Abstract
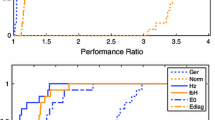
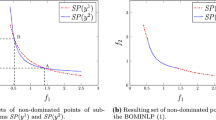
Aiming at the development of an exact solution method for registration problems, we present two different Branch & Bound algorithms for a mixed integer programming formulation of the problem. The first B&B algorithm branches on binary assignment variables and makes use of an optimality condition that is derived from a graph matching formulation. The second, geometric B&B algorithm applies a geometric branching strategy on continuous transformation variables. The two approaches are compared for synthetic test examples as well as for 2-dimensional medical data. The results show that medium sized problem instances can be solved to global optimality in a reasonable amount of time.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alt, H., & Guibas, L. J. (2000). Discrete geometric shapes: Matching, interpolation, and approximation. In J.-R. Sack & J. Urrutia (Eds.), Handbook of computational geometry. Amsterdam: Elsevier. Chap. 3.
Baird, H. S. (1984). Model-based image matching using location. PhD thesis, Princeton University.
Besl, P. J., & McKay, N. D. (1992). A method for registration of 3-D shapes. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 14, 239–256.
Bishnu, A., Das, S., Nandy, S. C., & Bhattacharya, B. B. (2006). Simple algorithms for partial set pattern matching under rigid motion. Pattern Recognition, 39, 1162–1671.
Breuel, T. M. (2002). A comparison of search strategies for geometric branch and bound algorithms. In Lecture notes in computer science : Vol. 2352. Proceedings of the 7th European conference on computer vision, Part III, Copenhagen, Denmark, May 28–31, 2002. Berlin: Springer.
Breuel, T. M. (2003a). Implementation techniques for geometric branch-and-bound matching methods. Computer Vision and Image Understanding, 90(3), 258–294.
Breuel, T. M. (2003b). On the use of interval arithmetic in geometric branch and bound algorithms. Pattern Recognition Letters, 24, 1375–1384.
Burkard, R. E. (1999). Selected topics on assignment problems. Discrete Applied Mathematics, 123, 257–302.
Chew, L. P., Goodrich, M. T., Huttenlocher, D. P., Kedem, K., Kleinberg, J. M., & Kravets, D. (1993). Geometric pattern matching under Euclidean motion. In Proceedings of the 5th Canadian conference on computational geometry (pp. 151–156).
Chui, H., & Rangarajan, A. (2003). A new point matching algorithm for non-rigid registration. Computer Vision and Image Understanding, 89, 114–141.
Eggert, D., Lorusso, A., & Fisher, R. (1997). Estimating 3-D rigid body transformations: A comparison of four major algorithms. Machine Vision and Applications, 9, 272–290.
Floudas, C. A., & Visweswaran, V. (1990). A global optimization algorithm (GOP) for certain classes of nonconvex NLPs I–II. Computers and Chemical Engineering, 14, 1398–1434.
Gorski, J., Pfeuffer, F., & Klamroth, K. (2007). Biconvex sets and optimization with biconvex functions—a survey and extensions. Mathematical Methods of Operations Research, 66(3), 373–407.
Hastreiter, P., Rezk-Salama, C., Soza, G., Bauer, M., Greiner, G., Fahlbusch, R., Ganslandt, O., & Nimsky, C. (2004). Strategies for brain shift evaluation. Medical Image Analysis, 8(4), 447–464.
Jian, B., & Vemuri, B. C. (2005). A robust algorithm for point set registration using mixture of Gaussians. IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, 2, 1246–1251. ISSN 1550-5499.
Liu, Y. (2004). Improving ICP with easy implementation for free-form surface matching. Pattern Recognition, 37(2), 211–226.
Loiola, E. M., de Abreu, N. M., Boaventura-Netto, P. O., Hahn, P., & Querido, T. (2007). A survey for the quadratic assignment problem. European Journal of Operational Research, 176, 657–690.
Maintz, J. B. A., & Viergever, M. A. (1998). A survey of medical image registration. Medical Image Analysis, 2(1), 1–36.
Mäkinen, V., & Ukkonen, E. (2002). Local similarity based point-pattern matching. In Lecture notes in computer science : Vol. 2373. Proceedings of the 13th annual symposium on combinatorial pattern matching, London, UK (pp. 115–132). Berlin: Springer.
Modersitzki, J. (2004). Numerical methods for image registration. New York: Oxford University Press.
Mount, D. M., Le Moigne, J., & Netanyahu, N. S. (1998). Efficient algorithms for robust feature matching. Pattern Recognition, 92, 17–38.
Myronenko, A., & Song, X. B. (2009). Point-set registration: Coherent point drift. Computing Research Repository, abs/0905.2635, 1–14.
Nemhauser, G. L., & Wolsey, L. A. (1988). Integer and combinatorial optimization. New York: Wiley-Interscience.
Pfeuffer, F. (2006). Registrierung medizinischer bilddaten auf basis verallgemeinerter zuordnungsprobleme. Master’s thesis, Universität Erlangen-Nürnberg, Institut für Angewandte Mathematik.
Rangarajan, A., Chui, H., & Mjolsness, E. (2001). A relationship between spline-based deformable models and weighted graphs in non-rigid matching. In IEEE CVPR 2001 (Vol. 01, p. 897). Los Alamitos: IEEE Comput. Soc.
Rohr, K. (2001). Computational imaging and vision: Vol. 21. Landmark-based image analysis. Dordrecht: Kluwer Academic.
Rusinkiewicz, S., & Levoy, M. (2001). Efficient variants of the ICP algorithm. In Proceedings of the 3rd intl. conf. on 3D digital imaging and modeling (pp. 145–152).
Stiglmayr, M., Pfeuffer, F., & Klamroth, K. (2008). A branch & bound algorithm for medical image registration. In V. Brimkov, R. Barneva & H. Hauptman (Eds.), Proceedings of the 12th international workshop on combinatorial image analysis, IWCIA 08 (Vol. 4958, pp. 218–227). Berlin: Springer.
Viola, P. A. (1995). Alignment by maximization of mutual information. PhD thesis, Massachusetts Institute of Technology.
Zheng, Y., & Doermann, D. (2006). Robust point matching for nonrigid shapes by preserving local neighborhood structures. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 28(4), 643–649.
Zitová, B., & Flusser, J. (2003). Image registration methods: A survey. Image and Vision Computing, 21, 977–1000.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
M. Stiglmayr and K. Klamroth were partially supported by German Research Foundation, Collaborative Research Center (SFB 603).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pfeuffer, F., Stiglmayr, M. & Klamroth, K. Discrete and geometric Branch and Bound algorithms for medical image registration. Ann Oper Res 196, 737–765 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10479-010-0760-8
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10479-010-0760-8