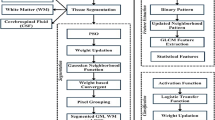
Abstract
This paper is an effort to encapsulate the various developments in the domain of different unsupervised, supervised and half supervised brain anomaly detection approaches or techniques proposed by the researchers working in the domain of the Medical image segmentation and classification. As researchers are constantly working hard in the domain of image segregation, interpretation and computer vision in order to automate the task of tumour segmentation, anomaly detection, classification and other structural disorder prediction at an early stage with the aid of computer. The different medical imaging modalities are used by the doctors in order to diagnose the brain tumour and other structural brain disorders which are an integral part of diagnosis and prognosis process. When these different medical image modalities are used along with various image segmentation methods and machine learning approaches tends to perform brain structural disorder detection and classification in a semi-automated or fully automated manner with high accuracy. This paper presents all such approaches using various medical image modalities for the accurate detection and classification of brain tumour and other brain structural disorders. In this paper, all the major phases of any brain tumour or brain structural disorder detection and classification approach is covered begin with the comparison of various medical image pre-processing techniques then major segmentation approaches followed by the approaches based on machine learning. This paper also presents an evaluation and comparison among the various popular texture and shape based feature extraction methods used in combination with different machine learning classifiers on the BRATS 2013 dataset. The fusion of MRI modalities used along with the hybrid features extraction methods and ensemble model delivers the best result in terms of accuracy.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adams R, Bischof L (1994) Seeded region growing. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 16:641–647
Adeli E, Shi F, An L, Wee CY, Wu G, Wang T et al (2016) Joint feature-sample selection and robust diagnosis of Parkinson’s disease from MRI data. J Neuroimage 141:206–219
Adhikari SK, Sing JK, Basu DK, Nasipuri M (2015) Conditional spatial fuzzy C-means clustering algorithm for segmentation of MRI images. Appl Soft Comput 34:758–769
Ain Q, Jaffar MA, Choi TS (2014) Fuzzy anisotropic diffusion based segmentation and texture based ensemble classification of brain tumor. Appl Soft Comput 21:330–340. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asoc.2014.03.019
AlBadawy EA, Saha A, Mazurowski MA (2018) Deep learning for segmentation of brain tumours: impact of cross-institutional training and testing. Med Phys 45(3):1150–1158
Alexander ME, Baumgartner R, Summers AR, Windischberger C, Klarhoefer M, Moser E, Somorjai RL (2000) A wavelet-based method for improving signal-to-noise ratio and contrast in MR images. Magn Reson Imaging 18:169–180
Alzheimer’s Disease Neuro-Imaging (ADNI) public database http://www.loni.ucla.edu/ADNI/Data. Accessed 20 Mar 2019
Amin J, Sharif M, Raza M, Saba T, Anjum MA (2019) Brain tumor detection using statistical and machine learning method. Comput Methods Programs Biomed. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cmpb.2019.05.015
Amoroso N, La Rocca M, Monaco A, Bellotti R, Tangaro S (2018) Complex networks reveal early MRI markers of Parkinson’s disease. Med Image Anal 48:12–24. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.media.2018.05.004
Anaraki AK, Ayati M, Kazemi F (2019) Magnetic resonance imaging-based brain tumour grades classification and grading via convolutional neural networks and genetic algorithm. J Bio-Cybern Biomed Eng 39:63–74. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbe.2018.10.004
Article on Neuroimaging (2019) https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Neuroimaging. Accessed on 12 March 2019
