Abstract
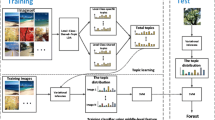
One of the greatest challenges for scene classification is the lack of sufficient training samples. Label distribution learning (LDL) is proven to be effective in handling insufficient samples by exploiting label ambiguity. However, LDL has never been used in scene classification because the correlations among scene classes are unavailable, making it impossible to construct label distribution vectors for images. In this paper, we aim to transform LDL into scene classification. To this end, we introduce a probabilistic topic model (PTM) to capture label correlations, and propose a method termed as topic-based LDL (TB-LDL). By treating scene classes as documents in the PTM, the discovered topics indicate typical scene patterns, and class-topic distributions provide label measurements on multiple topics. For each topic, scenes with similar label measurements can be considered as neighbouring labels. The label distributions smooth image truth labels based on label correlations, which can formulate the label ambiguity of scene images. Training networks with the label distributions can prevent over-fitting and assist feature learning. Extensive experiments on two challenging datasets, namely the aerial image dataset (AID) and NWPU_RESISC45 (NR), demonstrate that our method is effective, especially when the amount of training data is limited.












Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- HSR:
-
High spatial resolution
- SLL:
-
Single label learning
- CNN:
-
Convolutional neural networks
- LDL:
-
Label distribution learning
- MLL:
-
Multi-label learning
- PTM:
-
Probabilistic topic model
- TB-LDL:
-
Topic-based label distribution learning
- mm-LDA:
-
Multimodel latent Dirichlet allocation
References
Cheng G, Han J, Lu X (2017) Remote sensing image scene classification: benchmark and state of the art. Proc IEEE 105:1865–1883
Xia GS, Hu J, Hu F et al (2017) AID: a benchmark data set for performance evaluation of aerial scene classification. IEEE Trans Geosci Remote Sens 55:3965–3981. https://doi.org/10.1109/TGRS.2017.2685945
Lu X, Sun H, Zheng X (2019) A feature aggregation convolutional neural network for remote sensing scene classification. IEEE Trans Geosci Remote Sens 57:7894–7906. https://doi.org/10.1109/tgrs.2019.2917161
Wang L, Guo S, Huang W et al (2017) Knowledge guided disambiguation for large-scale scene classification with multi-resolution CNNs. IEEE Trans Image Process 26:2055–2068. https://doi.org/10.1109/TIP.2017.2675339
Lei Y, Dong Y, Xiong F et al (2018) Confusion weighted loss for ambiguous classification. In: VCIP 2018 - IEEE international conference on visual communications and image processing. https://doi.org/10.1109/VCIP.2018.8698693
Geng X (2016) Label distribution learning. IEEE Trans Knowl Data Eng 28:1734–1748. https://doi.org/10.1109/TKDE.2016.2545658
Bin GB, Xing C, Xie C et al (2017) Deep label distribution learning with label ambiguity. IEEE Trans Image Process 26:2825–2838. https://doi.org/10.1109/TIP.2017.2689998
Ling M, Geng X (2019) Indoor crowd counting by mixture of Gaussians label distribution learning. IEEE Trans Image Process 28:5691–5701. https://doi.org/10.1109/TIP.2019.2922818
Yang J, Chen L, Zhang L et al (2018) Historical context-based style classification of painting images via label distribution learning. In: MM 2018 - proceedings of the 2018 ACM multimedia conference. pp 1154–1162. https://doi.org/10.1145/3240508.3240593
Gao BB, Zhou HY, Wu J, Geng X (2018) Age estimation using expectation of label distribution learning. In: IJCAI international joint conference on artificial intelligence. pp 712–718. https://doi.org/10.24963/ijcai.2018/99
Wu X, Wen N, Liang J et al (2019) Joint acne image grading and counting via label distribution learning. In: Proceedings of the IEEE international conference on computer vision. pp 10641–10650. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICCV.2019.01074
Xu L, Chen J, Gan Y (2019) Head pose estimation with soft labels using regularized convolutional neural network. Neurocomputing 337:339–353. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neucom.2018.12.074
Liu Z, Chen Z, Bai J, et al (2019) Facial pose estimation by deep learning from label distributions. In: Proceedings - 2019 international conference on computer vision workshop, ICCVW 2019. pp 1232–1240. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICCVW.2019.00156
Li P, Hu Y, Wu X et al (2020) Deep label refinement for age estimation. Pattern Recognit. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.patcog.2019.107178
He Z, Li X, Zhang Z et al (2017) Data-dependent label distribution learning for age estimation. IEEE Trans Image Process 26:3846–3858. https://doi.org/10.1109/TIP.2017.2655445
Blei D, Carin L, Dunson D (2010) Probabilistic topic models. IEEE Signal Process Mag 27:55–65. https://doi.org/10.1109/MSP.2010.938079
Zhong Y, Zhu Q, Zhang L (2015) Scene classification based on the multifeature fusion probabilistic topic model for high spatial resolution remote sensing imagery. IEEE Trans Geosci Remote Sens 53:6207–6222. https://doi.org/10.1109/TGRS.2015.2435801
Farrahi K, Gatica-Perez D (2011) Discovering routines from large-scale human locations using probabilistic topic models. ACM Trans Intell Syst Technol. https://doi.org/10.1145/1889681.1889684
