Abstract
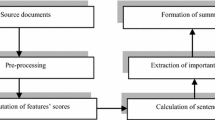
Multi-document summarization is becoming an important issue in the Information Retrieval community. It aims to distill the most important information from a set of documents to generate a compressed summary. Given a set of documents as input, most of existing multi-document summarization approaches utilize different sentence selection techniques to extract a set of sentences from the document set as the summary. The submodularity hidden in the term coverage and the textual-unit similarity motivates us to incorporate this property into our solution to multi-document summarization tasks. In this paper, we propose a new principled and versatile framework for different multi-document summarization tasks using submodular functions (Nemhauser et al. in Math. Prog. 14(1):265–294, 1978) based on the term coverage and the textual-unit similarity which can be efficiently optimized through the improved greedy algorithm. We show that four known summarization tasks, including generic, query-focused, update, and comparative summarization, can be modeled as different variations derived from the proposed framework. Experiments on benchmark summarization data sets (e.g., DUC04-06, TAC08, TDT2 corpora) are conducted to demonstrate the efficacy and effectiveness of our proposed framework for the general multi-document summarization tasks.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chen CM, Liu CY (2009) Personalized e-news monitoring agent system for tracking user-interested Chinese news events. Appl Intell 30(2):121–141
Dang HT (2007) Overview of DUC 2007. In: Document understanding conference, pp 1–10
Dang HT, Owczarzak K (2008) Overview of the TAC 2008 update summarization task. In: Proceedings of text analysis conference
Daumé H, Marcu D (2006) Bayesian query-focused summarization. In: Annual meeting—Association for Computational Linguistics, vol 44, p 305
Dimililer N, Varoğlu E, Altınçay H (2009) Classifier subset selection for biomedical named entity recognition. Appl Intell 31(3):267–282
Erkan G, Radev DR (2004) Lexpagerank: Prestige in multi-document text summarization. In: Proceedings of EMNLP, vol 4
Gérard C et al (1984) Submodular set functions, matroids and the greedy algorithm: tight worst-case bounds and some generalizations of the Rado-Edmonds theorem. Discrete Appl Math 7(3):251–274
Goldstein J, Mittal V, Carbonell J, Kantrowitz M (2000) Multi-document summarization by sentence extraction. In: NAACL-ANLP 2000 workshop on automatic summarization. Association for Computational Linguistics, Stroudsburg, pp 40–48
Haghighi A, Vanderwende L (2009) Exploring content models for multi-document summarization. In: Proceedings of human language technologies: The 2009 annual conference of the North American Chapter of the Association for Computational Linguistics on ZZZ. Association for Computational Linguistics, Stroudsburg, pp 362–370
Jurafsky D, Martin JH, Kehler A, Vander Linden K, Ward N (2000) Speech and language processing. Prentice Hall, New York
Khuller S, Moss A, Naor JS (1999) The budgeted maximum coverage problem. Inf Process Lett 70(1):39–45
Leskovec J, Krause A, Guestrin C, Faloutsos C, VanBriesen J, Glance N (2007) Cost-effective outbreak detection in networks. In: Proceedings of the 13th ACM SIGKDD international conference on knowledge discovery and data mining. ACM, New York, p 429
Li J, Li L, Li T (2011) MSSF: A multi-document summarization framework based on submodularity. In: Proceedings of SIGIR’11
Lin CY (2004) Rouge: A package for automatic evaluation of summaries. In: Proceedings of the workshop on text summarization branches out (WAS 2004), pp 25–26
Lin H, Bilmes J (2010) Multi-document summarization via budgeted maximization of submodular functions. In: NAACL/HLT
Mani I (2001) Automatic summarization. Comput Linguist 28(2)
Minoux M (1978) Accelerated greedy algorithms for maximizing submodular set functions. Optim Tech 234–243
Nastase V (2008) Topic-driven multi-document summarization with encyclopedic knowledge and spreading activation. In: Proceedings of the conference on empirical methods in natural language processing. Association for Computational Linguistics, Stroudsburg, pp 763–772
Nemhauser GL, Wolsey LA (1981) Maximizing submodular set functions: formulations and analysis of algorithms. Stud Graphs Discrete Program 11:279–301
Nemhauser GL, Wolsey LA, Fisher ML (1978) An analysis of approximations for maximizing submodular set functions. Math Program 14(1):265–294
Radev DR, Jing H, Sty M, Tam D (2004) Centroid-based summarization of multiple documents. Inf Process Manag 40(6):919–938
Saggion H, Bontcheva K, Cunningham H (2003) Robust generic and query-based summarisation. In: Proceedings of the European chapter of computational linguistics (EACL). Research notes and demos
Steinberger J, Jezek K (2004) Using latent semantic analysis in text summarization and summary evaluation. In: Proc. ISIM04, pp 93–100
Tang J, Yao L, Chen D (2009) Multi-topic based query-oriented summarization. In: Proceedings of SDM
Wan X, Yang J, Xiao J (2007) Manifold-ranking based topic-focused multi-document summarization. In: Proceedings of IJCAI, pp 2903–2908
Wan X, Yang J, Xiao J (2007) Towards an iterative reinforcement approach for simultaneous document summarization and keyword extraction. In: Annual meeting—Association for Computational Linguistics, vol 45, p 552
Wang D, Li T, Zhu S, Ding C (2008) Multi-document summarization via sentence-level semantic analysis and symmetric matrix factorization. In: Proceedings of the 31st annual international ACM SIGIR conference on Research and development in information retrieval. ACM, New York, pp 307–314
Wang D, Zhu S, Li T, Gong Y (2009) Comparative document summarization via discriminative sentence selection. In: Proceeding of the 18th ACM conference on information and knowledge management. ACM, New York, pp 1963–1966
Wei F, Li W, Lu Q, He Y (2008) Query-sensitive mutual reinforcement chain and its application in query-oriented multi-document summarization. In: Proceedings of the 31st annual international ACM SIGIR conference on research and development in information retrieval. ACM, New York, pp 283–290
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, J., Li, L. & Li, T. Multi-document summarization via submodularity. Appl Intell 37, 420–430 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10489-012-0336-1
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10489-012-0336-1