Bao P, Zhang L (2003) Noise reduction for magnetic resonance images via adaptive multi-scale products thresholding. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 22:1089–1099
BIRN Data Repository http://fbirnbdr.birncommunity.org:8080/BDR/, supported by grants to the Function BIRN (U24-RR021992). Accessed 20 Mar 2019
Buendia P, Taylor T, Ryan M, John N (2013) A grouping artificial immune network for segmentation of tumor images. Paper presented at the Proceedings of NCI-MICCAI Challenge on Multimodal Brain Tumor Segmentation (BRATS 2013), Nagoya, Japan
Castro E, Gupta CN, Martinez-Ramon M, Calhoun VD, Arbabshirani MR, Turner J (2014) Identification of patterns of gray matter abnormalities in schizophrenia using source-based morphometry and bagging. In: Conf Proc IEEE Eng Med Biology Society, pp 1513–1516
Chang J, Zhang L, Gu N, Zhang X, Minquan Yin R, Meng Q (2019) A mix-pooling CNN architecture with FCRF for brain tumor segmentation. J Vis Commun Image Represent 58:316–322. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jvcir.2018.11.047
Chen S, Ding C, Liu M (2019) Dual-force convolutional neural networks for accurate brain tumor segmentation. J Pattern Recogn. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.patcog.2018.11.009
Cheng H, Newman S, Goni J, Kent JS, Howell J, Bolbecker A et al (2015) Nodal centrality of functional network in the differentiation of schizophrenia. Schizophr Res 168(1–2):345–352
Choi H, Jin KH (2018) Alzheimer’s disease Neuroimaging: predicting cognitive decline with deep learning of brain metabolism and amyloid imaging. Behav Brain Res 344:103–109
Chu WL, Huang MW, Jian BL, Hsu CY, Cheng KS (2016) A correlative classification study of schizophrenic patients with results of clinical evaluation and structural magnetic resonance images. Behav Neurol 2016:7849526
Chuang KS, Tzeng HL, Chen S, Wu J, Chen TJ (2006) Fuzzy c-means clustering with spatial information for image segmentation. Comput Med Imaging Graph 30(1):9–15
Clark K, Vendt B, Smith K, Freymann J, Kirby J, Koppel P et al (2013) The Cancer Imaging Archive (TCIA): maintaining and operating a public information repository. J Digit Imaging 26(6):1045–1057
Cordier N, Menza B, Delingette H, Ayache N (2013) Patch-based Segmentation of Brain Tissues. Paper presented at the Proceedings of NCI-MICCAI Challenge on Multimodal Brain Tumor Segmentation (BRATS 2013), Nagoya, Japan
Davy A, Havaei M, Warder-Farley D et al (2014) Brain tumour segmentation with deep neural networks. In: Proceedings MICCAI-BRATS, Boston, MA, USA
Doan NT, Engvig A, Zaske K, Persson K, Lund MJ, Kaufmann T et al (2017) Distinguishing early and late brain aging from the Alzheimer’s disease spectrum: consistent morphological patterns across independent samples. Neuroimaging 158:282–295
Dvorak P, Menze B (2015) Structured prediction with convolutional neural networks for multimodal brain tumour segmentation. In: Proceedings of MICCAI-BRATS, Munich, Germany, pp 13–24
Dyrba M, Grothe M, Kirste T, Teipel SJ (2015) Multimodal analysis of functional and structural disconnection in Alzheimer’s disease using multiple kernels SVM. Hum Brain Map 36(6):2118–2131
Farzan A, Mashohor S, Ramli AR, Mahmud R (2015) Boosting diagnosis accuracy of Alzheimer’s disease using high dimensional recognition of longitudinal brain atrophy patterns. Behav Brain Res 290:124–130
Festa J, Pereira S, Maria J, Sousa N, Silva C (2013) Automatic Brain Tumor Segmentation of Multi-sequence MR images using Random Decision Forest. Paper presented at the Proceedings of NCIMICCAI Challenge on Multimodal Brain Tumor Segmentation (BRATS 2013), Nagoya, Japan
Garali I, Adel M, Bourennane S, Guedj E (2018) Histogram-based features selection and volume of interest ranking for brain PET image classification. IEEE J Transl Eng Health Med 6:2100212
Glozman T, Solomon J, Pestilli F, Guibas L (2017) Alzheimer’s diseaseNeuroimaging: shape-attributes of brain structures as biomarkers for Alzheimer’s disease. J Alzheimer’s Dis 56(1):287–295
