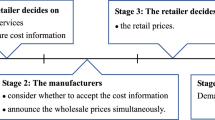
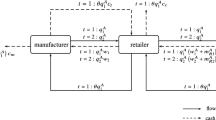
Abstract
This paper develops a series of two-echelon closed-loop supply chain (CLSC) game models in which the retailer acts as the Stackelberg leader of the channel power under the scenarios of information symmetry and information asymmetry. The manufacturer has fairness concern and undertakes corporate social responsibility (CSR) by recycling used products using the reverse channel. We aim to explore the impact of fairness concerns and information asymmetry on the performance of the CLSC. Under the information symmetry, we compare different models with fairness concerns and find that one participant’s unilateral fairness concern can be beneficial to her or his own interests but not to the other participant’s interests. That is, each participant is motivated to adopt his (her) own unilateral fairness concern while avoiding fairness concern of the other. The manufacturer’s CSR level is always negatively related to her fairness concern information. However, the fairness concern has mixed effects on unit wholesale price and retail price in the different models. Bilateral fairness concerns can lead the retailer to raise the retail price, but not always raise the manufacturer’s wholesale price. Under information asymmetry, we investigate the impact of asymmetric information on the performance of the CLSC and find that asymmetric information is not always beneficial to the manufacturer although she owns private information on fairness concern. In each scenario, when both participants are concerned with fairness, we find that under certain conditions the manufacturer’s CSR level is always positively related to the colleting rate, but her utility does not always increase with it. Finally, we evaluate the information value of fairness concerns to the channel participants and find that the information value is always positive for the retailer but may be negative for the manufacturer when the level of fairness concern is higher than a certain threshold.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arya, A., & Mittendorf, B. (2015). Supply chain consequences of subsidies for corporate social responsibility. Production and Operations Management, 24(8), 1346–1357.
Battini, D., Bogataj, M., & Choudhary, A. (2017). Closed loop supply chain (CLSC): Economics, modelling, management and control. International Journal of Production Economics, 183, 319–321.
Chai, J., Qian, Z., Wang, F., & Zhu, J. (2021). Process innovation for green product in a closed loop supply chain with remanufacturing. Annals of Operations Research. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10479-020-03888-y
Chernonog, T., & Avinadav, T. (2019). Pricing and advertising in a supply chain of perishable products under asymmetric information. International Journal of Production Economics, 209, 249–264.
Choi, T., Li, Y., & Xu, L. (2013). Channel leadership, performance and coordination in closed loop supply chains. International Journal of Production Economics, 146(1), 371–380.
Chuang, C., Wang, C. X., & Zhao, Y. (2014). Closed-loop supply chain models for a high-tech product under alternative reverse channel and collection cost structures. International Journal of Production Economics, 156, 108–123.
Cui, T. H., Raju, J. S., & Zhang, Z. J. (2007). Fairness and Channel Coordination. Management Science, 53(8), 1303–1314.
Dahlsrud, A. (2008). How corporate social responsibility is defined: An analysis of 37 definitions. Corporate Social Responsibility and Environmental Management, 15, 1–13.
Darbari, J. D., Kannan, D., Agarwal, V., & Jha, P. C. (2019). Fuzzy criteria programming approach for optimising the TBL performance of closed loop supply chain network design problem. Annals of Operations Research, 273, 693–738.
Dekker, R., Fleischmann, M., Inderfurth, K., & Van Wassenhove, L. N. (Eds.). (2004). Reverse logistics: Quantitative models for closed-loop supply chains. Springer.
Feng, Q., Lai, G., & Lu, L. X. (2015). Dynamic bargaining in a supply chain with asymmetric demand information. Management Science, 61(2), 301–315.
Forti, V., Baldé, C.P., Kuehr, R. and Bel, G., 2020. The global E-waste monitor 2020: Quantities, flows and the circular economy potential. United Nations University, International Telecommunication Union, and International Solid Waste Association. https://www.itu.int/en/ITU-D/Environment/Documents/Toolbox/GEM_2020_def.pdf.
Gao, J., Han, H., Hou, L., & Wang, H. (2016). Pricing and effort decisions in a closed-loop supply chain under different channel power structures. Journal of Cleaner Production, 112, 2043–2057.
Genc, T. S., & De Giovanni, P. (2018). Optimal return and rebate mechanism in a closed-loop supply chain game. European Journal of Operational Research, 269(2), 661–681.
