Abstract
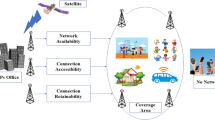
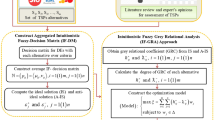
In India, Telecom sector has been enduring a massive growth for over two and half decades in the bandwidth, preference of services and depth of penetration in urban, semi-urban and rural areas. Exploring the service providers or selecting the best cellular mobile telephone service providers (CMTSPs/TSPs) according to operational performance parameter can help to achieve the goal of telecom service provider selection (TSPS). Here, this assessment generally comprises various TSPs alternatives and different operational performance criteria; therefore, TSPS could be considered as a multi-criteria decision-making (MCDM) problem. The analytical data have been taken from the Telecom Regulatory Authority of India (TRAI), Jan–Mar 2017. Most of the data vary from 1 month to another. Thus, these small ranges of variation in the data are incorporated with the intuitionistic fuzzy numbers (IFNs). In this paper, we develop an outranking method, intuitionistic fuzzy ELECTRE (IF-ELECTRE), for MCDM problems. Proposed method is based on divergence measure, operators of IFNs, some modifications of classical ELECTRE method. In the MCDM, the criterion weight determination is a vital issue for the accuracy of evaluation results. In the process of calculation of criterion weight, concordance and discordance values, we propose new Jensen–Shannon divergence (JS-divergence) for IFSs to overcome the shortcoming of the existing ones and demonstrate different elegant properties of the proposed one. Since the uncertainty is an inevitable feature of MCDM problems, the proposed method can be a valuable tool for decision-making in an uncertain atmosphere to determine the partial-preference outranking order. To express the strength and reasonableness of the proposed method in the real-world MCDM problems, a TSPS problem is implemented. Using the proposed framework, a decision expert can make a strategy to improve the performance by benchmarking operational parameters. Finally, a comparison is discussed between the results of the proposed method and the existing ones for validating the proposed method. This analysis shows that the proposed method is efficient and well consistent with the other methods.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ansari MD, Mishra AR, Ansari FT (2018) New divergence and entropy measures for intuitionistic fuzzy sets on edge detection. Int J Fuzzy Syst 20(2):474–487 https://doi.org/10.1007/s40815-017-0348-4
Atanassov KT (1986) Intuitionistic fuzzy sets. Fuzzy Sets Syst 20(1):87–96
Benayoun R, Roy B, Sussmann B (1966) Manuel de reference du programme ELECTRE, documentation Inria Mai (1966 August), pp 25–39
Bhandari D, Pal NR (1993) Some new information measure for fuzzy sets. Inf Sci 67:209–228
Boran FE, Genc S, Kurt M, Akay D (2009) A multi-criteria intuitionistic fuzzy group decision making for supplier selection with TOPSIS method. Expert Syst Appl 36:11363–11368
Bottero M, Ferretti V, Figueira JR, Greco S, Roy B (2015) Dealing with a multiple criteria environmental problem with interaction effects between criteria through an extension of the ELECTRE III method. Eur J Oper Res 245:837–850
Cobuloglu HI, Büyüktahtakın İE (2015) A stochastic multi-criteria decision analysis for sustainable biomass crop selection. Expert Syst Appl 42(15–16):6065–6074
De Luca A, Termini S (1972) A definition of non-probabilistic entropy in the setting of fuzzy sets theory. Inf Control 20(4):301–312
Debnath RM, Shankar R (2008) Benchmarking telecommunication service in India. Benchmarking Int J 15:584–598
Ebrahimnejad S, Naeini MA, Gitinavard H, Mousavi SM (2017) Selection of IT outsourcing services’ activities considering services cost and risks by designing an interval-valued hesitant fuzzy-decision approach. J Intell Fuzzy Syst 32(6):4081–4093
Espino DJ, Rodriguez-Hernandez J, Andrés-Valeri VC, Ballester-Muñoz F (2014) A fuzzy stochastic multi-criteria model for the selection of urban pervious pavements. Expert Syst Appl 41(15):6807–6817
Fan J, Xie W (1999) Distance measure and induced fuzzy entropy. Fuzzy Sets Syst 104(2):305–314
Galo NR, Rosso LDD, Carpinetti LCR (2018) A group decision approach for supplier categorization based on hesitant fuzzy and ELECTRE TRI. Int J Prod Econ 202:182–196