Goceri E (2011) PCA based bayesian approach for automatic multiple sclerosis lesion detection. In: The Intl symposium on computing in informatics and mathematics (ISCIM 2011), Tirana-Durres, Albania, pp 687–694
Goceri E (2017) Intensity normalization in brain MR images using spatially varying distribution matching. In: 11th Intl conference on computer graphics, visualization, computer vision and image processing (CGVCVIP 2017), Lisbon, Portugal, pp 300–304
Goceri E (2018a) Fully automated and adaptive intensity normalization using statistical features for brain MR images. Celal Bayar Üniversitesi Fen Bilimleri Dergisi 14(1):125–134. https://doi.org/10.18466/cbayarfbe.384729
Goceri E (2018b) Biomedical information technology: image based computer aided diagnosis systems. In: International conference on advanced technologies, Antalya, Turkey, p 132
Goceri E (2018c) Formulas behind deep Learning success. In: International conference on applied analysis and mathematical modeling (ICAAMM2018), Istanbul, Turkey, p 156
Goceri E (2019) Diagnosis of Alzheimer’s disease with Sobolev gradient based optimization and 3D convolutional neural network. Int J Numer Method Biomed Eng 35:e3225. https://doi.org/10.1002/cnm.3225
Goceri E, Goceri N (2017) Deep learning in medical image analysis: recent advances and future trends. In: 11th international conference on computer graphics, visualization, computer vision and image processing (CGVCVIP 2017), Lisbon, Portugal, pp 305–311
Goceri E, Songul C (2017) Automated detection and extraction of skull from MR head images: preliminary results. In: Int. Conf. on computer science and engineering (UBMK), Antalya, Turkey, pp 171–176. https://doi.org/10.1109/ubmk.2017.8093370
Goetz M, Weber C, Bloecher J, Stieltjes B, Meinzer HP, Maier-Hein K (2014) Extremely randomized trees based brain tumor segmentation. Paper presented at the Proceeding of BRATS Challenge—MICCAI
Golshan HM, Hasanzedeh RPR, Yousefzadeh SC (2013) An MRI de-noising method using data redundancy and local SNR estimation. Magn Reson Imaging 31:1206–1217
Guo H, Zhang F, Chen J, Xu Y, Xiang J (2017) Machine learning classification combining multiple features of a hyper-network of fMRI data in Alzheimer’s disease. Front Neurosci 11:615
Gupta N, Khanna P (2017) A non-invasive and adaptive CAD system to detect brain tumor from T2-weighted MRIs using customized Otsu’s thresholding with prominent features and supervised learning. J Signal Process Image Commun. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.image.2017.05.013
Gupta N, Bhatele P, Khanna P (2017) Identification of Gliomas from brain MRI through adaptive segmentation and run length of centralized patterns. J Comput Sci. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jocs.2017.02.009
Gupta N, Bhatele P, Khanna P (2019) Glioma detection on brain MRIs using texture and morphological features with ensemble learning. J Biomed Signal Process Control 47:115–125. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bspc.2018.06.003
Harvard Medical School Data http://www.med.harvard.edu/AANLIB/. Accessed 22 Mar 2019
Havaei M, Davy A, Warde-Farley D et al (2017) Brain tumour segmentation with deep neural networks. Med Image Anal 35:18–31
Hemanth DJ, Anitha J, Naaji A, Geman O, Popescu DE, Son LH (2019) A modified deep convolutional neural network for abnormal brain image classification. IEEE Access. https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2018.2885639
Houmani N, Dreyfus G, Vialatte FB (2015) Epoch-based entropy for early screening of Alzheimer’s disease. Int J Neural Syst 25(08):1550032
Hsieh KLC, Lo CM, Hsiao CJ (2017) Computer-aided grading of gliomas based on local and global MRI features. Comput Methods Programs Biomed 139:1–38
http://www.cma.mgh.harvard.edu/ibsr/. Accessed 22 Mar 2019
http://www.bic.mni.mcgill.ca/brainweb/. Accessed 22 Mar 2019
