Abstract
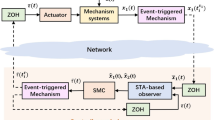
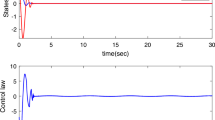
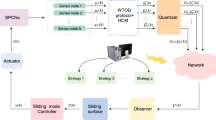
A robust super-twisting sliding mode control (SMC) based on a disturbance observer is firstly investigated for transmission control protocol (TCP) network systems with unknown disturbance in this paper. To reject chattering from SMC, a super-twisting algorithm (STA) based on integral SMC is introduced to TCP/AQM systems. Meanwhile, to improve the estimation accuracy of the model, a disturbance observer is designed. By selecting the appropriate sliding surface coefficients, the stability of the closed-loop control system is achieved. At last, simulation comparison results are given to illustrate the feasibility and the superiority of the proposed approach.
















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adams R (2013) Active queue management: a survey. IEEE Commun Surv Tutor 15:1425–1476
Wang K, Liu Y, Liu X et al (2019) Adaptive fuzzy funnel congestion control for TCP/AQM network. ISA Trans 95:11–17
Floyd S, Jacobson V (1993) Random early detection gateways for congestion avoidance. IEEE/ACM Trans Network 1:397–413
Liu S, Basar T, Srikant S (2005) Exponential-RED: a stabilizing AQM scheme for low-and high-speed TCP protocols. IEEE/ACM Trans Network 13(5):1068–1081
Zhou K, Yeung KL, Li VO (2006) Nonlinear RED: a simple yet efficient active queue management scheme. Comput Netw 50:3784–3794
Pei LJ, Mu XW, Wang RM et al (2011) Dynamics of the Internet TCP-RED congestion control system. Nonlinear Anal-Real World Appl 12:947–955
Woo S, Kim K (2010) Tight upper bound for stability of TCP/RED systems in AQM routers. IEEE Commun Lett 14(7):682–684
Low S (2003) A duality model of TCP and queue management algorithms. IEEE/ACM Trans Netw 11(4):525–36
Ajmone MM, Garetto M, Giaccone P et al (2005) Using partial differential equations to model TCP mice and elephants in large IP networks. IEEE/ACM Trans Netw 13(6):1289–301
Misra V, Gong WB, Towsley D (2000) Fluid-based analysis of a network of AQM routers supporting TCP flows with an application to RED. In: Proceedings. of the 19th IEEE international conference on SIGCOMM. Stockholm, Sweden, 30(4) (2000) 151–160
Hollot CV, Misra V, Towsley D et al. (2001) On designing improved controllers for AQM routers supporting TCP flows. In: Proceedings of IEEE INFOCOM. 1726–1734
Fridman E, Gil MM (2007) Stability of linear systems with time-varying delays: a direct frequency domain approach. J Comput Appl Math 200(1):61–66
Kim KB (2006) Design of feedback controls supporting TCP based on the state-space approach. IEEE Trans Autom Control 51(7):1086–1099
Ryu S, Rump C, Qiao C (2003) A predictive and robust active queue management for Internet congestion control. In: Proceedings of the eighth IEEE symposium on computers and communications. ISCC 2003. IEEE, 991–998
Liu Y, Liu XP, Jing YW, Zhang ZY, Chen XP (2019) Congestion tracking control for uncertain TCP/AQM network based on integral backstepping. ISA Trans 89:131–138
Cui Y Y, Fei M M, Du D (2016) Design of a robust observer-based memoryless \(H_{\infty }\) control for internet congestion. Int J Robust Nonlinear Control 26(8):1732–1747
Li F, Sun J, Zukerman M et al (2014) A comparative simulation study of TCP/AQM systems for evaluating the potential of neuron-based AQM schemes. J Netw Comput Appl 41:274–299
Wang K, Jing Y, Liu Y et al (2020) Adaptive finite-time congestion controller design of TCP/AQM systems based on neural network and funnel control. Neural Comput Appl 32(13):9471–9478
Wang K, Liu L, Liu XP et al (2019) Study on TCP/AQM network congestion with adaptive neural network and barrier Lyapunov function. Neurocomputing 363:27–34
Xu Q, Li F, Sun J, Zukerman M (2015) A new TCP/AQM system analysis. J Netw Comput Appl 57:43–60
Alaoui SB, Tissir EH, Chaibi C (2018) Active queue management based feedback control for TCP with successive delays in single and multiple bottleneck topology. Comput Commun 117:58–70
Ma L, Liu X, Wang H et al (2020) Congestion tracking control for multi-router TCP/AQM network based on integral backstepping. Comput Netw 175(5):107278
Wang K, Liu XP, Jing YW. Robust finite-time \( H_{\infty }\) congestion control for a class of AQM network systems. (2020) https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-020-05168-z
Wang K, Liu XP, Jing YW (2021) Command filtered finite-time control for nonlinear systems with state constraints and its application to TCP network. Inf Sci 550:189–206
Song J, Wang Z, Niu Y, Dong H (2020) Genetic-algorithm-assisted sliding-mode control for networked state-saturated systems over hidden Markov fading channels. IEEE Trans Cybern. https://doi.org/10.1109/TCYB.2020.2980109
Song J, Niu Y (2020) Co-design of 2-D event generator and sliding mode controller for 2-D Roesser model via genetic algorithm. IEEE Trans Cybern. https://doi.org/10.1109/TCYB.2019.2959139
