Abstract
The game world graph (GWG) framework is a taxonomy for analyzing and classifying computer game architectures. This article presents a systematic review of game architectures using the GWG framework. The review validates the usefulness of the GWG framework through classifying game architectures described in the literature into distinct categories according to the framework. The major contribution of the paper is a state-of-the-art presentation of 40 different game architectures, which covers architectures for all kinds of games from single player games to massively multiplayer online games (MMOGs). Previous reviews of game architectures have focused on a narrower selection of games such as only networked games, MMOGs or similar. Further, none of the previous reviews has used a systematic framework for analyzing the characteristics of game architectures. Using the framework, we can identify similarities and differences of the 40 game architectures in a systematic way. Finally, the paper outlines the evolution of the game architectures from the perspective of the GWG framework.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Xinbo, J., Safaei, F., Boustead, P.: Latency and scalability: a survey of issues and techniques for supporting networked games. In: Networks 2005. Jointly held with the 2005 IEEE 7th Malaysia International Conference on Communication (2005)
Fan, L., Trinder, P., Taylor, H.: Design issues for peer-to-peer massively multiplayer online games. Int. J. Adv. Media. Commun. 4(2), 108–125 (2010)
Dybå, T., Dingsøyr, T.: Empirical studies of agile software development: a systematic review. Inf. Softw. Technol. 50(9–10), 833–859 (2008)
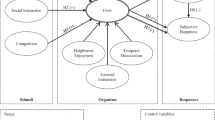
Sollenberger, D.J., Singh, M.P.: Architecture for affective social games. In: Tiergartenstrasse 17, Heidelberg, D-69121, Germany. Lecture Notes in Computer Science (including subseries Lecture Notes in Artificial Intelligence and Lecture Notes in Bioinformatics). Springer Verlag, pp. 79–94 (2009)
Nave, I., David, H., Shani, A., Tzruya, Y., Laikari, A., Eisert, P., Fechteler, P.: Games@large graphics streaming architecture. In: Consumer Electronics (2008)
Bangun, R.A., Beadle, H.W.P.: A network architecture for multiuser networked games on demand. In: Information, Communications and Signal Processing (1997)
Lages, W., Cordeiro, C., Guedes, D.: Performance analysis of a parallel multi-view rendering architecture using light fields. In, Tiergartenstrasse 17, Heidelberg, D-69121, Germany. Visual Computer. Springer Verlag, pp 947–958 (2009)
Caltagirone, S., Keys, M., Schlief, B., Willshire, M.J.: Architecture for a massively multiplayer online role playing game engine. J. Comput. Small Coll. 18(2), 105–116 (2002)
Chan, H.T., Chang, R.K.C.: Strifeshadow Fantasy: a massive multi-player online game. In: Consumer Communications and Networking Conference (2004)
Huang, J.-Y., Chang, J.-L., Li, C.-W., Lin, K.: Design of a multiple participant 3D war game environment over WWW. In: Orlando, FL, United states,. Proceedings of SPIE, The International Society for Optical Engineering. SPIE, pp. 303–312 (1998)
Quax, P., Geuns, B., Jehaes, T., Lamotte, W., Vansichem, G.: On the applicability of remote rendering of networked virtual environments on mobile devices. In: Systems and Networks Communications (2006)
Trinta, F., Pedrosa, D., Ferraz, C., Ramalho, G.: Evaluating a middleware for crossmedia games. Comput. Entertain. (CIE) 6(3) (2008)
Jardine, J., Zappala, D.: A hybrid architecture for massively multiplayer online games. In:Proceedings of the 7th ACM SIGCOMM Workshop on Network and System Support for Games, NetGames’08. Association for Computing Machinery, Worcester, MA, United states, pp. 60–65 (2008)