http://brainmaps.org/index.php. Accessed 22 Mar 2019
http://cancerimagingarchive.net/ of the National Cancer Institute, a portal containing 21 images of TCGA patients for image analysis. Accessed 22 Mar 2019
https://www.financialexpress.com/india-news/doctor-population-ratio-inindia-one-allopathic-doctor-for-11082-people-official-data-shows-bihar-up-worst-.Hit/1213243. Accessed on 12 March 19
Hu Q, Hou Z, Nowinski W (2006) Supervised range-constrained thresholding. IEEE Trans Image Process 15:228–240
Hussain S, Anwar SM, Majid M (2018) Segmentation of glioma tumors in brain using deep convolutional neural network. Neurocomputing 282:248–261
IXI Dataset http://brain-development.org/ixi-dataset/. Accessed 25 Mar 2019
Ji ZX, Sun QS, Xia DSA (2011) Modified possibilistic fuzzy c-means clustering algorithm for bias field estimation and segmentation of brain MR image. Comput Med Imaging Graph 35(5):383–397
Ji Z, Xia Y, Sun Q, Chen Q, Feng D (2014a) Adaptive scale fuzzy local Gaussian mixture model for brain MR image segmentation. Neurocomputing 134:60–69
Ji Z, Liu J, Cao G, Sun Q, Chen Q (2014b) Robust spatially constrained fuzzy c-means algorithm for brain MR image segmentation. Pattern Recogn 47(7):2454–2466
Joliot M, Mazoyer BM (1993) Three-dimensional segmentation and interpolation of magnetic resonance brain images. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 12(2):269–277
Jui SL, Zhang S, Xiong W, Yu F, Fu M, Wang D, Hassanien AE, Xiao X (2016) Brain MRI tumor segmentation with 3D intracranial structure deformation features. IEEE Intell Syst 31:66–76. https://doi.org/10.1109/MIS.2015.93
Juneja A, Rana B, Agrawal RK (2018) A novel fuzzy rough selection of non-linearly extracted features for schizophrenia diagnosis using fMRI. Comput Methods Programs Biomed 155:139–152. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cmpb.2017.12.001
Kamnitsas K, Ledig C, Newcombe VFJ et al (2017) Efficient multi-scale 3D CNN with fully connected CRF for accurate brain lesion segmentation. Med Image Anal 36:61–78
Kapur JN, Sahoo PK, Wong AK (1985) A new method for gray-level picture thresholding using the entropy of the histogram. Comput Vis Graph Image Process 29:273–285
Kaus MR, Warfield SK, Nabavi A, Black PM, Jolesz FA, Kikinis R (2001a) Automated segmentation of MRI images of brain tumors. Radiology 218:586–591
Kaus M, Warfield S, Nabavi A, Black P, Jolesz F, Kikinis R (2001b) Automated segmentation of MRI of brain tumors. Radiology 218(2):586–591
Krinidis S, Chatzis VA (2010) Robust fuzzy local information C means clustering algorithm. IEEE Trans Image Process 19(5):1328–1337
Li C, Xu C, Anderson AW, Gore JC (2009) MRI tissue classification and bias field estimation based on coherent local intensity clustering: A unified energy minimization framework. Information Processing in Medical Imaging. Springer, Berlin, pp 288–299
Li M, Qin Y, Gao F, Zhu W, He X (2014a) Discriminative analysis of multivariate features from structural MRI and diffusion tensor images. Magn Reson Imaging 32(8):1043–1051
Li M, Oishi K, He X, Qin Y, Gao F, Mori S et al (2014b) An efficient approach for differentiating Alzheimer’s disease from normal elderly based on multicentre MRI using gray-level invariant features. J PLoS One 9(8):e105563
Li Y, Jiao L, Shang R, Stolkin R (2015) Dynamic-context cooperative quantum-behaved particle swarm optimization based on multilevel thresholding applied to medical image segmentation. Inf Sci 294:408–422
Liao L, Lin TS (2007) A fast spatial constrained fuzzy kernel clustering algorithm for MRI brain image segmentation. Wavel Anal Pattern Recogn 1:82–87
Lyksborg M, Puonti O, Agn M, Larsen R (2015) An ensemble of 2D convolutional neural networks for tumor segmentation. In: Scandinavian conference on image analysis, SCIA, p 9127
Ma J, Plonka G (2007) Combined curve let shrinkage and nonlinear anisotropic diffusion. IEEE Trans Image Process 16:2198–2206