Garg H, Agarwal N, Tripathi A (2017) A new generalized directed divergence measure for intuitionistic fuzzy sets and applications in expert systems. Ann Fuzzy Math Inform 13(6):699–723
Garg H (2016) A new generalized improved score function of interval-valued intuitionistic fuzzy sets and applications in expert systems. Appl Soft Comput 38:988–999
Garg H (2017) Novel intuitionistic fuzzy decision making method based on an improved operation laws and its application. Eng Appl Artif Intell 60:164–174
Garg H (2017) Generalized Pythagorean fuzzy geometric aggregation operators using Einstein t-norm and t-conorm for multi-criteria decision-making process. Int J Intell Syst 32(6):597–630
Garg H (2017) Some picture fuzzy aggregation operators and their applications to multi-criteria decision-making. Arab J Sci Eng 42(12):5275–5290
Garg H (2018) Some robust improved geometric aggregation operators under interval-valued intuitionistic fuzzy environment for multi-criteria decision-making process. J Ind Manag Optim 14(1):283–308. https://doi.org/10.3934/jimo.2017047
Garg H, Kumar K (2018) Distance measures for connection number sets based on set pair analysis and its applications to decision-making process. Appl Intell. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10489-018-1152-z
Garg H, Arora R (2018) Novel scaled prioritized intuitionistic fuzzy soft interaction averaging aggregation operators and their application to multi criteria decision making. Eng Appl Artif Intell 71:100–112
Garg H, Singh S (2018) A novel triangular interval type-2 intuitionistic fuzzy sets and their aggregation operators. Iran J Fuzzy Syst. https://doi.org/10.22111/IJFS.2018.3559
Ghaderi H, Gitinavard H, Mousavi SM, Vahdani B (2017) A hesitant fuzzy cognitive mapping approach with risk preferences for student accommodation problems. Int J Appl Manag Sci 9(4):253–293
Giokas DI, Pentzaropoulos GC (2000) Evaluating productive efficiency in telecommunications: evidence from Greece. Telecommun Policy 24:781–794
Gitinavard H, Mousavi SM, Vahdani B (2017) Soft computing-based new interval-valued hesitant fuzzy multi-criteria group assessment method with last aggregation to industrial decision problems. Soft Comput 21(12):3247–3265
Gitinavard H, Mousavi SM, Vahdani B (2017) Soft computing based on hierarchical evaluation approach and criteria interdependencies for energy decision-making problems: a case study. Energy 118:556–577
Hashemi H, Mousavi SM, Zavadskas EK, Chalekaee A, Turskis Z (2018) A new group decision model based on grey-intuitionistic fuzzy-ELECTRE and VIKOR for contractor assessment problem. Sustainability 10(5):16–35
Hung WL, Yang MS (2008) On the J-divergence of intuitionistic fuzzy sets with its applications to pattern recognition. Inf Sci 178(6):1641–1650
Hwang C, Yoon K (1981) Multiple attribute decision making. Springer, Berlin
Hwang CH, Yang MS (2008) On entropy of fuzzy sets. Int J Uncertain Fuzziness Knowl Based Syst 16(4):519–527
Kumar K, Garg H (2018) TOPSIS method based on the connection number of set pair analysis under interval-valued intuitionistic fuzzy set environment. Comput Appl Math 37(2):1319–1329
Kumar A, Shankar R, Debnath RM (2015) Analyzing customer preference and measuring relative efficiency in telecom sector: a hybrid fuzzy AHP/DEA study. Telemat Inform 32:447–462
Kumar P, Singh RK, Kharab K (2017) A comparative analysis of operational performance of cellular mobile telephone service providers in the Delhi working area using an approach of fuzzy ELECTRE. Appl Soft Comput 59:438–447. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asoc.2017.06.019
Kumar S, Kumar YS (2013) Evaluation of comparative performance of telecom service providers in India using TOPSIS and AHP. Int J Bus Excell 6:192–213
Lin J (1991) Divergence measure based on Shannon entropy. IEEE Trans Inf Theory 37(1):145–151
Mao J, Dengbao Y, Cuicui W (2013) A novel cross-entropy and entropy measures of IFSs and their applications. Knowl Based Syst 48:37–45
Mishra AR (2016) Intuitionistic fuzzy information measures with application in rating of township development. Iran J Fuzzy Syst 13(3):49–70
Mishra AR, Jain D, Hooda DS (2016) On fuzzy distance and induced fuzzy information measures. J Inf Optim Sci 37:193–211
Mishra AR, Jain D, Hooda DS (2016) On logarithmic fuzzy measures of information and discrimination. J Inf Optim Sci 37:213–231
