Abstract
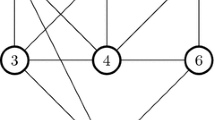
Graph clustering (partitioning) is a helpful tool in understanding complex systems and analyzing their structure and internal properties. One approach for graph clustering is based on partitioning the graph into cliques. However, clique models are too restrictive and prone to errors given imperfect data. Thus, using clique relaxations instead may provide a more reasonable and applicable partitioning of the graph. An s-club is a distance-based relaxation of a clique and is formally defined as a subset of vertices inducing a subgraph with a diameter of at most s. In this work, we study the minimum s-club partitioning problem, which is to partition the graph into a minimum number of non-overlapping s-club clusters. Integer programming techniques and combinatorial branch-and-bound framework are employed to develop exact algorithms to solve this problem. We also study and compare the computational performance of the proposed algorithms for the special cases of \(s=2\) and \(s=3\) on a test-bed of randomly generated instances and real-life graphs.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abbasi, A. A., & Younis, M. (2007). A survey on clustering algorithms for wireless sensor networks. Computer Communications, 30(14), 2826–2841.
Abbas, N., & Stewart, L. (1999). Clustering bipartite and chordal graphs: Complexity, sequential and parallel algorithms. Discrete Applied Mathematics, 91(1), 1–23.
Balasundaram, B., Butenko, S., & Trukhanov, S. (2005). Novel approaches for analyzing biological networks. Journal of Combinatorial Optimization, 10(1), 23–39.
Berry, N., Ko, T., Moy, T., Smrcka, J., Turnley, J., & Wu, B. (2004) Emergent clique formation in terrorist recruitment. The AAAI-04 workshop on agent organizations: Theory and practice, July 25, 2004, San Jose, California. http://www.cs.uu.nl/~virginia/aotp/papers.htm.
Bourjolly, J. M., Laporte, G., & Pesant, G. (2000). Heuristics for finding \(k\)-clubs in an undirected graph. Computers and Operations Research, 27(6), 559–569.
Bourjolly, J. M., Laporte, G., & Pesant, G. (2002). An exact algorithm for the maximum \(k\)-club problem in an undirected graph. European Journal of Operational Research, 138(1), 21–28.
Buchanan, A., Sung, J., Butenko, S., & Pasiliao, E. L. (2015). An integer programming approach for fault-tolerant connected dominating sets. INFORMS Journal on Computing, 27, 178–188.
Chang, J. M., Yang, J. S., & Peng, S. L. (2014). On the complexity of graph clustering with bounded diameter. In 2014 international computer science and engineering conference (ICSEC) (pp. 18–22). IEEE.
Csardi, G., & Nepusz, T. (2006). The igraph software package for complex network research. InterJournal Complex Systems, 1695(5), 1–9.
De Amorim, S. G., Barthélemy, J. P., & Ribeiro, C. C. (1992). Clustering and clique partitioning: Simulated annealing and tabu search approaches. Journal of Classification, 9(1), 17–41.
Deogun, J. S., Kratsch, D., & Steiner, G. (1997). An approximation algorithm for clustering graphs with dominating diametral path. Information Processing Letters, 61(3), 121–127.
De, T., Pal, A., & Sengupta, I. (2010). Traffic grooming, routing, and wavelength assignment in an optical wdm mesh networks based on clique partitioning. Photonic Network Communications, 20(2), 101–112.
DIMACS (2012) Algorithm implementation challenge: Graph partitioning and graph clustering. The tenth DIMACS implementation challenge. http://dimacs.rutgers.edu/Challenges/.
Dorndorf, U., Jaehn, F., & Pesch, E. (2008). Modelling robust flight-gate scheduling as a clique partitioning problem. Transportation Science, 42(3), 292–301.
Dorndorf, U., & Pesch, E. (1994). Fast clustering algorithms. ORSA Journal on Computing, 6(2), 141–153.
Du, D. Z., & Wan, P. J. (2013). Connected dominating set: Theory and applications. New York: Springer.
European Bioinformatics Institute. (2017). IntAct molecular interaction database. http://www.ebi.ac.uk/intact/. Accessed May, 2017.
Fernandess, Y., & Malkhi, D. (2002). K-clustering in wireless ad hoc networks. In Proceedings of the second ACM international workshop on principles of mobile computing (pp. 31–37). ACM.
Fortunato, S. (2010). Community detection in graphs. Physics Reports, 486(3), 75–174.
Garey, M. R., & Johnson, D. S. (1979). Computers and intractability: A guide to the theory of NP-completeness. New York: WH Freeman.
Gendreau, M., Soriano, P., & Salvail, L. (1993). Solving the maximum clique problem using a tabu search approach. Annals of Operations Research, 41(4), 385–403.