Maggioni M, Katkovnik V, Egiazarian K, Foi A (2013) Nonlocal transform-domain filter for volumetric data de-noising and reconstruction. IEEE Trans Image Process 22(1):119–133
Maitra M, Chatterjee A (2008) A novel technique for multilevel optimal magnetic resonance brain image thresholding using bacterial foraging. Measurement 41(10):1124–1134
Manikandan S, Ramar K, Iruthayarajan MW, Srinivasagan KG (2014) Multilevel thresholding for segmentation of medical brain images using real coded genetic algorithm. Measurement 47:558–568
Mekhmoukh A, Mokrani K (2015) Improved fuzzy C-means based Particle Swarm Optimization initialization and outlier rejection with level set methods for MR brain image segmentation. Comput Methods Programs Biomed 122(2):266–281
Menze BH, Jakab A, Bauer S, Kalpathy-Cramer J, Farahani K, Kirby J, Burren Y, Porz N, Slotboom J, Wiest R, Lanczi L, Gerstner E, Weber MA, Arbel T et al (2015) The multimodal brain tumor image segmentation benchmark (BRATS). IEEE Trans Med Imaging 34:1993–2024. https://doi.org/10.1109/tmi.2014.2377694
Mohan J, Krishnaveni V, Guo Y (2014) A survey on the magnetic resonance image de-noising methods. Biomed Signal Process Control 9:56–69
Morabito FC, Campolo M, Ieracitano C, Ebadi JM, Bonanno L, Bramanti A, Bramanti P (2016) Deep convolutional neural networks for classification of mild cognitive impaired and Alzheimer’s disease patients from scalp EEG recordings. In: 2016 IEEE 2nd international forum on research and technologies for society and industry leveraging a better tomorrow (RTSI). https://doi.org/10.1109/rtsi.2016.7740576
Mustaqeem A, Javed A, Fatima T (2012) An efficient brain tumor detection algorithm using watershed & thresholding based segmentation. Int J Image Graph Signal Process 4(10):34–39
Nabizadeh M, Kubat M (2015) Brain tumors detection and segmentation in MR images: Gabor wavelet vs. statistical features. J Comput Electr Eng 45:286–301. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compeleceng.2015.02.007
Ni H, Zhou L, Ning X, Wang L (2016) Alzheimer’s disease Neuroimaging: exploring multi fractal-based features for mild Alzheimer’s disease classification. Magn Reson Med 76(1):259–269
Oliveira FPM, Faria DB, Costa DC, Castelo-Branco M, Tavares JMRS (2017) Extraction, selection and comparison of features for an effective automated computer-aided diagnosis of Parkinson’s disease based on FP-CIT SPECT images. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 45(6):1052–1062. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00259-017-3918-7
Orban P, Dansereau C, Desbois L, Mongeau-Pérusse V, Giguère CÉ, Nguyen H, Bellec P (2018) Multisite generalizability of schizophrenia diagnosis classification based on functional brain connectivity. Schizophr Res 192:167–171. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.schres.2017.05.027
Otsu N (1975) A threshold selection method from gray-level histograms. Automatica 11:23–27
Pedano N, Flanders AE, Scarpace L, Mikkelsen T, Eschbacher JM, Hermes B et al (2016) Radiology data from the cancer genome atlas low grade glioma [TCGA-LGG] collection. Cancer Imaging Archive. https://doi.org/10.7937/K9/TCIA.2016.L4LTD3TK. Accessed 29 Mar 2019
Peng B, Wang S, Zhou Z, Liu Y, Tong B, Zhang T et al (2017) A multilevel-ROI-features-based machine learning method for detection of morph metric biomarkers in Parkinson’s disease. Neurosci Lett 651:88–94
Pereira S, Pinto A, Alves V, Silva CA (2016) Brain tumor segmentation using convolutional neural networks in MR images. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 35(5):1240–1251
Pereira S, Meier R, McKinley R, Wiest R, Alves V, Silva CA, Reyes M (2018) Enhancing interpretability of automatically extracted machine learning features: application to a RBM-Random Forest system on brain lesion segmentation. Med Image Anal. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.media.2017.12.009
