Abstract
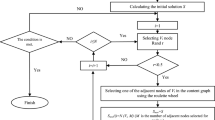
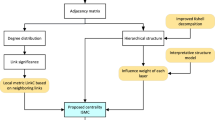
Community detection is a significant research problem in various fields such as computer science, sociology and biology. The singular characteristic of communities in social networks is the multimembership of a node resulting in overlapping communities. But dealing with the problem of overlapping community detection is computationally expensive. The evolution of communities in social networks happens due to the self-interest of the nodes. The nodes of the social network acts as self-interested players, who wish to maximize their benefit through interactions in due course of community formation. Game theory provides a systematic framework tox capture the interactions between these selfish players in the form of games. In this paper, we propose a Community Detection Game (CDG) that works under the cooperative game framework. We develop a greedy community detection algorithm that employs Shapley value mechanism and majority voting mechanism in order to disclose the underlying community structure of the given network. Extensive experimental evaluation on synthetic and real-world network datasets demonstrates the effectiveness of CDG algorithm over the state-of-the-art algorithms.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Al-Dhanhani A, Mizouni R, Otrok H, Al-Rubaie A (2014) A game theoretical model for collaborative groups in social applications. Expert Syst Appl 41(11):5056–5065
Badie R, Aleahmad A, Asadpour M, Rahgozar M (2013) An efficient agent-based algorithm for overlapping community detection using nodes closeness. Physica A 392(20):5231–5247
Bazzi M, Porter MA, Williams S, McDonald M, Fenn DJ, Howison SD (2016) Community detection in temporal multilayer networks, with an application to correlation networks. Multiscale Model Simul 14(1):1–41
Cavallari S, Zheng VW, Cai H, Chang KCC, Cambria E (2017) Learning community embedding with community detection and node embedding on graphs. In: CIKM
Chen W, Liu Z, Sun X, Wang Y (2010) A game-theoretic framework to identify overlapping communities in social networks. Data Min Knowl Discov 21(2):224–240
Cremonesi P, Turrin R, Lentini E, Matteucci M (2008) An evaluation methodology for collaborative recommender systems. In: International conference on automated solutions for cross media content and multi-channel distribution, 2008. AXMEDIS’08. IEEE, pp 224–231
Drago C, Ricciuti R (2017) Communities detection as a tool to assess a reform of the italian interlocking directorship network. Physica A 466:91–104
Fortunato S (2010) Community detection in graphs. Phys Rep 486(3):75–174
Fortunato S, Barthelemy M (2007) Resolution limit in community detection. Proc Nat Acad Sci 104(1):36–41
Girvan M, Newman ME (2002) Community structure in social and biological networks. Proc Nat Acad Sci 99(12):7821–7826
Gregory S (2007) An algorithm to find overlapping community structure in networks. In: European conference on principles of data mining and knowledge discovery. Springer, pp 91–102
Gregory S (2010) Finding overlapping communities in networks by label propagation. New J Phys 12(10):103,018
Havens TC, Bezdek JC, Leckie C, Ramamohanarao K, Palaniswami M (2013) A soft modularity function for detecting fuzzy communities in social networks. IEEE Trans Fuzzy Syst 21(6):1170–1175
Jonnalagadda A, Kuppusamy L (2016) A survey on game theoretic models for community detection in social networks. Soc Netw Anal Min 6(1):83
Kitchovitch S, Liò P (2011) Community structure in social networks: applications for epidemiological modelling. PLoS ONE 6(7):e22,220
Knuth DE (1993) The Stanford GraphBase: a platform for combinatorial computing, vol 37. Addison-Wesley, Reading
Lancichinetti A, Fortunato S (2009) Benchmarks for testing community detection algorithms on directed and weighted graphs with overlapping communities. Phys Rev E 80(1):016,118
