Abstract
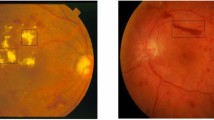
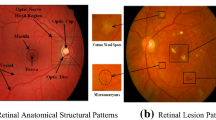
Many health-related problems arise with aging. One of the diseases that is prevalent among the elderly is the loss of sight. Various eye diseases, namely age-related macular degeneration (AMD), diabetic retinopathy (DR), and glaucoma are the prime causes of vision loss as we grow old. Nevertheless, early detection of such eye diseases can impede the progression of this problem. Therefore, the elderly are encouraged to attend regular eye checkups for early detection of eye diseases. However, it is time-consuming and laborious to conduct a mass eye screening session frequently. Hence, we proposed a novel approach to develop an automated retinal health screening system in this work. This paper discusses a retinal screening system to automatically differentiate normal image from abnormal (AMD, DR, and glaucoma) fundus images. The fundus images are subjected to the pyramid histogram of oriented gradients (PHOG) and speeded up robust features (SURF) techniques. Then, the extracted data are subjected to adaptive synthetic sampling to balance the number of data in the two classes (normal and abnormal). Subsequently, we employed the canonical correlation analysis approach to fuse the highly-correlated features extracted from the two (PHOG and SURF) descriptors. We have achieved 96.21% accuracy, 95.00% sensitivity, and 97.42% specificity with ten-fold cross-validation strategy using k-nearest neighbor (kNN) classifier. This novel algorithm has high potential in the diagnosis of normal eyes during the mass eye screening session or in polyclinics quickly and reliably. Hence, the patients having abnormal eyes can be sent to the main hospitals which will reduce the workload for the ophthalmologists.

Proposed system



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abràmoff MD, Reinhardt JM, Russell SR, Folk JC, Mahajan VB, Niemeijer M, Quellec G (2010) Automated early detection of diabetic retinopathy. Ophthalmology 117(6):1147–1154
Abràmoff MD, Suttorp-Schulten MSA (2005) Web-based screening for diabetic retinopathy in a primary care population. The EyeCheck project Telemedicine and e-Health 11(6):668–674
Acharya UR, Chua KC, Ng EYK, Yu W, Chee C (2008) Application of higher order spectra identification of diabetes retinopathy stages. J Med Syst 32(6):481–488
Acharya UR, Ng EYK, Suri JS (2008) Image modeling of the human eye, Artech House
Acharya UR, Lim CM, Ng EYK, Chee C, Tamura T (2009) Computer-based detection of diabetes retinopathy stages using digital fundus images. In: Proceedings of the institution of mechanical engineers, part H: journal of engineering in medicine, vol 223, pp 545–553
Acharya UR, Dua S, Du X, Sree VS, Chua KC (2011) Automated diagnosis of glaucoma using texture and higher order spectra features. IEEE Transactions on Information Technology in biomedicine: A Publication of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society 15(3):449–455
Acharya UR, Ng EYK, Tan JH, Sree SV, Ng KH (2012) An integrated index for the identification of diabetic retinopathy stages using texture parameters. J Med Syst 36(3):2011–2020
Acharya UR, Ng EYK, Lim WJE, Noronha KP, Lim CM, Nayak KP, Bhandary SV (2015) Decision support system for the glaucoma using Gabor transformation. Biomed Signal Process Control 15:18–26
Acharya UR, Mookiah MRK, Koh JEW, Tan JH, Bhandary SV, Rao AK, Fujita H, Hagiwara Y, Chua KC (2016) Automated screening system for retinal health using bi-dimensional empirical mode decomposition and integrated index. Comput Biol Med 75:54–62
Acharya UR, Mookiah MRK, Koh JEW, Tan JH, Noronha K, Bhandary SV, Rao AK, Hagiwara Y, Chua KC, Laude A (2016) Novel risk index for the identification of age-related macular degeneration using radon transform and DWT features. Comput Biol Med 73:131–140
