Abstract
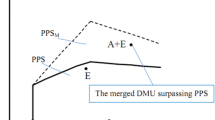
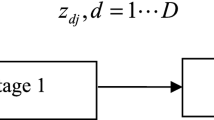
Estimating potential gains from mergers is an important strategic decision-making problem. This paper introduces a new inverse data envelopment analysis (DEA) based on a cost efficiency model for estimating potential gains from mergers. There are restructuring scenarios for firms that want to minimize cost. The existing inverse DEA technical efficiency models are not appropriate for estimating merger gains in these situations. It is also shown that the proposed inverse DEA cost efficiency model can reveal more merger gains than the inverse DEA technical efficiency model. The applicability of the proposed method is shown through an application in Canada’s banking sector to determine the required level of inputs and outputs for a merged bank to achieve target levels of cost and technical efficiencies. The results highlight the potential financial gains to improving both technical and cost efficiencies as efficiency-seeking banks increasingly become large and complex institutions through growth, mergers and acquisitions in a financial environment that is being shaped by reforms and technological innovation.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amin, G. R., & Al-Muharrami, S. (2018). A new inverse DEA model for merger with negative data. IMA Journal of Management Mathematics, 29(2), 137–149.
Amin, G. R., Al-Muharrami, S., & Toloo, M. (2019). A combined goal programming and inverse DEA method for target setting in mergers. Expert Systems with Applications, 115, 412–417.
Amin, G. R., Emrouznejad, A., & Gattoufi, S. (2017a). Modelling generalized firms’ restructuring using inverse DEA. Journal of Productivity Analysis, 48(1), 51–61.
Amin, G. R., Emrouznejad, A., & Gattoufi, S. (2017b). Minor and major consolidations in inverse DEA: Definition and determination. Computers & Industrial Engineering, 103, 193–200.
Amin, G. R., & Oukil, A. (2019). Flexible target setting in mergers using inverse data envelopment analysis. International Journal of Operational Research, 35(3), 301–317.
Bogetoft, P., & Wang, D. (2005). Estimating the potential gains from mergers. Journal of Productivity Analysis, 23, 145–171.
Emrouznejad, A., & Yang, G. (2018). A survey and analysis of the first 40 years of scholarly literature in DEA: 1978–2016. Socio-Economic Planning Sciences, 61, 4–8.
Emrouznejad, A., Yang, G., & Amin, G. R. (2019). A novel inverse DEA model with application to allocate the CO2 emissions quota to different regions in Chinese manufacturing industries. Journal of the Operational Research Society, 70(7), 1079–1090.
Eyni, M., Tohidi, G., & Mehrabeian, S. (2017). Applying inverse DEA and cone constraint to sensitivity analysis of DMUs with undesirable inputs and outputs. Journal of the Operational Research Society, 68(1), 34–40.
Fang, L. (2013). A generalized DEA model for centralized resource allocation. European Journal of Operational Research, 228(2), 405–412.
Gattoufi, S., Amin, G. R., & Emrouznejad, A. (2014). A new inverse DEA method for merging banks. IMA Journal of Management Mathematics, 25, 73–87.
Ghiyasi, M. (2017). Inverse DEA based on cost and revenue efficiency. Computers & Industrial Engineering, 114, 258–263.
Ghiyasi, M. (2018). Efficiency improvement and resource estimation: A tradeoff analysis. International Journal of Productivity and Quality Management, 25(2), 151–169.
Ghiyasi, M. (2019). Novel criterion models in the inverse DEA problem. International Journal of Operational Research, 35(1), 20–36.
Guo, C., Shureshjani, R. A., Foroughi, A. A., & Zhu, J. (2017). Decomposition weights and overall efficiency in two-stage additive network DEA. European Journal of Operational Research, 257(3), 896–906.
Hadi-Vencheh, A., Foroughi, A. A., & Soleimani-damaneh, M. (2008). A DEA model for resource allocation. Economic Modelling, 25(5), 983–993.
Hagendorff, J., & Keasey, K. (2009). Post-merger strategy and performance: Evidence from the US and European banking industries. Accounting and Finance, 49(4), 725–751.
Hankir, Y., Rauch, C., & Umber, M. P. (2011). Bank M&A: A market power story? Journal of Banking & Finance, 35(9), 2341–2354.
Hannan, T., & Pilloff, S. (2009). Acquisition targets and motives in the banking industry. Journal of Money, Credit and Banking, 41(6), 1167–1187.