Genc, T. S., & De Giovanni, P. (2020). Closed-loop supply chain games with innovation-led lean programs and sustainability. International Journal of Production Economics, 219, 440–456.
Govindan, K., & Soleimani, H. (2017). A review of reverse logistics and closed-loop supply chains: a Journal of Cleaner Production focus. Journal of Cleaner Production, 142, 371–384.
Han, X., Feng, B., & Pu, X. (2015). Modelling decision behaviours in pricing game of closed-loop supply chains. Journal of the Operational Research Society, 66(6), 1052–1060.
He, P., He, Y., & Xu, H. (2019). Channel structure and pricing in a dual-channel closed-loop supply chain with government subsidy. International Journal of Production Economics, 213, 108–123.
He, Q., Wang, N., Yang, Z., He, Z., & Jiang, B. (2019). Competitive collection under channel inconvenience in closed-loop supply chain. European Journal of Operational Research, 275(1), 155–166.
Hsueh, C. (2014). Improving corporate social responsibility in a supply chain through a new revenue sharing contract. International Journal of Production Economics, 151, 214–222.
Inderfurth, K., Sadrieh, A., & Voigt, G. (2013). The impact of information sharing on supply chain performance under aymmetric information. Production and Operations Management, 22(2), 410–425.
Jena, S. K., & Sarmah, S. P. (2014). Price competition and cooperation in a duopoly closed-loop supply chain. International Journal of Production Economics, 156, 346–360.
Katok, E., & Pavlov, V. (2013). Fairness in supply chain contracts: A laboratory study. Journal of Operations Management, 31(3), 129–137.
Kuiti, M. R., Ghosh, D., Basu, P., & Bisi, A. (2020). Do cap-and-trade policies drive environmental and social goals in supply chains: Strategic decisions, collaboration, and contract choices. International Journal of Production Economics, 223, 107537.
Lamata, M. T., Liern, V., & Pérez-Gladish, B. (2018). Doing good by doing well: A MCDM framework for evaluating corporate social responsibility attractiveness. Annals of Operations Research, 267(1–2), 249–266.
Lexmark, 2020. Lexmark 2020 Corporate Social Responsibility Report. https://csr.lexmark.com/pdfs/Lexmark -2020-CSR-report.pdf.
Liu, M., Zhao, Y., Huang, R., & Perera, S. (2021). Vertical value-added cost information sharing in a supply chain. Annals of Operations Research. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10479-021-04021-3
Liu, W., Shen, X., Wang, D., & Zhu, D. (2020). Service quality guarantee design: Obedience behavior, demand updating and information asymmetry. Annals of Operations Research. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10479-020-03623-7
Liu, W., Wang, S., Zhu, D. L., Wang, D., & Shen, X. (2018). Order allocation of logistics service supply chain with fairness concern and demand updating: Model analysis and empirical examination. Annals of Operations Research, 268(1–2), 177–213.
Ma, P., Li, K. W., & Wang, Z. (2017). Pricing decisions in closed-loop supply chains with marketing effort and fairness concerns. International Journal of Production Research, 55(22), 6710–6731.
Ma, P., Shang, J., & Wang, H. (2017). Enhancing corporate social responsibility: Contract design under information asymmetry. Omega, 67, 19–30.
Ma, Z., Zhang, N., Dai, Y., & Hu, S. (2016). Managing channel profits of different cooperative models in closed-loop supply chains. Omega, 59, 251–262.
Mobini, Z., Van den Heuvel, W., & Wagelmans, A. (2019). Designing multi-period supply contracts in a two-echelon supply chain with asymmetric information. European Journal of Operational Research, 277(2), 542–560.
Modak, N. M., Kazemi, N., & Cárdenas-Barrón, L. E. (2019). Investigating structure of a two-echelon closed-loop supply chain using social work donation as a Corporate Social Responsibility practice. International Journal of Production Economics, 207, 19–33.
Modak, N. M., & Kelle, P. (2019). Managing a dual-channel supply chain under price and delivery-time dependent stochastic demand. European Journal of Operational Research, 272(1), 147–161.
Modak, N. M., Modak, N., Panda, S., & Sana, S. S. (2018). Analyzing structure of two-echelon closed-loop supply chain for pricing, quality and recycling management. Journal of Cleaner Production, 171, 512–528.
Nikoofal, M. E., & Gümüş, M. (2019). Supply diagnostic incentives under endogenous information asymmetry. Production and Operations Management, 28(3), 588–609.