Acharya UR, Bhat S, Koh JEW, Bhandary SV, Adeli H (2017) A novel algorithm to detect glaucoma risk using texton and local configuration pattern features extracted from fundus images. Comput Biol Med 88:72–83
Acharya UR, Hagiwara Y, Koh JEW, Tan JH, Bhandary SV, Rao AK, Raghavendra U (2017) Automated screening method for dry and wet age-related macular degeneration (ARMD) using pyramid of histogram of oriented gradients (PHOG) and nonlinear features. J Comput Sci 20:41–51
Acharya UR, Mookiah MRK, Koh JEW, Tan JH, Bhandary SV, Rao AK, Hagiwara Y, Chua KC, Laude A (2017) Automated diabetic macular edema (DME) grading system using DWT, DCT features and maculopathy index. Comput Biol Med 84:59–68
Agurto C, Murray V, Barriga E, Murillo S, Pattichis M, Davis H, Russell S, Abràmoff M, Soliz P (2010) Multiscale AM-FM methods for diabetic retinopathy lesion detection. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 29(2):502–512
Agurto C, Barriga ES, Murray V, Nemeth S, Crammer R, Bauman W, Zamora G, Pattichis MS, Soliz P (2011) Automatic detection of diabetic retinopathy and age-related macular degeneration in digital fundus images. Investig Ophthalmol Vis Sci 52(8):5862–5871
Antal B, Hajdu A (2012) An ensemble-based system for microaneurysm detection and diabetic retinopathy grading. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng 59(6):1720–1726
Bay H, Ess A, Tuytelaars T, Gool LV (2008) SURF Speeded up robust features. Comput Vis Image Underst 110(3):346–359
Bock R, Meier J, Nyul LG, Hornegger J, Michelson G (2010) Glaucoma risk index: Automated glaucoma detection from color fundus images. Med Image Anal 14:471–481
Bosch A, Zisserman A, Munoz X (2007) Representing shape with a spatial pyramid kernel. In: Proceedings of the 6th ACM international conference on image and video retrieval, pp 410–408
Boyd K, McKinney JK (2017) What is glaucoma? American Academy of Ophthalmology. https://www.aao.org/eye-health/diseases/what-is-glaucoma. (last accessed 24 May 2017)
Cover TM, Hart PE (1967) Nearest neighbor pattern classification. IEEE Trans Inf Theory 13(1):21–27
Dua S, Acharya UR, Chowriappa P, Sree SV (2012) Wavelet based energy features for glaucomatous image classification. IEEE Trans Inf Technol Biomed 16(1):80–87
Duda RO, Hart PE, Stork DG (2001) Pattern classification, 2nd edn. Wiley, New York
Faust O, Acharya UR, Ng EYK, Ng KH, Suri JS (2012) Algorithms for the automated detection of diabetic retinopathy using digital fundus images: a review. J Med Syst 36(1):145–157
Fraser CE, D’Amico DJ, Nathan DM, Trobe J, Mulder JE (2017) Diabetic retinopathy: Classification and clinical features. UpToDate. http://www.uptoyear.com/contents/diabetic-retinopathy-classification-and-clinical-features. (last accessed 12 May 2017)
Ganesan K, Martis RJ, Acharya UR, Chua KC, Lim CM, Ng EYK, Laude A (2014) Computer-aided diabetic retinopathy detection using trace transform on digital fundus images. Biomedical and Biological Engineer 52:663–672
Garcia V, Sánchez JS, Mollineda RA (2012) On the effectiveness of preprocessing methods when dealing with different levels of class imbalance. Knowl-Based Syst 25(1):13–21
Gardner GG, Keating D, Williamson TH, Elliott AT (1996) Automatic detection of diabetic retinopathy using an artificial neural network: a screening tool. Br J Ophthalmol 840:940–944
Group ETDRSR (1991) Grading diabetic retinopathy from stereoscopic color fundus photographs: An extension of the modified Airlie house classification. Ophthalmology 98(10):786–806
Haddrill M, Slonim C All about vision What is age-related macular degeneration? http://www.allaboutvision.com/conditions/amd.htm. (last accessed 24 2017)
He H, Bai Y, Garcia E A, Li S (2008) ADASYN: adaptive synthetic sampling approach for imbalanced learning. In: 2008 IEEE International Joint Conference on Neural Networks (IEEE World Congress on Computational Intelligence), Hong Kong, 2008, pp. 1322–1328. http://doi.org/10.1109/IJCNN.2008.4633969