González, R. C., & Tou, J. T. (1974). Pattern recognition principles. Applied mathematics and computation. Reading, MA: Addison-Wesley.
Grötschel, M., & Wakabayashi, Y. (1989). A cutting plane algorithm for a clustering problem. Mathematical Programming, 45(1–3), 59–96.
Grötschel, M., & Wakabayashi, Y. (1990). Facets of the clique partitioning polytope. Mathematical Programming, 47(1–3), 367–387.
GUROBI. (2016). Gurobi optimizer. http://www.gurobi.com.
Kershenbaum, A. (1993). Telecommunications network design algorithms. New York: McGraw-Hill.
Kochenberger, G., Glover, F., Alidaee, B., & Wang, H. (2005). Clustering of microarray data via clique partitioning. Journal of Combinatorial Optimization, 10(1), 77–92.
Krishna, P., Vaidya, N. H., Chatterjee, M., & Pradhan, D. K. (1997). A cluster-based approach for routing in dynamic networks. ACM SIGCOMM Computer Communication Review, 27(2), 49–64.
Levy, E. D., Pereira-Leal, J. B., Chothia, C., & Teichmann, S. A. (2006). 3D complex: A structural classification of protein complexes. PLoS Computational Biology, 2(11), e155.
Li, Y., Lao, L., & Cui, J. H. (2006). Sdc: A distributed clustering protocol for peer-to-peer networks. In International conference on research in networking (pp. 1234–1239). Springer.
Mahdavi Pajouh, F., & Balasundaram, B. (2012). On inclusionwise maximal and maximum cardinality \(k\)-clubs in graphs. Discrete Optimization, 9(2), 84–97.
Mehrotra, A., & Trick, M. A. (1998). Cliques and clustering: A combinatorial approach. Operations Research Letters, 22(1), 1–12.
Mokken, R. J. (1979). Cliques, clubs and clans. Quality and Quantity, 13(2), 161–173.
Newman, M. E. J., & Girvan, M. (2004). Finding and evaluating community structure in networks. Physical Review E, 69(2), 026,113.
Oosten, M., Rutten, J. H. G. C., & Spieksma, F. C. R. (2001). The clique partitioning problem: Facets and patching facets. Networks, 38(4), 209–226.
Parley, A., Hedetniemi, S., & Proskurowski, A. (1981). Partitioning trees: Matching, domination, and maximum diameter. International Journal of Computer and Information Sciences, 10(1), 55–61.
Pasupuleti, S. (2008). Detection of protein complexes in protein interaction networks using \(n\)-clubs. In Proceedings of the 6th European conference on evolutionary computation, machine learning and data mining in bioinformatics. Lecture notes in computer science (Vol. 4973, pp. 153–164). Springer.
Pattillo, J., Youssef, N., & Butenko, S. (2013). On clique relaxation models in network analysis. European Journal of Operational Research, 226(1), 9–18.
Rothenberg, R. B., Potterat, J. J., & Woodhouse, D. E. (1996). Personal risk taking and the spread of disease: Beyond core groups. Journal of Infectious Diseases, 174(Supp. 2), S144–S149.
Sageman, M. (2004). Understanding terrorist networks. Philadelphia, PA: University of Pennsylvania Press.
Sampson, R. J., & Groves, B. W. (1989). Community structure and crime: Testing social-disorganization theory. American Journal of Sociology, 94, 774–802.
Shahinpour, S., & Butenko, S. (2013a). Algorithms for the maximum \(k\)-club problem in graphs. Journal of Combinatorial Optimization, 26(3), 520–554.
Shahinpour, S., & Butenko, S. (2013b). Dinstance-based clique relaxations in networks: \(s\)-cliques and \(s\)-clubs. In B. I. Goldengorin, V. A. Kalyagin, & P. M. Pardalos (Eds.), Models, algorithms, and technologies for network analysis. Springer proceedings in mathematics and statistics (Vol. 59, pp. 149–174). New York: Springer.
Sharan, R., Maron-Katz, A., & Shamir, R. (2003). Click and expander: A system for clustering and visualizing gene expression data. Bioinformatics, 19(14), 1787–1799.
Wu, Z., & Leahy, R. (1993). An optimal graph theoretic approach to data clustering: Theory and its application to image segmentation. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 15(11), 1101–1113.
Acknowledgements
This material is based upon work supported by the AFRL Mathematical Modeling and Optimization Institute. Partial support by AFOSR under Grant FA8651-14-2-0005, and NSF Grant CMMI-1538493 is also gratefully acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yezerska, O., Mahdavi Pajouh, F., Veremyev, A. et al. Exact algorithms for the minimum s-club partitioning problem. Ann Oper Res 276, 267–291 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10479-017-2665-2
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10479-017-2665-2