Abstract
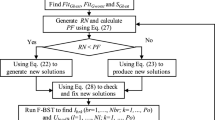
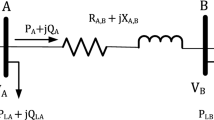
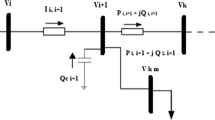
In this paper, an enhanced sitting–sizing scheme for shunt capacitors (4SCs) in a radial distribution system (RDS) based on an improved atom search optimization (IASO) algorithm is proposed. IASO emulates the model of atomic motion in nature based on interaction forces among atoms. The main goal of the 4SCs problem is to reduce the line losses and minimize the capacitor installation cost by searching for the optimal location and sizing of the capacitors. This leads to improvements in the voltage profile and reliability of the system. The IASO algorithm is introduced to achieve the optimal sitting and sizing of capacitors for RDSs. The proposed IASO algorithm is benchmarked and validated on different radial systems, including the IEEE 33-bus, IEEE 34-bus, IEEE 65-bus, IEEE 85-bus and Marsa Matrouh networks, to demonstrate its performance in real-world applications. The results obtained by the proposed IASO algorithm are compared with the standard ASO, PSO, SCA, GWO and SSA algorithms. Furthermore, the significance of the obtained results is confirmed by performing a nonparametric statistical test, i.e., the Wilcoxon’s rank-sum at the 5% significance level. The comprehensive results demonstrate that the results obtained by the proposed IASO algorithm denominate the results obtained by the other algorithms and that IASO minimizes the operating costs while achieving better voltage profiles.




























Similar content being viewed by others
References
Prakash DB, Lakshminarayana C (2017) Optimal siting of capacitors in radial distribution network using Whale Optimization Algorithm. Alex Eng J 56(4):499–509
Schmill JV (1965) Optimum size and location of shunt capacitors on distribution feeders. IEEE Trans Power Apparat Syst 84:825–832
Duran H (1968) Optimum number, location and size of shunt capacitors in radial distribution feeders: a dynamic programming approach. IEEE Trans Power Apparat Syst 87:1769–1774
Grainger JJ, Lee SH (1981) Optimum size and location of shunt capacitors for reduction of losses on distribution feeders. IEEE Trans Power Apparat Syst 100(3):1105–1118
Grainger JJ, Civanlar S (1985) Volt/var control on distribution systems with lateral branches using shunt capacitors as voltage regulators-part I, II and III. IEEE Trans Power Apparat Syst 104(11):3278–3297
Baran ME, Wu FF (1989) Optimal sizing of capacitors placed on a radial distribution system. IEEE Trans Power Deliv 1:735–743
Baran ME, Wu FF (1989) Optimal capacitor placement on radial distribution system. IEEE Trans Power Deliv 4(1):725–734
Liu Zhao, Li Han, Zhu Ping (2019) Diversity enhanced particle swarm optimization algorithm and its application in vehicle lightweight design. J Mech Sci Technol 33(2):695–709
Rizk-Allah RM, El-Sehiemy RA, Wang G-G (2018) A novel parallel hurricane optimization algorithm for secure emission/economic load dispatch solution. Appl Soft Comput 63:206–222
Rizk-Allah RM, Hassanien AE (2018) New binary bat algorithm for solving 0–1 knapsack problem. Complex Intell Syst 4(1):31–53
Rizk-Allah RM (2018) An improved sine cosine algorithm based on orthogonal parallel information for global optimization. Soft Comput. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00500-018-3355-y
Rizk-Allah RM, El-Sehiemy RA, Deb S, Wang G-G (2017) A novel fruit fly framework for multi-objective shape design of tubular linear synchronous motor. J Supercomput 73(3):1235–1256
Rizk-Allah RM (2018) Hybridizing sine cosine algorithm with multi-orthogonal search strategy for engineering design problems. J Comput Design Eng 5:249–273
Mirjalili S, Mirjalili SM, Lewis A (2014) Grey wolf optimizer. Adv Eng Softw 69:46–61
Mirjalili S et al (2017) Salp swarm algorithm: a bio-inspired optimizer for engineering design problems. Adv Eng Softw 114:163–191
Rizk-Allah RM, Hassanien AE, Bhattacharyya S (2018) Chaotic crow search algorithm for fractional optimization problems. Appl Soft Comput 71:1161–1175
Rizk-Allah RM, Hassanien AE, Elhoseny M (2018) A new binary salp swarm algorithm: development and application for optimization tasks. In: Neural computing and applications. Accepted, 22 June 2018
Rizk-Allah RM (2016) Hybridization of fruit fly optimization algorithm and firefly algorithm for solving nonlinear programming problems. Int J Swarm Intel Evol Comput 5(2):1–10
El-Sawy AA, Zaki EM, Rizk-Allah RM (2013) A novel hybrid ant colony optimization and firefly algorithm for solving constrained engineering design problems. J Nat Sci Math 6(1):1–22
El-Sawy AA, Zaki EM, Rizk-Allah RM (2013) Novel hybrid ant colony optimization and firefly algorithm for multi-objective optimization problems. Int J Math Arch 4(1):152–161
Rizk-Allah RM, Zaki Elsayed M, El-Sawy AA (2013) Hybridizing ant colony optimization with firefly algorithm for unconstrained optimization problems. Appl Math Comput 224(1):473–483
Anitescu C, Atroshchenko E, Alajlan N, Rabczuk T (2019) Artificial neural network methods for the solution of second order boundary value problems. Comput Mater Continua 59(1):345–359
Ghasemi H, Park HS, Rabczuk T (2018) A multi-material level set-based topology optimization of flexoelectric composites. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 332:47–62
Prakash K, Sydulu M (2007) Particle swarm optimization based capacitor placement on radial distribution system. In: Proceedings of IEEE power engineering society general meeting, pp 1–5
Levitin G, Kalyuzhny A, Shenkaman A (2000) Optimal capacitor allocation in distribution system using genetic algorithm and a fast energy loss computation technique. IEEE Trans Power Deliv 15(2):623–628
Mohamed Shuaib Y, Surya Kalavathi M, Christober Asir Rajan C (2015) Optimal capacitor placement in radial distribution system using gravitational search algorithm. Int J Electr Power Energy Syst 64:384–397
El-Fergany A (2015) Optimal allocation of multi-type distributed generators using backtracking search optimization algorithm. Int J Electr Power Energy Syst 64:1197–1205
Niknam T, Azizipanah-Abarghooee R, Narimani MR (2012) A new multi objective optimization approach based on TLBO for location of automatic voltage regulators in distribution systems. Eng Appl Artif Intel 25:1577–1588
Ali ES, Abd-Elazim SM, Abdelaziz AY (2016) Improved harmony algorithm and power loss index for optimal locations and sizing of capacitors in radial distribution systems. Int J Electr Power Energy Syst 80:252–263
Tamilselvan V, Jayabarathi T, Raghunathan T, Yang X-S (2018) Optimal capacitor placement in radial distribution systems using flower pollination algorithm. Alex Eng J 57(4):2775–2786
Zhao Weiguo, Wang Liying, Zhang Zhenxing (2019) Atom search optimization and its application to solve a hydrogeologic parameter estimation problem. Knowl Based Syst 163:283–304
Teng JH (2003) A direct approach for distribution system load flow solutions. IEEE Trans Power Deliv 18(3):882–887
Goldstein H, Poole CP, Safko JL (2001) Classical mechanics. Addison Wesley, Boston
Ryckaert JP, Ciccotti G, Berendsen HJC (1977) Numerical integration of the Cartesian equations of motion of a system with constraints: molecular dynamics of n-alkanes. J Comput Phys 23(3):327–341
Lennard-Jones JE (1924) On the determination of molecular fields. Proc R Soc Lond A Math Phys Eng Sci 106(738):463–477
Srinivasas Rao R, Narasimham SVL, Ramalingaraju M (2011) Optimal capacitor placement in radial distribution system using plant growth simulation algorithm. Int J Electr Power Energy Syst 33:1133–1139
Derrac J, García S, MolinaD Herrera F (2011) A practical tutorial on the use of nonparametric statistical tests as a methodology for comparing evolutionary and swarm intelligence algorithms. Swarm Evol Comput 1(1):3–18. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.swevo.2011.02.002
Ela E, Abou AA, Allam SM, Shehata NK (2017) Assessment of hybrid renewable energy with energy storage system for supplying distribution networks in Egypt. In: 2017 19th international middle east power systems conference (MEPCON). IEEE
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rizk M. Rizk-Allah and Aboul Ella Hassanien: Scientific Research Group in Egypt. http://www.egyptscience.net.
Appendix: Benchmark optimization problems with their characteristics
Appendix: Benchmark optimization problems with their characteristics
This section provides the description of each benchmark function regarding the mathematical model, function nature (i.e., unimodal, multimodal) and graph. The major motivation for this representation is to concentrate on the more challenging and complicated benchmark problems while validating the performance of a certain algorithm to depict a fire validation.
-
1.
Schaffer (F1)
Characteristics: unimodal, nonconvex, continuous, non-separable, differentiable and defined on an n-dimensional space.
Search space: \( {\mathbf{x}} = (x_{1} ,x_{2} ) \in \left[ { - 100,\,100} \right] \)
Global minimum: \( f({\mathbf{x}}) = 0 \) at \( {\mathbf{x}} = (0,0) \)