Yuan B, Gao X, Niu Z, Tian Q (2019) Discovering latent topics by Gaussian latent dirichlet allocation and spectral clustering. ACM Trans Multimed Comput Commun Appl. https://doi.org/10.1145/3290047
Wang Y, Lin X, Wu L, Zhang W (2017) Effective multi-query expansions: collaborative deep networks for Robust landmark retrieval. IEEE Trans Image Process 26:1393–1404. https://doi.org/10.1109/TIP.2017.2655449
Zhang J, Wu Q, Shen C et al (2018) Multilabel image classification with regional latent semantic dependencies. IEEE Trans Multimed 20:2801–2813. https://doi.org/10.1109/TMM.2018.2812605
Hua Y, Mou L, Zhu XX (2019) Label relation inference for multi-label aerial image classification. In: International geoscience and remote sensing symposium (IGARSS). pp 5244–5247. https://doi.org/10.1109/IGARSS.2019.8898934
Wang Z, Liao J, Cao Q et al (2015) Friendbook: a semantic-based friend recommendation system for social networks. IEEE Trans Mob Comput 14:538–551. https://doi.org/10.1109/TMC.2014.2322373
Pan T, Zhang W, Wang Z, Xu L (2016) Recommendations based on LDA topic model in android applications. In: Proceedings - 2016 IEEE international conference on software quality, reliability and security-companion, QRS-C 2016. https://doi.org/10.1109/QRS-C.2016.24
Sun CY, Lee AJT (2017) Tour recommendations by mining photo sharing social media. Decis Support Syst 101:28–39. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dss.2017.05.013
Yao J, Wang Y, Zhang Y et al (2018) Joint latent dirichlet allocation for social tags. IEEE Trans Multimed 20:224–237. https://doi.org/10.1109/TMM.2017.2716829
Ou Y, Luo J, Li B, He B (2019) A classification model of railway fasteners based on computer vision. Neural Comput Appl 31:9307–9319. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-019-04337-z
Li Y, Kong X, Fu H, Tian Q (2018) Aggregating hierarchical binary activations for image retrieval. Neurocomputing 314:65–77. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neucom.2018.06.014
Bahmanyar R, Espinoza-Molina D, Datcu M (2018) Multisensor earth observation image classification based on a multimodal latent Dirichlet allocation model. IEEE Geosci Remote Sens Lett 15:459–463. https://doi.org/10.1109/LGRS.2018.2794511
Du P, Li E, Xia J et al (2019) Feature and model level fusion of pretrained CNN for remote sensing scene classification. IEEE J Sel Top Appl Earth Obs Remote Sens 12:2600–2611. https://doi.org/10.1109/JSTARS.2018.2878037
Yuan B, Han L, Gu X et al (2020) Multi-deep features fusion for high-resolution remote sensing image scene classification. Neural Comput Appl. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-020-05071-7
Das P, Xu C, Doell RF, Corso JJ (2013) A thousand frames in just a few words: lingual description of videos through latent topics and sparse object stitching. In: Proceedings of the IEEE computer society conference on computer vision and pattern recognition. pp 2634–2641. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2013.340
Zhang M, Gunturk BK (2008) Multiresolution bilateral filtering for image denoising. IEEE Trans Image Process 17:2324–2333. https://doi.org/10.1109/TIP.2008.2006658
Hessam B, Maxwell H, Mohammad R et al (2018) Label refinery improving ImageNet classification through label progression. In: IEEE computer society conference on computer vision and pattern recognition. arXiv:1805.02641
Müller R, Kornblith S, Hinton G (2019) When does label smoothing help? In: Neural information processing systems workshops, NIPS 2019, proceedings of the conference. arXiv:1906.02629
Hou J, Zeng H, Cai L et al (2019) Multi-label learning with multi-label smoothing regularization for vehicle re-identification. Neurocomputing 345:15–22. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neucom.2018.11.088
Yun S, Park J, Lee K, Shin J (2020) Regularizing class-wise predictions via self-knowledge distillation. In: Proceedings of the IEEE computer society conference on computer vision and pattern recognition. pp 13873–13882. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR42600.2020.01389
Pereyra G, Tucker G, Chorowski J et al (2017) Regularizing neural networks by penalizing confident output distributions. In: 5th international conference on learning representations, ICLR 2017, proceedings of the conference. arXiv:1701.06548
Szegedy C, Vanhoucke V, Ioffe S et al (2016) Rethinking the inception architecture for computer vision. In: Proceedings of the IEEE computer society conference on computer vision and pattern recognition. pp 2818–2826. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2016.308
He N, Fang L, Li S et al (2018) Remote sensing scene classification using multilayer stacked covariance pooling. IEEE Trans Geosci Remote Sens. https://doi.org/10.1109/TGRS.2018.2845668
Liu Y, Suen CY, Liu Y, Ding L (2019) Scene classification using hierarchical wasserstein CNN. IEEE Trans Geosci Remote Sens 57:2494–2509. https://doi.org/10.1109/TGRS.2018.2873966
Yuan Y, Fang J, Lu X et al (2019) Remote sensing image scene classification using rearranged local features. IEEE Trans Geosci Remote Sens 57:1779–1792. https://doi.org/10.1109/TGRS.2018.2869101