Hijazi MHA, Coenen F, Zheng Y (2012) Data mining techniques for the screening of age-related macular degeneration. Knowl-Based Syst 29:83–92
Hijazi MHA, Coenen F, Zheng Y (2014) Data mining for AMD screening: A classification based approach. Int J Simul Syst Sci Technol 15(2):57–69
Kennedy J, Eberhart R (1995) Particle swarm optimization. In: Proceedings of the IEEE international conference on neural networks, pp 1942–1945
Kennedy J, Eberhart R, Shi Y (2001) Swarm intelligence. Kaufmann Publishers Evolutionary Computation Series, San Francisco, Calif, USA Morgan
Koh JEW, Acharya UR, Hagiwara Y, Raghavendra U, Tan JH, Sree SV, Bhandary SV, Rao A, Sivaprasad S, Chua KC, Laude A, Tong L (2017) Diagnosis of retinal health in digital fundus images using continuous wavelet transform (CWT) and entropies. Comput Biol Med 84:89–97
Kolar R, Jan J (2008) Detection of glaucomatous eye via color fundus images using fractal dimensions. Radio Eng 17(3):109–114
Köse C, Şevik U, Gençalioğlu O (2008) Automatic segmentation of age-related macular degeneration in retinal fundus images. Comput Biol Med 38(5):611–619
Köse C, Şevik U, Gençalioğlu O, İkibaş C, Kayikiçioğlu T (2010) A statistical segmentation method for measuring age-related macular degeneration in retinal fundus images. J Med Syst 34(1):1–13
Lim TH, Laude A (2007) Age-related macular degeneration – An Asian perspective. In: Proceedings of the eye institute 3 rd, research day, vol 36, pp S15–S21
Maheshwari S, Pachori RB, Acharya UR (2017) Automated diagnosis of glaucoma using empirical wavelet transform and correntropy features extracted from fundus images. IEEE Journal of Biomedical and Health Informatics 21(3):803–813
Maheshwari S, Pachori RB, Kanhangad V, Bhandary SV, Acharya UR (2017) Iterative variational mode decomposition based automated detection of glaucoma using fundus images computers in biology and medicine. http://doi.org/10.1016/j.compbiomed.2017.06.017
Mookiah MRK, Acharya UR, Lim CM, Petznick A, Suri JS (2012) Data mining technique for automated diagnosis of glaucoma using higher order spectra and wavelet energy features. Knowl-Based Syst 33:73–82
Mookiah MRK, Acharya UR, Martis RJ, Chua KC, Lim CM, Ng EYK, Laude A (2013) Evolutionary algorithm based classifier parameter tuning for automatic diabetic retinopathy grading. A hybrid feature extraction approach, Knowledge-Based Systems 39:9–22
Mookiah MRK, Acharya UR, Koh JEW, Chandran V, Chua KC, Tan JH, Lim CM, Ng EYK, Noronha K, Tong L, Laude A (2014) Automated diagnosis of age-related macular degeneration using greyscale features from digital fundus images. Comput Biol Med 53:55–64
Mookiah MRK, Acharya UR, Koh JEW, Chua KC, Tan JH, Chandran V, Lim CM, Noronha K, Laude A, Tong L (2014) Decision support system for age-related macular degeneration using discrete wavelet transform. Med Biol Eng Comput 52(9):781– 796
Mookiah MRK, Acharya UR, Fujita H, Koh JEW, Tan JH, Chua KC, Bhandary SV, Noronha K, Laude A, Tong L (2015) Automated detection of age-related macular degeneration using empirical mode decomposition. Knowl-Based Syst 89:654–668
Mookiah MRK, Acharya UR, Fujita H, Koh JEW, Tan JH, Noronha K, Bhandary SV, Chua KC, Lim CM, Laude A, Tong L (2015) Local configuration pattern features for age-related macular degeneration characterization and classification. Comput Biol Med 63:208–218
Nayak J, Bhat PS, Acharya UR, Lim CM, Kagathi M (2007) Automated identification of diabetic retinopathy stages using digital fundus images. J Med Syst 32(2):107–115
Nayak J, Acharya UR, Bhat PS, Shetty N, Min TC (2009) Automated diagnosis of glaucoma using fundus images. J Med Syst 33(5):337–346
Niemeijer M, et al (2010) Retinopathy Online Challenge: Automatic detection of microaneurysms in digital color fundus photographs. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 29(1):185–195