Pellegrino, J.D., Dovrolis, C.: Bandwidth requirement and state consistency in three multiplayer game architectures. Paper presented at the Proceedings of the 2nd workshop on Network and system support for games, Redwood City, California (2003)
Ramakrishna, V., Robinson, M., Eustice, K., Reiher, P.: An active self-optimizing multiplayer gaming architecture. In: Autonomic Computing Workshop (2003)
Ahmed, D.T., Shirmohammadi, S., De Oliveira, J.C.: A hybrid P2P communications architecture for zonal MMOGs. Multimed. Tools Appl. 45(1–3), 313–345 (2009)
Rooney, S., Bauer, D., Deydier, R.: A federated peer-to-peer network game architecture. Commun. Mag. IEEE42(5), 114–122 (2004)
Hampel, T., Bopp, T., Hinn, R.: A peer-to-peer architecture for massive multiplayer online games. Paper presented at the Proceedings of 5th ACM SIGCOMM workshop on Network and system support for games, Singapore (2006)
Buyukkaya, E., Abdallah, M., Cavagna, R.: VoroGame: A hybrid P2P architecture for massively multiplayer games. In: Consumer Communications and Networking Conference CCNC 2009. 6th IEEE, pp. 1–5 (2009)
Fan, L., Taylor, H., Trinder, P.: Mediator: a design framework for P2P MMOGs. Paper presented at the Proceedings of the 6th ACM SIGCOMM workshop on Network and system support for games, Melbourne, Australia (2007)
Norden, S., Guo, K.: Support for resilient Peer-to-Peer gaming. Comput. Netw. 51(14), 4212–4233 (2007)
Huey-Ing, L., Bing-Rong, T.: DACA: dynamic anti-cheating architecture for MMOGs. In: Advanced Information Networking and Applications (2009)
Knutsson, B.: Peer-to-peer support for massively multiplayer games IEEE INFOCOM 2004 INFCOM-04 (2004)
Assiotis, M., Tzanov, V.: A distributed architecture for MMORPG. Paper presented at the Proceedings of 5th ACM SIGCOMM workshop on Network and system support for games, Singapore (2006)
McCaffery, D.J., Finney, J.: The need for real time consistency management in P2P mobile gaming environments. Paper presented at the Proceedings of the 2004 ACM SIGCHI International Conference on Advances in computer entertainment technology, Singapore (2004)
Min, D., Choi, E., Lee, D., Park, B.: Load balancing algorithm for a distributed multimedia game server architecture. Int. Conf. Multimed. Comput. Syst. Proc. 2, 882–886 (1999)
Vleeschauwer, B.D., Bossche, B.V.D., Verdickt, T., Turck, F.D., Dhoedt, B., Demeester, P.: Dynamic microcell assignment for massively multiplayer online gaming. Paper presented at the Proceedings of 4th ACM SIGCOMM workshop on Network and system support for games, Hawthorne, NY (2005)
Hori, M., Iseri, T., Fujikawa, K., Shimojo, S., Miyahara, H.: Scalability issues of dynamic space management for multiple-server networked virtual environments. In: IEEE Pacific RIM Conference on Communications, Computers, and Signal Processing—Proceedings. Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers Inc., Victoria, BC, Canada, pp. 200–203 (2001)
Hsu, C.-C., Ling, J., Li. Q., Kuo, C.C.J.: On the design of multiplayer online video game systems. In: Proceedings of SPIE - The International Society for Optical Engineering. SPIE, Orlando, FL, United states, pp. 180–191 (2003)
Beskow, P.B., Vik, K.-H., Halvorsen, P., Griwodz, C.: The partial migration of game state and dynamic server selection to reduce latency. Multimed. Tools Appl. 45(1–3), 83–107 (2009)
Powers, S.J., Hinds, M.R., Morphett, J.: Distributed entertainment environment. Br. Telecom Technol. J. 15(4), 173–180 (1997)
Merabti, M., El Rhalibi, A.: Peer-to-peer architecture and protocol for a massively multiplayer online game. In: Global Telecommunications Conference Workshops, GlobeCom Workshops IEEE 2004, pp. 519–528 (2004)