Huang, C. W. (2018). Assessing the performance of tourism supply chains by using the hybrid network data envelopment analysis model. Tourism Management, 65, 303–316.
Ibn Boamah, M. (2018). Real interest parity: Evidence from trade partnerships. Review of Financial Economics, 36(3), 199–205.
Jahanshahloo, G. R., Soleimani-Damaneh, M., & Ghobadi, S. (2015). Inverse DEA under inter-temporal dependence using multiple-objective programming. European Journal of Operational Research, 240(2), 447–456.
Kaffash, S., & Marra, M. (2017). Data envelopment analysis in financial services: A citations network analysis of banks, insurance companies and money market funds. Annals of Operations Research, 253(1), 307–344.
Kalantary, M., & Saen, R. F. (2019). Assessing sustainability of supply chains: An inverse network dynamic DEA model. Computers & Industrial Engineering, 135, 1224–1238.
Kapelko, M. (2019). Measuring productivity change accounting for adjustment costs: evidence from the food industry in the European Union. Annals of Operations Research, 278(1–2), 215–234.
Knapp, M., Gart, A., & Becher, D. (2005). Post-merger performance of bank holding companies, 1987–1998. The Financial Review, 40(4), 549–574.
LaPlante, A. E., & Paradi, J. C. (2015). Evaluation of bank branch growth potential using data envelopment analysis. Omega, 52, 33–41.
Li, Y., Abtahi, A. R., & Seyedan, M. (2019a). Supply chain performance evaluation using fuzzy network data envelopment analysis: A case study in automotive industry. Annals of Operations Research, 275(2), 461–484.
Li, Y., Li, F., Emrouznejad, A., Liang, L., & Xie, Q. (2019b). Allocating the fixed cost: an approach based on data envelopment analysis and cooperative game. Annals of Operations Research, 274(1–2), 373–394.
Lim, D. J. (2016). Inverse DEA with frontier changes for new product target setting. European Journal of Operational Research, 254(2), 510–516.
Liu, X., Sun, J., Yang, F., & Wu, J. (2018). How ownership structure affects bank deposits and loan efficiencies: an empirical analysis of Chinese commercial banks. Annals of Operations Research. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10479-018-3106-6.
Lozano, S. (2013). Using DEA to find the best partner for a horizontal cooperation. Computers & Industrial Engineering, 66(2), 286–292.
Lozano, S., & Villa, G. (2010). DEA-based pre-merger planning tool. Journal of the Operational Research Society, 61, 1485–1497.
Mayston, D. J. (2017). Data envelopment analysis, endogeneity and the quality frontier for public services. Annals of Operations Research, 250(1), 185–203.
Niepmann, F., & Schmidt-Eisenlohr, T. (2017). International trade, risk and the role of banks. Journal of International Economics, 107, 111–126.
Panetta, F., Schivardi, F., & Shum, M. (2009). Do mergers improve information? Evidence from the loan market. Journal of Money, Credit and Banking, 41, 673–710.
Seccareccia, M. (2012). Financialization and the transformation of commercial banking: understanding the recent Canadian experience before and during the international financial crisis. Journal of Post Keynesian Economics, 35(2), 277–300.
Wang, K., Wei, Y. M., & Huang, Z. (2018). Environmental efficiency and abatement efficiency measurements of China’s thermal power industry: A data envelopment analysis based materials balance approach. European Journal of Operational Research, 269(1), 35–50.
Wegener, M., & Amin, G. R. (2019). Minimizing GHG emissions using inverse DEA with an application in oil and gas. Expert Systems with Applications, 122, 369–375.
Wei, Q., Zhang, J., & Zhang, X. (2000). An inverse DEA model for inputs/outputs estimate. European Journal of Operational Research, 121(1), 151–163.
Xiao, S., Li, Y., Emrouznejad, A., Xie, J., & Liang, L. (2017). Estimation of potential gains from bank mergers: A novel two-stage cost efficiency DEA model. Journal of the Operational Research Society, 68(9), 1045–1055.
Yan, H., Wei, Q., & Hao, G. (2002). DEA models for resource reallocation and production input/output estimation. European Journal of Operational Research, 136(1), 19–31.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Appendix
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Amin, G.R., Ibn Boamah, M. A new inverse DEA cost efficiency model for estimating potential merger gains: a case of Canadian banks. Ann Oper Res 295, 21–36 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10479-020-03667-9
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10479-020-03667-9