Noronha K, Acharya UR, Nayak KP, Kamath S, Bhandary SV (2013) Decision support system for diabetic retinopathy using discrete wavelet transform. J Eng Med 227(3):251–261
Noronha KP, Acharya UR, Nayak KP, Martis RJ, Bhandary SV (2014) Automated classification of glaucoma stages using higher order cumulant features. Biomed Signal Process Control 10:174–183
Piramuthu S (2004) Evaluating feature selection methods for learning in data mining applications. Eur J Oper Res 156:483– 494
Pizer SM, Amburn EP, Austin JD, Cromarrtie R, Geselowitz A, Greer T, Romeny B, Zimmerman JB, Zuiderveld K, variations its (1987) Adaptive histogram equalization ter Haar Computer Vision. Graphics Image Process 39(3):355–368
Reza AM (2004) Realization of the contrast limited adaptive histogram equalization (CLAHE) for real-time image enhancement. Journal of VLSI Signal Processing-Systems for Signal, Image, and Video Technology 35:35–44
Ryan SJ, Schachat AP, Wilkinson CP, Hinton DR, Sadda SR, Wiedemann P (2012) Retina, 5 th Edition, Expert Consult Premium Edition: Enhanced online features and print 3-Volume set
Sun QS, Zeng SG, Liu Y, Heng PA, Xia DS (2005) A new method of feature fusion and its application in image recognition. Pattern Recogn 38(12):2437–2448
Tan JH, Acharya UR, Bhandary SV, Chua KC, Sivaprasad S (2017) Segmentation of optic disc, fovea, and retinal vasculature using a single convolutional neural network. J. Comput Sci 20:70–79. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jocs.2017.02.006
Usher D, Dumskyj M, Himaga M, Williamson TH, Nussey S, Boyce J (2004) Automated detection of diabetic retinopathy in digital retinal images: a tool for diabetic retinopathy screening. Diabet Med 21(1):84–90
VISION 2020 The right to sight. https://www.iapb.org/vision-2020 https://www.iapb.org/vision-2020. (last accessed 24 May 2017)
Wang X, Wong BS, Guan TC (2005) Image enhancement for radiography inspection. In: 3rd international conference on experimental mechanics and 3rd conference of the asian committee on experimental mechanics, p 462
WebMD Diabetic retinopathy – topic overview. http://www.webmd.com/diabetes/tc/diabetic-retinopathy-topic-overview#1 (last accessed 11 May 2017)
Wong LY, Acharya UR, Venkatesh YV, Chee C, Lim CM, Ng EYK (2008) Identification of different stages of diabetic retinopathy using retinal optical images. Inf Sci 178:106–121
World Health Organization (2015) Aging and health, http://www.who.int/mediacentre/factsheets/fs404/en/ (last accessed 26 May 2017)
World Health Organization (2016) Global reports on diabetes, http://apps.who.int/iris/bitstream/10665/204871/1/9789241565257_eng.pdf (last accessed 12 May 2017)
World Health Organization Priority eye diseases. http://www.who.int/blindness/causes/priority/en/ (last accessed 24 May 2017)
Zhang Z, Srivastava R, Liu H, Chen X, Duan L, Wong DWK, Kwoh CK, Wong TY, Liu J (2014) A survey on computer aided diagnosis for ocular diseases. BMC Med Inform Decis Mak 14:80. https://doi.org/10.1186/1472-6947-14-80
Zheng Y, Hijazi MHA, Coenen F (2012) Automated disease/ no disease grading of age-related macular degeneration by an image mining approach. Investig Ophthalmol Vis Sci 53(13):8310– 8318
(1989) National health and nutrition examination survey. Fundus photography for health technicians manual
Acknowledgements
Authors would like to thank the Social Innovation Research Fund (Project Title: Automated Eye Screening: A Direct Approach for Referral), Singapore for providing us a grant for this research. We would also like to express our sincere thanks to Manipal University, Manipal, India for providing us the images for this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Koh, J.E.W., Ng, E.Y.K., Bhandary, S.V. et al. Automated detection of retinal health using PHOG and SURF features extracted from fundus images. Appl Intell 48, 1379–1393 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10489-017-1048-3
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10489-017-1048-3