Kabus, P., Buchmann, A.P.: Design of a cheat-resistant P2P online gaming system. Paper presented at the Proceedings of the 2nd international conference on Digital interactive media in entertainment and arts, Perth, Australia (2007)
Muller, J., Jan, H.M., Alexander, P., Maraike, S., Sergei, G.: Rokkatan: scaling an RTS game design to the massively multiplayer realm. Comput. Entertain. 4(3), 11 (2006)
Guo, Y., Fujinoki, H.: Tree-based server-middleman-client architecture: Improving scalability and reliability for voting-based network games in Ad-Hoc wireless networks. In, Boston, MA, USA (2006)
Chan, L., Yong, J., Bai, J., Leong, B., Tan, R.: Hydra: a massively-multiplayer peer-to-peer architecture for the game developer. Paper presented at the Proceedings of the 6th ACM SIGCOMM workshop on Network and system support for games, Melbourne, Australia (2007)
Lee, H.-H., Sun, C.-H.: Load-balancing for peer-to-peer networked virtual environment. Paper presented at the Proceedings of 5th ACM SIGCOMM workshop on Network and system support for games, Singapore (2006)
Mauve, M., Fischer, S., Jorg, W.: A generic proxy system for networked computer games. Paper presented at the Proceedings of the 1st workshop on Network and system support for games, Braunschweig, Germany (2002)
Aggarwal, S., Christofoli, J., Mukherjee, S., Rangarajan, S.: Authority assignment in distributed multi-player proxy-based games. Paper presented at the Proceedings of 5th ACM SIGCOMM workshop on Network and system support for games, Singapore (2006)
Quax, P., Dierckx, J., Cornelissen, B., Vansichem, G., Lamotte, W.: Dynamic server allocation in a real-life deployable communications architecture for networked games. In: Proceedings of the 7th ACM SIGCOMM Workshop on Network and System Support for Games, NetGames’08. Association for Computing Machinery Worcester, MA, USA, pp. 66–71 (2008)
Yang, L., Sutinrerk, P.: Mirrored arbiter architecture: a network architecture for large scale multiplayer games. Paper presented at the Proceedings of the 2007 summer computer simulation conference, San Diego, California (2007)
Bettinger, C., Baumann, A., Hausen, F., Schneider, G., Schloss, H.: HERA: design framework for decentralized distributed virtual environments and games. In: INC, IMS and IDC (2009)
Webb, S.D., Soh, S., Lau, W.: Enhanced mirrored servers for network games. Paper presented at the proceedings of the 6th ACM SIGCOMM workshop on Network and system support for games, Melbourne, Australia (2007)
Rowstron, A., Druschel, P.: Pastry: Scalable, Decentralized Object Location, and Routing for Large-Scale Peer-to-Peer Systems. In: Guerraoui, R. (ed.) Middleware 2001, vol 2218. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, pp. 329–350. Springer, Heidelberg (2001)
Stoica, I., Morris, R., Karger, D., Kaashoek, M.F., Balakrishnan, H.: Chord: a scalable peer-to-peer lookup service for internet applications. SIGCOMM Comput. Commun. Rev. 31(4), 149–160 (2001)
Aurenhammer, F.: Voronoi diagrams: a survey of a fundamental geometric data structure. ACM Comput. Surv. 23(3), 345–405 (1991)
Matuszek, S., Freelander, J.: Othecko: A Distributed Voting-Based Game System. University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill (1999)
Zhu, M., Wang, A.I., Guo, H., Trætteberg, H.: Graph of Game Worlds: New Perspectives on Video Game Architectures, (2012, Manuscript submitted for publication)
Acknowledgments
The authors want to thank the anonymous reviewers for their many suggestions that improve the content much.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhu, M., Wang, A.I. & Guo, H. From 101 to nnn: a review and a classification of computer game architectures. Multimedia Systems 19, 183–197 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00530-012-0274-0
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00530-012-0274-0