Abstract
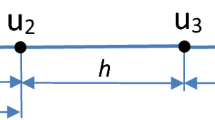
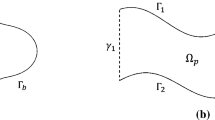
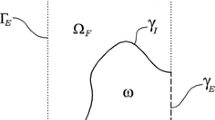
Biharmonic equations have many applications, especially in fluid and solid mechanics, but is difficult to solve due to the fourth order derivatives in the differential equation. In this paper a fast second order accurate algorithm based on a finite difference discretization and a Cartesian grid is developed for two dimensional biharmonic equations on irregular domains with essential boundary conditions. The irregular domain is embedded into a rectangular region and the biharmonic equation is decoupled to two Poisson equations. An auxiliary unknown quantity Δu along the boundary is introduced so that fast Poisson solvers on irregular domains can be used. Non-trivial numerical examples show the efficiency of the proposed method. The number of iterations of the method is independent of the mesh size. Another key to the method is a new interpolation scheme to evaluate the residual of the Schur complement system. The new biharmonic solver has been applied to solve the incompressible Stokes flow on an irregular domain.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adams, J., Swarztrauber, P., Sweet, R.: Fishpack: efficient Fortran subprograms for the solution of separable elliptic partial differential equations. http://www.netlib.org/fishpack/
Brenner, S.C.: An optimal-order nonconforming multigrid method for the biharmonic equation. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 26, 1124–1138 (1989)
Chan, R.H., DeLillo, T.K., Horn, M.A.: The numerical solution of the biharmonic equation by conformal mapping. SIAM J. Sci. Comput. 18(6), 1571–1582 (1997)
Chen, G.: Immersed interface method for biharmonic equations defined on irregular domains and its application to the Stokes flow, Ph.D. thesis, North Carolina State University (2003)
Davini, C., Pitacco, I.: An unconstrained mixed method for the biharmonic problem. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 38, 820–836 (2000)
W.E., Liu, J.: Vorticity boundary condition and related issues for finite difference schemes. J. Comput. Phys. 124, 368–382 (1996)
Ehrlich, L.W.: Solving the biharmonic equation as coupled finite difference equations. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 8 (1971)
Glowinski, R., Pironneau, O.: Numerical methods for the first biharmonic equation and for the two-dimensional stokes problem. SIAM Rev. 21, 167–212 (1979)
Greenbaum, A., Greengard, L., Mayo, A.: On the numerical-solution of the biharmonic equation in the plane. Phy. D 60, 216–225 (1992)
Gupta, M.M.: Spectrum transformation methods for divergent iteration. NASA Techinal Memorandum 103745 (ICOMP-91-02) (1991)
Gupta, M.M., Manohar, R.: Direct solution of biharmonic equation using noncoupled approach. J. Comput. Phys. 33, 236–248 (1979)
Hanisch, M.R.: Multigrid preconditioning for the biharmonic Dirichlet problem. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 30(1), 184–214 (1993)
Hou, T., Li, Z., Osher, S., Zhao, H.: A hybrid method for moving interface problems with application to the Hele-Shaw flow. J. Comput. Phys. 134, 236–252 (1997)
Hunter, J., Li, Z., Zhao, H.: Autophobic spreading of drops. J. Comput. Phys. 183, 335–366 (2002)
Jiang, G., Peng, D.: Weighted ENO schemes for Hamilton–Jacobi equations. SIAM J. Sci. Comput. 21, 2126–2143 (2000)
Kupferman, R.: A central-difference scheme for a pure stream function formulation of incompressible viscous flow. SIAM J. Sci. Statist. Comput. 23 (2001)
LeVeque, R.J., Li, Z.: The immersed interface method for elliptic equations with discontinuous coefficients and singular sources. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 31, 1019–1044 (1994)
Li, Z.: A fast iterative algorithm for elliptic interface problems. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 35, 230–254 (1998)
Li, Z.: IIMPACK: a collection of fortran codes for interface problems. Anonymous ftp at ftp.ncsu.edu under the directory: /pub/math/zhilin/Package and http://www4.ncsu.edu/~zhilin/IIM, last updated (2005)
Li, Z., Ito, K., Lai., M.-C.: An augmented approach for Stokes equations with a discontinuous viscosity and singular forces. NCSU-CRSC Tech. Report: CRSC-TR04-23, North Carolina State Univeristy (2004), Computers & Fluids, 36, 622–635 (2007)
Li, Z., Wan, X., Ito, K., Lubkin, S.: An augmented pressure boundary condition for a Stokes flow with a non-slip boundary condition. Commun. Comput. Phys. 1, 874–885 (2006)
Li, Z., Zhao, H., Gao, H.: A numerical study of electro-migration voiding by evolving level set functions on a fixed cartesian grid. J. Comput. Phys. 152, 281–304 (1999)
Mayo, A.: The fast solution of Poisson’s and the biharmonic equations on irregular regions. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 21, 285–299 (1984)
Mayo, A., Greenbaum, A.: Fast parallel iterative solution of Poisson’s and the biharmonic equations on irregular regions. SIAM J. Sci. Statist. Comput. 13, 101–118 (1992)
McLaurin, J.W.: A general coupled equation approach for solving the biharmonic boundary value problem. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 11, 14–33 (1974)
Osher, S., Fedkiw, R.: Level Set Methods and Dynamic Implicit Surfaces. Springer, New York (2002)
Bjørstad, P.: Fast numerical solution of the biharmonic dirichlet problem on rectangles. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 20 (1983)
Saad, Y.: GMRES: a generalized minimal residual algorithm for solving nonsymmetric linear systems. SIAM J. Sci. Statist. Comput. 7, 856–869 (1986)
Sethian, J.A.: Level Set Methods and Fast Marching Methods, 2nd edn. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge (1999)
Smith, J.: The coupled equation approach to the numerical solution of the biharmonic equation by finite differences, I. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 5, 323–339 (1968)
Smith, J.: The coupled equation approach to the numerical solution of the biharmonic equation by finite differences, II. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 7, 104–112 (1970)
Stephenson, J.W.: Single cell discretizations of order two and four for biharmonic problems. J. Comput. Phys. 55, 65–80 (1984)
Swarztrauber, P.N.: Fast Poisson solver. In: Golub, G.H. (ed.) Studies in Numerical Analysis, vol. 24, pp. 319–370. MAA (1984)
Thatcher, R.W.: A least squares method for solving biharmonic problems. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 38, 1523–1539 (2000)
Timoshenko, S., Goodier, J.: Theory of Elasticity. McGraw-Hill, New York (1970)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by Z. Chen.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, G., Li, Z. & Lin, P. A fast finite difference method for biharmonic equations on irregular domains and its application to an incompressible Stokes flow. Adv Comput Math 29, 113–133 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10444-007-9043-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10444-007-9043-6
Keywords
- Biharmonic equation
- Irregular domain
- Augmented method
- Immersed interface method
- Incompressible Stokes flow