Abstract
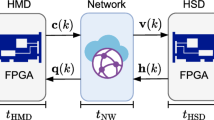
A data filtering scheme is proposed for transmission and error control of haptic events in haptic-based network virtual environments; this scheme is called as priority-based haptic event filtering. Because a high update rate of approximately 1 kHz is required for haptic rendering, sophisticated transmission rate control and reduction schemes are necessary for the haptic events. Although existing schemes can reduce the transmission rate without any perception impairment, they are very sensitive to packet losses. In this paper, we prioritize the haptic events according to the delay and loss effects. Utilizing the proposed haptic event prioritization, the proposed filtering scheme adapts the transmission rate and updates the predicted loss rate according to the current network state. Our simulation and experiment results confirm that the proposed scheme can effectively select important haptic events and guarantee an improved haptic interaction quality over a bandwidth-limited lossy network than existing transmission schemes tailored for networked haptics.
Similar content being viewed by others
Explore related subjects
Discover the latest articles and news from researchers in related subjects, suggested using machine learning.References
Aggarwal, S., Banavar, H., Khandelwal, A., Mukherjee, S., Rangarajan, S.: Accuracy in dead-reckoning based distributed multi-player games. In: Proceedings of ACM NetGames’04, pp. 161–165 (2004)
Alhalabi M.O., Horiguchi S., Kunifuji S.: An experimental study on the effects of network delay in cooperative shared haptic virtual environment. Comput. Graph. 27, 205–213 (2003)
Anderson R., Spong M.: Bilateral control of teleoperators with time delay. IEEE Trans. Automat. Contr. 34(5), 494–501 (1989)
Andrews, S., Mora, J., Lang, J., Lee, W.: Hapticast: a physically-based 3D game with haptic feedback. In: Futureplay’06 (2006)
Basdogan, C., Srinivasan, M.A.: Haptic rendering in virtual environments, pp. 117–134. Lawrence erlbaum associates, NJ (2001)
Belghit, I., Hennion, B., Guerraz, A.: Predictive algorithms for distant touching. In: Proceedings of EuroHaptics’02, pp. 1–5 (2002)
Bolot, J.C., Fosse-parisis, S., Towsley, D.: Adaptive FEC-based error control for internet telephony. In: Proceedings of IEEE INFOCOM’99, vol. 3, pp. 1453–1460 (1999)
Carson M., Santay D.: NIST Net: A linux-based network emulation tool. SIGCOMM Comput. Commun. Rev. 33(3), 111–126 (2003)
Cen, Z., Mutka, M.W., Zhu, D., Xi, N.: Supermedia transport for teleoperations over overlay networks. In: Proceedings of Networking’05, pp. 1409–1412 (2005)
Cheong, J., Niculescu, S., Annaswamyand, A., Srinivasan, M.: Motion synchronization in virtual environments with shared haptics and large time delays. In: Proceedigns of IEEE WHC’05, pp. 277–282 (2005)
Clarke S., Schillhuber G., Zaeh M., Ulbrich H.: Prediction-based methods for teleoperation across delayed networks. Multimedia Syst. 13(4), 253–261 (2008)
Conti, F., Barbagli, F., Morris, D., Sewell, C.: CHAI: an open-source library for the rapid development of haptic scenes. Demo paper presented at IEEE World Haptics. http://www.chai3d.org (2005)
Dodeller, S., Georganas, N.: Transport layer protocols for telehaptics update messages. In: Proceedings of Biennial Symposium On Communications’04 (2004)
Eid M., Orozco M., El Saddik A.: A guided tour in haptic audio visual environments and applications. Int. J. Adv. Media Commun. 1(3), 265–297 (2007)
Fujimoto, M., Ishibashi, Y.: Packetization interval of haptic media in networked virtual environments. In: Proceedings of ACM NetGames’05, pp. 1–6 (2005)
Gautier L., Diot C.: A distributed architecture for multiplayer interactive applications on the internet. IEEE Netw. Mag. 13, 6–15 (1999)
Handley, M., Floyd, S., Pahdye, J., Widmer, J.: TCP-Friendly Rate Control (TFRC): Protocol specification. Request For Comments 3448, IETF (2003)
Hikichi, K., Morino, H., Arimoto, I., Fukuda, I., Matsumoto, S., Iijima, M., Sezaki, K., Yasuda, Y.: Architecture of haptics communication system for adaptation to network environments. In: Proceedings of IEEE ICME’01, pp. 563–566 (2001)
Hikichi, K., Morino, H., Arimoto, I., Sezaki, K., Yasuda, Y.: The evaluation of delay jitter for haptics collaboration over the internet. In: Proceedings of IEEE GLOBECOM’02, vol. 2, pp. 1492–1496 (2002)
Hinterseer, P., Steinbach, E., Munich, G.: Psychophysically motivated compression of haptic data. In: Proceedings of the Joint International COE/HAM SFB453 Workshop on Human Adaptive Mechatronics and High Fidelity Telepresence (2005)
Hirche, S.: Haptic telepresence in packet switched communication networks. Ph.D. thesis, Technical University of Munich (2005)
Hirche, S., Buss, M., Hinterseer, P., Steinbach, E.: Network traffic reduction in haptic telepresence systems by deadband control. In: Proceedings of IFAC World Congress’05 (2005)
