembly line balancing problem. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 36:169–177
Meng T, Pan Q-K, Li J-Q et al (2017) An improved migrating birds optimization for an integrated lot-streaming flow shop scheduling problem. Swarm Evol Comput 38:64–78
Miltenburg GJ, Wijingaard J (1994) The U-line line balancing problem. Manag Sci 40:1378–1388
Miralles C, García-Sabater JP, Andrés C et al (2008) Branch and bound procedures for solving the assembly line worker assignment and balancing problem: application to sheltered work centres for disabled. Discrete Appl Math 156:352–367
Moreira MCO, Ritt M, Costa AM et al (2012) Simple heuristics for the assembly line worker assignment and balancing problem. J Heuristics 18:505–524
Mutlu PO, Supciller AA (2013) An iterative genetic algorithm for the assembly line worker assignment and balancing problem of type-II. Comput Oper Res 40:418–426
Nourmohammadi A, Zandieh M, Tavakkoli-Moghaddam R (2013) An imperialist competitive algorithm for multi-objective U-type assembly line design. J Comput Sci 4:393–400
Ogan D, Azizoglu M (2015) A branch and bound method for the line balancing problem in U-shaped assembly lines with equipment requirements. J Manuf Syst 36:46–54
Oksuz MK, Buyukozkan K, Satoglu SI (2017) U-shaped assembly line worker assignment and balancing problem: a mathematical model and two meta-heuristics. Comput Ind Eng 112:246–263
Rabbani M, Kazemi SM, Manavizadeh N (2012) Mixed model U-line balancing type-1 problem: a new approach. J Manuf Syst 31:131–138
Rabbani M, Montazeri M, Farrokhi-Asl H et al (2016) A multi-objective genetic algorithm for a mixed-model assembly U-line balancing type-I problem considering human-related issues, training, and learning. J Ind Eng Int 12:485–497
Ramezanian R, Ezzatpanah A (2015) Modeling and solving multi-objective mixed-model assembly line balancing and worker assignment problem. Comput Ind Eng 87:74–80
Roshani A, Giglio D (2016) Simulated annealing algorithms for the multi-manned assembly line balancing problem: minimising cycle time. Int J Prod Res 55:2731–2751
Roshani A, Roshani A, Roshani A et al (2013) A simulated annealing algorithm for multi-manned assembly line balancing problem. J Manuf Syst 32:238–247
Rukhaiyar S, Alam MN, Samadhiya NK (2017) A PSO-ANN hybrid model for predicting factor of safety of slope. Int J Geotech Eng. https://doi.org/10.1080/19386362.2017.1305652
Şahin M, Kellegöz T (2017) An efficient grouping genetic algorithm for U-shaped assembly line balancing problems with maximizing production rate. Memet Comput 9:213–229
Saif U, Guan Z, Liu W et al (2014) Multi-objective artificial bee colony algorithm for simultaneous sequencing and balancing of mixed model assembly line. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 75:1809–1827
Saif U, Guan Z, Liu W et al (2014) Pareto based artificial bee colony algorithm for multi objective single model assembly line balancing with uncertain task times. Comput Ind Eng 76:1–15
Sioud A, Gagné C (2017) Enhanced migrating birds optimization algorithm for the permutation flow shop problem with sequence dependent setup times. Eur J Oper Res 264:66–73
Toksarı MD, İşleyen SK, Güner E et al (2008) Simple and U-type assembly line balancing problems with a learning effect. Appl Math Model 32:2954–2961
Vilà M, Pereira J (2014) A branch-and-bound algorithm for assembly line worker assignment and balancing problems. Comput Oper Res 44:105–114
Yang C, Gao J, Sun L (2013) A multi-objective genetic algorithm for mixed-model assembly line rebalancing. Comput Ind Eng 65:109–116
Yuguang Z, Bo A, Yong Z (2016) A PSO algorithm for multi-objective hull assembly line balancing using the stratified optimization strategy. Comput Ind Eng 98:53–62
Zacharia PT, Nearchou AC (2016) A population-based algorithm for the bi-objective assembly line worker assignment and balancing problem. Eng Appl Artif Intell 49:1–9
Zha J, Yu J-J (2014) A hybrid ant colony algorithm for U-line balancing and rebalancing in just-in-time production environment. J Manuf Syst 33:93–102
Zhang B, Pan Q-K, Gao L et al (2017) An effective modified migrating birds optimization for hybrid flowshop scheduling problem with lot streaming. Appl Soft Comput 52:14–27
Zhang H-Y (2017) An improved immune algorithm for simple assembly line balancing problem of type 1. J. Algorithms Comput Technol. https://doi.org/10.1177/1748301817710924
Zhao X, Hsu C-Y, Chang P-C et al (2016) A genetic algorithm for the multi-objective optimization of mixed-model assembly line based on the mental workload. Eng Appl Artif Intell 47:140–146
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank the anonymous reviewers for their helpful comments and constructive suggestions. This work is supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 51275366, 51305311).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
We are the authors ensuring that there is no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, Z., Tang, Q., Han, D. et al. Enhanced migrating birds optimization algorithm for U-shaped assembly line balancing problems with workers assignment. Neural Comput & Applic 31, 7501–7515 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-018-3596-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-018-3596-9