Pal, B., Cárdenas-Barrón, L. E., & Chaudhuri, K. S. (2021). Price, delivery time, and retail service sensitive dual-channel supply chain. Scientia Iranica E, 28(3), 1765–1779.
Panda, S., Modak, N. M., Basu, M., & Goyal, S. K. (2015). Channel coordination and profit distribution in a social responsible three-layer supply chain. International Journal of Production Economics, 168, 224–233.
Panda, S., Modak, N. M., & Cárdenas-Barrón, L. E. (2017). Coordinating a socially responsible closed-loop supply chain with product recycling. International Journal of Production Economics, 188, 11–21.
Panda, S., Modak, N.M., Cárdenas-Barrón, L.E., 2020. Does extended warranty depict competitive advantage to a retailer in a retail-e-tail channel supply chain. Computers & Industrial Engineering, 149, 106770.
Panda, S., & Modak, N. M. (2016). Exploring the effects of social responsibility on coordination and profit division in a supply chain. Journal of Cleaner Production, 139, 25–40.
Qin, Y., Wei, G., & Dong, J. (2019). The signaling game model under asymmetric fairness-concern information. Cluster Computing, 22(S3), 5547–5562.
Reverte, C., Gómez-Melero, E., & Cegarra-Navarro, J. G. (2016). The influence of corporate social responsibility practices on organizational performance: evidence from Eco-Responsible Spanish firms. Journal of Cleaner Production, 112, 2870–2884.
Savaskan, R. C., Bhattacharya, S., & Van Wassenhove, L. N. (2004). Closed-Loop supply chain models with product remanufacturing. Management Science, 50(2), 239–252.
Servaes, H., & Tamayo, A. (2013). The impact of corporate social responsibility on firm value: the role of customer awareness. Management Science, 59(5), 1045–1061.
Soleimani, H., Govindan, K., Saghafi, H., & Jafari, H. (2017). Fuzzy multi-objective sustainable and green closed-loop supply chain network design. Computers and Industrial Engineering, 109, 191–203.
Souza, G. C. (2013). Closed-loop supply chains: a critical review, and future research. Decision Sciences, 44(1), 7–38.
Stindt, D., & Sahamie, R. (2014). Review of research on closed loop supply chain management in the process industry. Flexible Services and Manufacturing Journal, 26, 268–293.
Wang, X., Guo, H., Yan, R., & Wang, X. (2018). Achieving optimal performance of supply chain under cost information asymmetry. Applied Mathematical Modelling, 53, 523–539.
Wu, X., & Niederhoff, J. A. (2014). Fairness in Selling to the Newsvendor. Production and Operations Management, 23(11), 2002–2022.
Yang, J., Xie, J., Deng, X., & Xiong, H. (2013). Cooperative advertising in a distribution channel with fairness concerns. European Journal of Operational Research, 227(2), 401–407.
Yang, R., & Ma, L. (2017). Two-part tariff contracting with competing unreliable suppliers in a supply chain under asymmetric information. Annals of Operations Research, 257(1–2), 559–585.
Zhang, L., Zhou, H., Liu, Y., & Lu, R. (2019). Optimal environmental quality and price with consumer environmental awareness and retailer’s fairness concerns in supply chain. Journal of Cleaner Production, 213, 1063–1079.
Zheng, X., Liu, Z., Li, K. W., Huang, J., & Chen, J. (2019). Cooperative game approaches to coordinating a three-echelon closed-loop supply chain with fairness concerns. International Journal of Production Economics, 212, 92–110.
Zhou, J., Zhao, R., & Wang, W. (2019). Pricing decision of a manufacturer in a dual-channel supply chain with asymmetric information. European Journal of Operational Research, 278(3), 809–820.
Zhuo, W., Yang, H., Cárdenas-Barrón, L. E., & Wan, H. (2021). Loss-averse supply chain decisions with a capital constrained retailer. Journal of Industrial and Management Optimization, 17(2), 711–732.
Acknowledgements
The authors thank the editor and anonymous referees for their constructive comments and encouragement that have helped improve our paper greatly. The work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China under Grants (71971113).
Funding
National Natural Science Foundation of China, 71971113, Kebing Chen.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, Q., Chen, K., Wang, S. et al. Optimal decisions in a closed-loop supply chain: fairness concerns, corporate social responsibility and information value. Ann Oper Res 309, 277–304 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10479-021-04456-8
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10479-021-04456-8