Hudson, T., Weigle, M.C., Jeffay, K., II R.T.: Experiments in best-effort multimedia networking for a distributed virtual environment. In: Proceedings of SPIE Multimedia Computing and Networking’01, vol. 4312, pp. 88–98 (2001)
Iglesias R., Casado S., Gutierrez T., Garcia-Alonso A., Yu W., Marshall A.: Simultaneous remote haptic collaboration for assembling tasks. Multimedia Syst. 13(4), 263–274 (2008)
IP Infusion Inc.: GNU Zebra. http://www.zebra.org (2003)
Ishibashi Y., Kaneoka H.: Group synchronization for haptic media in a networked real-time game. Trans. Commun. Spec. Sect. Multimedia QoS Eval. Manage. Technol. E89-B(2), 313–319 (2006)
Ishibashi Y., Tasaka S.: A synchronization mechanism for continuous media in multimedia communications. In: Proceedings of IEEE INFOCOM’95, pp. 1010–1019 (1995)
Ishibashi, Y., Tasaka, S., Hasegawa, T.: The virtual-time rendering algorithm for haptic media synchronization in networked virtual environments. In: Proceedings of International Workshop on Communication Quality and Reliablility (CQR)’02, pp. 213–217 (2002)
Ishibashi Y., Kanbara T., Tasaka S.: Inter-stream synchronization between haptic media and voice in collaborative virtual environments. In: Proceedings of ACM Multimedia’04, pp. 604–611 (2004a)
Ishibashi, Y., Kasugai, H., Fujimoto, M.: An intra-stream synchronization algorithm for haptic media in networked virtual environments. In: Proceedings of ACM SIGCHI International Conference on Advances in Computer Entertainment Technology (ACE)’04, pp. 127–133 (2004b)
Joslin C., Pandzic I.S., Thalmann N.M.: Trends in networked collaborative virtual environments. Comput. Commun. 26(5), 430–437 (2003)
Kanbara, T., Ishibashi, Y., Tasaka, S.: Haptic media synchronization control with dead-reckoning in networked virtual environments. In: Proceedings of World Multi-Conference on Systemics, Cybernetics, and Informatics (SCI)’04, vol. 3, pp. 158–163 (2004)
Kim, J., Shin, J., Kuo, C.C.J.: Dynamic network adaptation framework employing layered relative priority index for adaptive video delivery. In: Advances in Multimedia Information Processing—PCM. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol. 2532, pp. 936–943 (2002)
Kim J., Shin J., Kuo C.C.J.: Dynamic network adaptation framework employing layered relative priority index for adaptive video delivery. Adv. Multimedia Inf. Proc. PCM, LNCS (Lecture Notes in Computer Science) 2532, 936–943 (2002)
Kim J.G., Kim J., Shin J., Kuo C.C.J.: Coordinated packet-level protection with a corruption model for robust video transmission. In: Proceedings of SPIE Visual Communication Image Processing (VCIP)’01 (2001)
Lawrence D.: Stability and transparency in bilateral tele-operation. IEEE Trans. Robotics Autom. pp. 624–637 (1993)
Lee S., Kim J.: Transparency analysis and delay compensation scheme for haptic-based networked virtual environments. Comput. Commun. 32(5), 992–999 (2009)
Lee S., Moon S., Kim J.: Performance evaluation of transport protocols for networked haptic collaboration. In: Proceedings of SPIE ITCOM’06 (2006)
Marshall A., Yap K., Yu W.: Providing QoS for networked peers in distributed haptic virtual environments. Adv. Multimedia 2008, 1–14 (2008)
McLaughlin M., Hespanha J., Sukhatme G.: Touch in virtual environments: Haptics and the design of interactive systems. Prentice Hall, Englewood Cliffs (2002)
Morris, D., Joshi, N., Salisbury, K.: Haptic battle pong: High-degree-of-freedom haptics in a multiplayer gaming environment. In: Proceedings of Experimental Gameplay Workshop at Game Developers Conference (GDC)’04 (2004)
Ohlin, M., Henriksson, D., Cervin, A.: TrueTime 1.5 - Reference Manual. Department of Automatic Control, Lund University, Sweden (2007)
Sankaranarayanan, G., Hannaford, B.: Virtual coupling schemes for position coherency in networked haptic environments. In: Proceedings of IEEE/RAS-EMBS BioRob’06, pp. 853–858 (2006)
SensAble Technologies (2008) PHANToM Omni Haptic Device. http://www.sensable.com/haptic-phantom-omni.htm
Shirmohammadi S., Georganas N.: An end-to-end communication architecture for collaborative virtual environments. Comput. Netw. 35(2–3), 351–367 (2001)
Smith, R.: Open dynamics engine. http://www.ode.org (2000)
Srinivasan M.A., Basdogan C.: Haptics in virtual environments: Taxonomy research status, and challenges. Comput. Graph. 21(4), 393–404 (1997)
Zadeh M., Wang D., Kubica E.: Perception-based lossy haptic compression considerations for velocity-based interactions. Multimedia Syst. 13(4), 275–282 (2008)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by P. Shenoy.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lee, S., Kim, J. Priority-based haptic event filtering for transmission and error control in networked virtual environments. Multimedia Systems 15, 355–367 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00530-009-0170-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00530-009-0170-4