Lindelauf R, Hamers H, Husslage B (2013) Cooperative game theoretic centrality analysis of terrorist networks: the cases of jemaah islamiyah and al qaeda. Eur J Oper Res 229(1):230–238
McSweeney PJ, Mehrotra K, Oh JC (2014) Game-theoretic framework for community detection. Encyclopedia of social network analysis and mining. Springer, Berlin, pp 573–588
Myerson RB (2013) Game theory. Harvard University Press, Cambridge
Narayanam R, Narahari Y (2011) A shapley value-based approach to discover influential nodes in social networks. IEEE Trans Autom Sci Eng 8(1):130–147
Newman ME (2006) Finding community structure in networks using the eigenvectors of matrices. Phys Rev E 74(3):036,104
Palla G, Derényi I, Farkas I, Vicsek T (2005) Uncovering the overlapping community structure of complex networks in nature and society. Nature 435(7043):814–818
de Paulo MA, Nascimento MC, Rosset V (2016) Improving the connectivity of community detection-based hierarchical routing protocols in large-scale wsns. Proc Comput Sci 96:521–530
Shamshirband S, Patel A, Anuar NB, Kiah MLM, Abraham A (2014) Cooperative game theoretic approach using fuzzy q-learning for detecting and preventing intrusions in wireless sensor networks. Eng Appl Artif Intell 32:228–241
Shapley LS (1971) Cores of convex games. Int J Game Theory 1(1):11–26
Shen H, Cheng X, Cai K, Hu MB (2009) Detect overlapping and hierarchical community structure in networks. Physica A 388(8):1706–1712
Shi C, Cai Y, Fu D, Dong Y, Wu B (2013) A link clustering based overlapping community detection algorithm. Data Knowl Eng 87:394–404
Shoham Y, Leyton-Brown K (2008) Multiagent systems: algorithmic, game-theoretic, and logical foundations. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Sun PG (2015) Community detection by fuzzy clustering. Physica A 419:408–416
Wang Q, Fleury E (2013) Overlapping community structure and modular overlaps in complex networks. Mining social networks and security informatics. Springer, Berlin, pp 15–40
Wasserman S, Faust K (1994) Social network analysis: methods and applications, vol 8. Cambridge University Press
Watts DJ, Strogatz SH (1998) Collective dynamics of small-worldnetworks. Nature 393(6684):440–442
Winter E (1989) A value for cooperative games with levels structure of cooperation. Int J Game Theory 18(2):227–240
Xie J, Kelley S, Szymanski BK (2013) Overlapping community detection in networks: the state-of-the-art and comparative study. ACM Comput Surv (CSUR) 45(4):43
Xie J, Szymanski BK (2012) Towards linear time overlapping community detection in social networks. In: Pacific-Asia conference on knowledge discovery and data mining. Springer, pp 25–36
Yu L, Wu B, Wang B (2013) Lblp: link-clustering-based approach for overlapping community detection. Tsinghua Sci Technol 18(4):387–397
Zachary WW (1977) An information flow model for conflict and fission in small groups. J Anthropol Res 33(4):452–473
Zhang S, Wang RS, Zhang XS (2007) Identification of overlapping community structure in complex networks using fuzzy c-means clustering. Physica A 374(1):483–490
Zhou L, Lü K, Cheng C, Chen H (2013) A game theory based approach for community detection in social networks. In: British national conference on databases. Springer, pp 268–281
Zhou L, Lü K, Yang P, Wang L, Kong B (2015) An approach for overlapping and hierarchical community detection in social networks based on coalition formation game theory. Expert Syst Appl 42(24):9634–9646
Zhou X, Liu Y, Zhang J, Liu T, Zhang D (2015) An ant colony based algorithm for overlapping community detection in complex networks. Physica A 427:289–301
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jonnalagadda, A., Kuppusamy, L. Overlapping community detection in social networks using coalitional games. Knowl Inf Syst 56, 637–661 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10115-017-1150-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10115-017-1150-1