Mishra AR, Jain D, Hooda DS (2016) Intuitionistic fuzzy similarity and information measures with physical education teaching quality assessment. Adv Intell Syst Comput 379:387–399
Mishra AR, Rani P (2017) Shapley divergence measures with VIKOR method for multi-attribute decision making problems. Neural Comput Appl. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-017-3101-x
Mishra AR, Jain D, Hooda DS (2017) Exponential intuitionistic fuzzy information measure with assessment of service quality. Int J Fuzzy Syst 19(3):788–798. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40815-016-0278-6
Mishra AR, Rani P, Jain D (2017) Information measures based TOPSIS method for multi-criteria decision making problem in intuitionistic fuzzy environment. Iran J Fuzzy Syst 14(6):41–63. https://doi.org/10.22111/ijfs.2017.2796
Mishra AR, Kumari R, Sharma DK (2017) Intuitionistic fuzzy divergence measure-based multi-criteria decision-making method. Neural Comput Appl. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-017-3187-1
Mishra AR, Rani P (2018) Biparametric information measures based TODIM technique for interval-valued intuitionistic fuzzy environment. Arab J Sci Eng 43(6):3291–3309. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-018-3069-6
Mishra AR, Rani P, Pardasani KR (2018) Multiple-criteria decision making for service quality selection based on Shapley COPRAS method under hesitant fuzzy sets. Granul Comput. https://doi.org/10.1007/s41066-018-0103-8
Mishra AR, Singh RK, Motwani D (2018) Multi-criteria assessment of cellular mobile telephone service providers using intuitionistic fuzzy WASPAS method with similarity measures. Granul Comput. https://doi.org/10.1007/s41066-018-0114-5
Mohagheghi V, Mousavi SM, Aghamohagheghi M, Vahdani B (2017) A new approach of multi-criteria analysis for the evaluation and selection of sustainable transport investment projects under uncertainty: a case study. Int J Comput Intell Syst 10(1):605–626
Mohagheghi V, Mousavi SM, Vahdani B, Shahriari MR (2017) R&D project evaluation and project portfolio selection by a new interval type-2 fuzzy optimization approach. Neural Comput Appl 28(12):3869–3888
Montes I, Pal NR, Janis V, Montes S (2015) Divergence measures for intuitionistic fuzzy sets. IEEE Trans Fuzzy Syst 23:444–456
Montes S, Couso I, Gil P, Bertoluzza C (2002) Divergence measure between fuzzy sets. Int J Approx Reason 30(2):91–105
Mousavi M, Gitinavard H, Mousavi SM (2017) A soft computing based modified ELECTRE model for renewable energy policy selection with unknown information. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 68:774–787
Nigam V, Thakur T, Sethi VK, Singh RP (2012) Benchmarking of Indian mobile telecom operators using DEA with sensitivity analysis. Benchmarking Int J 19:219–238
Pal NR, Pal SK (1989) Object-background segmentation using new definitions of entropy. IEEE Proc 136(4):284–295
Peng JJ, Wang JQ, Wang J, Yang LJ, Chen XH (2015) An extension of ELECTRE to multi-criteria decision-making problems with multi-hesitant fuzzy sets. Inf Sci 307:113–126
Rani P, Jain D (2017) Intuitionistic fuzzy PROMETHEE technique for multi-criteria decision making problems based on entropy measure. In: Proceedings of communications in computer and information science (CCIS), vol 721, pp 290–301
Rani P, Jain D, Hooda DS (2018) Shapley function based interval-valued intuitionistic fuzzy VIKOR technique for correlative multi-criteria decision making problems. Iran J Fuzzy Syst 15(1):25–54
Rani P, Jain D, Hooda DS (2018) Extension of intuitionistic fuzzy TODIM technique for multi-criteria decision making method based on Shapley weighted divergence measure. Granul Comput. https://doi.org/10.1007/s41066-018-0101-x
Rashid T, Faizi S, Xu ZS, Zafar S (2018) Electre-based outranking method for multi-criteria decision making using hesitant intuitionistic fuzzy linguistic term sets. Int J Fuzzy Syst 20(1):78–92
Resende M (2008) Efficiency measurement and regulation in US telecommunications: a robustness analysis. Int J Prod Econ 114:205–218
Rouyendegh BD (2018) The intuitionistic fuzzy ELECTRE model. Int J Manag Sci Eng Manag 13(2):139–145
Saxena V, Thakur T, Singh RP (2009) Evaluating the performance of mobile telecom operators in India. Int J Simul Syst Sci Technol 10:58–63