Pergola G, Trizio S, Di Carlo P, Taurisano P, Mancini M, Amoroso N, Blasi G (2017) Grey matter volume patterns in thalamic nuclei are associated with familial risk for schizophrenia. Schizophr Res 180:13–20. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.schres.2016.07.005
Pinaya WHL, Gadelha A, Doyle OM, Noto C, Zugman A, Cordeiro Q, Sato JR (2016) Using deep belief network modelling to characterize differences in brain morphometry in schizophrenia. Sci Rep 6(1):38897. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep38897
Qadar MA, Zhaowen Y (2014) Brain tumour segmentation: a comparative analysis. IJCSI Int J Comput Sci Issues 11(6):1694-0784
Rajan J, den Dekker AJ, Sijbers J (2014) A new non-local maximum likelihood estimation method for Rician noise reduction in magnetic resonance images using the Kolmogorov–Smirnov test. Signal Process 103:16–23
Rembrandt dataset. https://wiki.cancerimagingarchive.net/display/Public/REMBRAND. Accessed 25 Mar 2019
Rexilius J, Hahn H, Klein J, Lentschig M, Peitgen H (2007) Multispectral brain tumour segmentation based on histogram model adaptation. In: SPIE Conf Med Image Comput, p 65140V1-10
Reza S, Iftekharuddin KM (2013) Multi-class abnormal brain tissue segmentation using texture features. Paper presented at the Proceedings of NCI-MICCAI Challenge on Multimodal Brain Tumour Segmentation (BRATS 2013), Nagoya, Japan
Reza S, Iftekharuddin KM (2014) Improved brain tumor tissue segmentation using texture features. Paper presented at the Proceeding of BRATS Challenge—MICCAI
Rondina JM, Ferreira LK, de Souza Duran FL, Kubo R, Ono CR, Leite CC et al (2018) Selecting the most relevant brain regions to discriminate Alzheimer’s disease patients from healthy controls using multiple kernel learning: a comparison across functional and structural imaging modalities and atlases. Neuroimage Clin 17:628–641
Saha P, Udupa J (2001) Optimum image thresholding via class uncertainty and region homogeneity. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 12(7):689–706
Salman Y (2009) Modified technique for volumetric brain tumour measurements. J Biomed Sci Eng 2:16–19
Salman Y, Badawi A, Assal M, Alian S (2005) New automatic technique for tracking brain tumor response. In: International conference on biological and medical physics, pp 1–4
Sanchez A, Mammone N, Morabito FC, Marino S, Adeli H (2019) A novel methodology for automated differential diagnosis of mild cognitive impairment and the Alzheimer’s disease using EEG signals. J Neurosci Methods 322:88–95
Sathya PD, Kayalvizhi R (2011) Optimal segmentation of brain MRI based on adaptive bacterial foraging algorithm. Neurocomputing 74(14):2299–2313
Sato M, Lakare S, Wan M, Kaufman A (2000) A gradient magnitude based region growing algorithm for accurate segmentation. Int Conf Image Process 3:448–451
Scarpace L, Flanders AE, Jain R, Mikkelsen T, Andrews DW (2015) Data from REMBRANDT. Cancer Imaging Arch 10:K9
Scarpace L, Mikkelsen T, Cha S, Rao S, Tekchandani S, Gutman D et al (2016) Radiology data from the cancer genome atlas glioblastoma multiforme [TCGA-GBM] collection. Cancer Imaging Archive. https://doi.org/10.7937/K9/TCIA.2016.RNYFUYE9. Accessed 30 Mar 2019
Schnack HG, Nieuwenhuis M, van Haren NE, Abramovic L, Scheewe TW, Brouwer RM et al (2014) Can structural MRI aid inclinical classification? A machine learning study in two independent samples of patients with schizophrenia, bipolar disorder and healthy subjects. Neuroimage 84:299–306
Shanthi KJ, Kumar MS (2007) Skull stripping and automatic segmentation of brain MRI using seed growth and threshold techniques. In: International conference on intelligent and advanced systems, Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICIAS.2007.4658421
Sijbers J, Poot D, den Dekker AJ, Pintjens W (2007) Automatic estimation of the noise variance from the histogram of a magnetic resonance image. Phys Med Biol 52:1335–1348
Sikka K, Sinha N, Singh PK, Mishra AK (2009) A fully automated algorithm under modified FCM framework for improved brain MR image segmentation. Magn Reson Imaging 27(7):994–1004