Zhang Z, Niu Y, Cao Z et al (2021) Security sliding mode control of interval type-2 fuzzy systems subject to cyber attacks: the stochastic communication protocol case. IEEE Trans Fuzzy Syst 29(2):240–251
Song J, Daniel WC, Ho, Y. Niu (2021) Model-based event-triggered sliding-mode control for multi-input systems: performance analysis and optimization. IEEE Trans Cybern
Li J, Niu Y, Song J (2020) Finite-time boundedness of sliding mode control under periodic event-triggered strategy. Int J Robust Nonlinear Control 1:2. https://doi.org/10.1002/rnc.5298
Xu L, Yu X, Feng Y et al. (2015) A fast terminal sliding mode observer for TCP/IP network anomaly traffic detection. In: 2015 IEEE international conference on industrial technology (ICIT). IEEE, 28–33
Zhong T, Jing YW, Ye CY (2014) Global sliding mode control based on observer for TCP network. The 26th Chinese control and decision conference, et al (2014) CCDC). IEEE 4946–4950
Utkin V, Shi J (1996) Integral sliding mode in systems operating under uncertainty conditions. In: Proceedings of 35th IEEE conference on decision and control. IEEE 4:4591–4596
Sam YM, Osman JHS, Ghani MRA (2004) A class of proportional integral sliding model control with application to active suspension system. Syst Control Lett 51(3/4):217–223
Hu Q (2007) Robust integral variable structure controller and pulse-width pulse-frequency modulated input shaper design for flexible spacecraft with mismatched uncertainty/disturbance. ISA Trans 46(4):505–518
Hu Q, Xie L, Wang Y, Du C (2008) Robust tracking-following control of hard disk drives using improved integral sliding mode combined with phase lead peak filter. Int J Adapt Control Signal Process 22(4):413–430
Levant A (1993) Sliding order and sliding accuracy in sliding mode control. Int J Control 58(6):1247–1263
Levant A (1998) Robust exact differentiation via sliding mode technique. Automatica 34(3):379–384
Davila J, Fridman L, Levant A (2005) Second-order sliding-mode observer for mechanical systems. IEEE Trans Autom Control 50(11):1785–1789
Moreno JA, Osorio M (2008) A Lyapunov approach to second-order sliding mode controllers and observers. In: 47th IEEE conference on decision and control. IEEE, 2856–2861
Derafa L, Benallegue A, Fridman L (2012) Super twisting control algorithm for the attitude tracking of a four rotors UAV. J Frankl Inst 349(2):685–699
Shtessel Y, Taleb M, Plestan F (2012) A novel adaptive-gain supertwisting sliding mode controller: methodology and application. Automatica 48(5):759–769
Chen WH, Ballance DJ, Gawthrop PJ et al (2000) A nonlinear disturbance observer for robotic manipulators. IEEE Trans Industr Electron 47(4):932–938
Li Z, Su CY, Wang L et al (2015) Nonlinear disturbance observer-based control design for a robotic exoskeleton incorporating fuzzy approximation. IEEE Trans Industr Electron 62(9):5763–5775
Huang J, Zhang M, Ri S et al (2019) High-order disturbance-observer-based sliding mode control for mobile wheeled inverted pendulum systems. IEEE Trans Industr Electron 67(3):2030–2041
Sariyildiz E, Oboe R, Ohnishi K (2019) Disturbance observer-based robust control and its applications: 35th anniversary overview. IEEE Trans Industr Electron 67(3):2042–2053
Kubo R, Kani J, Fujimoto Y (2008) Internet advanced, congestion control using a disturbance observer. In: IEEE GLOBECOM, (2008) IEEE Global Telecommunications Conference. IEEE, 1–5
Wang P, Zhu CJ, Yang XP (2018) A novel AQM algorithm based on feedforward model predictive control. Int J Commun Syst 31(12):e3711
Yang J, Li SH, Yu XH (2012) Sliding-mode control for systems with mismatched uncertainties via a disturbance observer. IEEE Trans Industr Electron 60(1):160–169
Wei XJ, Guo L (2009) Composite disturbance-observer-based control and terminal sliding mode control for non-linear systems with disturbances. Int J Control 82(6):1082–1098
Moreno JA, Osorio M (2012) Strict Lyapunov functions for the super-twisting algorithm. IEEE Trans Autom Control 57(4):1035–1040
Huang SJ, Zhang DQ, Guo LD et al. (2018) Adaptive estimation and output feedback FTC for nonlinear systems with unknown nonlinearities and faults. Int J Robust Nonlinear Control 28
Acknowledgements
This work is supported by the National Nature Science Foundation of China under Grant (61773108) and China Scholarship Council (201806080067).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest regarding the publication of this work.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, K., Liu, X. & Jing, Y. Super twisting sliding mode network congestion control based on disturbance observer. Neural Comput & Applic 34, 9689–9699 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-022-06957-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-022-06957-4