Zhang W, Tang P, Zhao L et al (2019) Remote sensing image scene classification using CNN-CapsNet. Remote Sens. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs11050494
Bi Q, Qin K, Zhang H et al (2020) RADC-Net: a residual attention based convolution network for aerial scene classification. Neurocomputing 377:345–359. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neucom.2019.11.068
Liu Y, Huang C (2018) Scene classification via triplet networks. IEEE J Sel Top Appl Earth Obs Remote Sens 11:220–237. https://doi.org/10.1109/JSTARS.2017.2761800
Xie J, He N, Fang L et al (2019) Scale-free convolutional neural network for remote sensing scene classification. IEEE Trans Geosci Remote Sens 57:6916–6928. https://doi.org/10.1109/TGRS.2019.2909695
Yu Y, Li X, Liu F (2020) Attention GANs: unsupervised deep feature learning for aerial scene classification. IEEE Trans Geosci Remote Sens 58:519–531. https://doi.org/10.1109/TGRS.2019.2937830
Simonyan K, Zisserman A (2015) Very deep convolutional networks for large-scale image recognition. In: 3rd international conference on learning representations, ICLR 2015 - conference track proceedings. arXiv: 1409.1556.
Maaten L.v.d, Hinton G (2008) Visualizing data using t-SNE. J Mach Learn Res 9:2579–2625
Chang CC, Lin CJ (2011) LIBSVM: a Library for support vector machines. ACM Trans Intell Syst Technol. https://doi.org/10.1145/1961189.1961199
Stevens K, Kegelmeyer P, Andrzejewski D, Buttler D (2012) Exploring topic coherence over many models and many topics. In: EMNLP-CoNLL 2012 - 2012 joint conference on empirical methods in natural language processing and computational natural language learning, proceedings of the conference. pp 952–961
Chen S, Wang Y, Lin C et al (2019) Semi-supervised feature learning for improving writer identification. Inf Sci (Ny) 482:156–170. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ins.2019.01.024
Du Y, Yang R, Chen Z et al (2020) A deep learning network-assisted bladder tumour recognition under cystoscopy based on Caffe deep learning framework and EasyDL platform. Int J Med Robot Comput Assist Surg. https://doi.org/10.1002/rcs.2169
Zeng Y, Zhang J (2020) A machine learning model for detecting invasive ductal carcinoma with Google Cloud AutoML Vision. Comput Biol Med. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compbiomed.2020.103861
Chen Z, Wei X, Wang P, Guo Y (2019) Multi-label image recognition with graph convolutional networks. In: Proceedings of the IEEE computer society conference on computer vision and pattern recognition. pp 5172–5181. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2019.00532
Zhang T, Mouchère H, Viard-Gaudin C (2020) A tree-BLSTM-based recognition system for online handwritten mathematical expressions. Neural Comput Appl 32:4689–4708. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-018-3817-2
Liu Y, Chen W, Qu H et al (2021) Weakly supervised image classification and pointwise localization with graph convolutional networks. Pattern Recognit. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.patcog.2020.107596
Xie K, Wei Z, Huang L et al (2021) Graph convolutional networks with attention for multi-label weather recognition. Neural Comput Appl. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-020-05650-8
Hinton G, Vinyals O, Dean J. (2015) Distilling the knowledge in a neural network. In: Neural information processing systems workshops, NIPS 2015, proceedings of the conference. arXiv:1503.02531
Wang L, Yoon KJ (2021) Knowledge distillation and student-teacher learning for visual intelligence: a review and new outlooks. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell. https://doi.org/10.1109/TPAMI.2021.3055564
Wang Z, Du J (2021) Joint architecture and knowledge distillation in CNN for Chinese text recognition. Pattern Recognit. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.patcog.2020.107722
Yuan L, Tay FEH, Li G et al (2020) Revisiting knowledge distillation via label smoothing regularization. In: Proceedings of the IEEE computer society conference on computer vision and pattern recognition. pp 3902–3910. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR42600.2020.00396
Zhang Y, Xiang T, Hospedales TM, Lu H (2018) Deep mutual learning. In: Proceedings of the IEEE computer society conference on computer vision and pattern recognition. pp 4320–4328. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2018.00454
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Major Science and Technology Program of Sichuan Province (Grant No. 2018GZDZX0031) and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 51275431). The authors would like to express their gratitude to the reviewers for their valuable suggestions.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
JL: Conceptualization, Methodology, Software, Writing-Original Draft; BH: Visualization, Investigation; YO: Validation, Writing-Reviewing and Editing; BL: Supervision; KW: Validation, Investigation.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Luo, J., He, B., Ou, Y. et al. Topic-based label distribution learning to exploit label ambiguity for scene classification. Neural Comput & Applic 33, 16181–16196 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-021-06218-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-021-06218-w