-
2.
Griewank (F2)
Characteristics: unimodal, nonconvex, continuous, non-separable and defined on an n-dimensional space.
Search space: \( {\mathbf{x}} \in \left[ { - 600,\,600} \right] \)
Global minimum: \( f({\mathbf{x}}) = 0 \) at \( {\mathbf{x}} = 0. \)

-
3.
Rastrigin (F3)
Characteristics: multimodal, differentiable, continuous, separable, convex and defined on an n-dimensional space.
Search space: \( {\mathbf{x}} \in \left[ { - 5.12,\,5.12} \right] \)
Global minimum: \( f({\mathbf{x}}) = 0 \) at \( {\mathbf{x}} = 0 \)

-
4.
Rosenbrock (F4)
Characteristics: Unimodal, differentiable, continuous, non-separable, convex and defined on an n-dimensional space.
Search space: \( {\mathbf{x}} \in \left[ { - 30,\,30} \right] \)
Global minimum: \( f({\mathbf{x}}) = 0 \) at \( {\mathbf{x}} = 1. \)

-
5.
Ackley (F5)
Characteristics: multimodal, nonconvex, continuous, non-separable and defined on an n-dimensional space.
Search space: \( {\mathbf{x}} \in \left[ { - 32,\,32} \right] \)
Global minimum: \( f({\mathbf{x}}) = 0 \) at \( {\mathbf{x}} = 0. \)

-
6.
Penalized (F6)
Characteristics: multimodal, nonconvex, continuous, non-separable and defined on an n-dimensional space.
Search space: \( {\mathbf{x}} \in \left[ { - 50,\,50} \right] \)
Global minimum: \( f({\mathbf{x}}) = 0 \) at \( {\mathbf{x}} = 0. \)

Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rizk-Allah, R.M., Hassanien, A.E. & Oliva, D. An enhanced sitting–sizing scheme for shunt capacitors in radial distribution systems using improved atom search optimization. Neural Comput & Applic 32, 13971–13999 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-020-04799-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-020-04799-6