Song G, Huang Z, Zhao Y, Zhao X, Liu Y, Bao M, Han J, Li P (2019) A noninvasive system for the automatic detection of gliomas based on hybrid features and PSO-KSVM. IEEE Access. https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2894435
Stadlbauer A, Moser E, Gruber S, Buslei R, Nimsky C, Fahlbusch R, Ganslandt O (2004) Improved delineation of brain tumours: an automated method for segmentation based on pathologic changes of 1H-MRSI metabolites in gliomas. J Neuroimage 23:454–461
Subashini MM, Sahoo SK, Sunil V, Easwaran S (2016) A non-invasive methodology for the grade identification of astrocytoma using image processing and artificial intelligence techniques. Expert Syst Appl 43:186–196
Sung YC, Han KS, Song CJ, Noh SM, Park JW (2000) Threshold estimation for region segmentation on mri image of brain having the partial volume artifact. In: 5th international conference on signal processing proceedings, 2000. WCCC-ICSP 2000. IEEE, vol 2, pp 1000–1009
Taloa M, Baloglu UB, Yıldırıma O, Acharya UR (2019) Application of deep transfer learning for automated brain abnormality classification using MR images. J Cognit Syst Res 54:176–188. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cogsys.2018.12.007
The Cancer Imaging Archive GBM dataset TCIA http://cancergenome.nih.gov/. Accessed 26 Mar 2019
The PPMI cohort will comprise 400 recently diagnosed PD and 200 healthy subjects followed longitudinally for clinical, imaging and bio specimen biomarker assessment using standardized data acquisition protocols at twenty-one clinical sites. https://www.ppmi-info.org/access-data-specimens/download-data/. Accessed 27 Mar 2019
Tustison NJ, Shrinidhi KL, Wintermark M, Durst CR, Kandel BM, Gee JC, Grossman MC, Avants BB (2015) Optimal symmetric multimodal templates and concatenated random forests for supervised brain tumour segmentation (simplified) with ANTsR. Neuroinformatics 13:209–225. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12021-014-9245-2
Urban G, Bendszus M, Hamprecht F, Kleesiek J (2014) Multimodal brain tumor segmentation using deep convolutional neural networks. In: MICCAI BraTS (Brain Tumour Segmentation) Challenge. Proceedings, Winning Contribution 31–35, Boston, MA, USA
Vijayakumar C, Gharpure DC (2011) Development of image-processing software for automatic segmentation of brain tumors in MRI images. J Med Phys/Assoc Med Phys India 36(3):147
Wang SH, Phillips P, Sui Y, Liu B, Yang M, Cheng H (2018) Classification of Alzheimer’s disease based on eight-layer convolutional neural network with leaky rectified linear unit and max pooling. J Med Syst 42(5):85
Weaver JB, Xu Y, Healy DM, Cromwell LD (1991) Filtering noise from images with wavelet transforms. Magn Reson Imaging 21:288–295
Wong KP (2005) Medical image segmentation: methods and applications in functional imaging. Handbook of Biomedical Image Analysis. Springer, Berlin, pp 111–182
Zarogianni E, Storkey AJ, Johnstone EC, Owens DGC, Lawrie SM (2017) Improved individualized prediction of schizophrenia in subjects at familial high risk, based on neuroanatomical data, schizotypal and neurocognitive features. Schizophr Res 181:6–12. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.schres.2016.08.027
Zeng LL, Wang H, Hu P, Yang B, Pu W, Shen H et al (2018) Multi-site diagnostic classification of schizophrenia using discriminant deep learning with functional connectivity MRI. EBioMedicine 30:74–85
Zikic D, Ioannou Y, Brown M, Criminisi A (2014) Segmentation of brain tumour tissues with convolutional neural networks. In: Proceedings of MICCAI workshop on multimodal brain tumor segmentation challenge (BRATS), Boston, Massachusetts, USA
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bhatele, K.R., Bhadauria, S.S. Brain structural disorders detection and classification approaches: a review. Artif Intell Rev 53, 3349–3401 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10462-019-09766-9
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10462-019-09766-9