Szmidt E, Kacprzyk J (2001) Entropy for intuitionistic fuzzy sets. Fuzzy Sets Syst 118:467–477
Tolga AC (2012) A real options approach for software development projects using fuzzy ELECTRE. J Mult Valued Logic Soft Comput 18:541–560
TRAI (2017) The Indian Telecom services performance indicators, New Delhi, India. http://trai.gov.in/sites/default/files/Performance_Indicator_Reports_28092017.pdf. Accessed Jan–Mar 2017
TRAI (2017) Audit wireless report for MP (including CG) circle, Regional office Bhopal. http://www.trai.gov.in/sites/default/files/Audit_Report_MP_25072017.pdf. Accessed Jan–Mar 2017
Vahdani B, Mousavi SM, Tavakkoli-Moghaddam R, Hashemi H (2013) A new design of the elimination and choice translating reality method for multi-criteria group decision making in an intuitionistic fuzzy environment. Appl Math Model 37(4):1781–1799
Vahdani B, Mousavi SM, Tavakkolli-Maghaddam R, Hashemi H (2013) A new design of the elimination and choice translating reality method for multi-criteria group decision making in an intuitionistic fuzzy environment. Appl Math Model 37(4):1781–1799
Vahdani B, Salimi M, Mousavi SM (2017) A new compromise solution model based on Dantzig–Wolfe decomposition for solving belief multi-objective nonlinear programming problems with block angular structure. Int J Inf Technol Decis Mak 16(02):333–387
Verma R, Maheshwari S (2017) A new measure of divergence with its application to multi-criteria decision making under fuzzy environment. Neural Comput Appl 28(8):2335–2350. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-016-2311-y
Vlachos I, Sergiadis GD (2007) Intuitionistic fuzzy information: applications to pattern recognition. Pattern Recogn Lett 28(2):197–206
Walters SJ (2009) Quality of life outcomes in clinical trials and health-care evaluation: a practical guide to analysis and interpretation. Wiley, New York
Wei CP, Wang P, Zhang YZ (2011) Entropy, similarity measure of interval-valued intuitionistic fuzzy sets and their applications. Inf Sci 181:4273–4286
Xia MM, Xu ZS (2012) Entropy/cross entropy-based group decision making under intuitionistic fuzzy environment. Inf Fusion 13(1):31–47
Xu ZS (2007) Intuitionistic fuzzy aggregation operators. IEEE Trans Fuzzy Syst 15:1179–1187
Xu ZS, Yager RR (2006) Some geometric aggregation operators based on intuitionistic fuzzy sets. Int J Gen Syst 35:417–433
Yadav N (2014) Total interpretive structural modelling (TISM) of strategic performance management for Indian telecom service providers. Int J Product Perform Manag 63:421–445
Yager RR (1988) On ordered weighted averaging aggregation operators in multi-criteria decision making. IEEE Trans Syst Man Cybern 18(1):183–190
Yue Z, Jia Y (2017) A projection-based approach to intuitionistic fuzzy group decision making. Sci Iran Trans E Ind Eng 24(3):1505–1518
Zadeh LA (1965) Fuzzy sets. Inf Control 8(3):338–353
Zarghami M, Szidarovszky F, Ardakanian R (2008) A fuzzy-stochastic OWA model for robust multi-criteria decision making. Fuzzy Optim Decis Mak 7(1):1–15
Zavadskas EK, Turskis Z, Antucheviciene J, Zakarevicius A (2012) Optimization of weighted aggregated sum product assessment. Elektron Elektrotech 122(6):3–6
Zhang QS, Jiang SY (2008) A note on information entropy measures for vague sets and its applications. Inf Sci 178(21):4184–4191
Zhao H, Xu ZS, Ni M, Liu S (2010) Generalized aggregation operators for intuitionistic fuzzy sets. Int J Intell Syst 25(1):1–30
Zhong L, Yao L (2017) An ELECTRE I-based multi-criteria group decision making method with interval type-2 fuzzy numbers and its application to supplier selection. Appl Soft Comput 57:556–576
Zhu J (2003) Quantitative models for performance evaluation and benchmarking: data envelopment analysis with spreadsheets. Kluwer Academic Publishers, Boston
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Author(s) declares that there is no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
Present article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mishra, A.R., Singh, R.K. & Motwani, D. Intuitionistic fuzzy divergence measure-based ELECTRE method for performance of cellular mobile telephone service providers. Neural Comput & Applic 32, 3901–3921 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-018-3716-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-018-3716-6