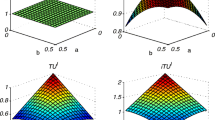
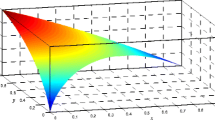
Abstract
Uncertainty measure in Dempster-Shafer (D-S) evidence theory is crucial to assess the quality of information conveyed by belief structures. Most of the previous studies consider this issue from the perspective of viewing the D-S evidence theory as a generalization of probability theory. However, the inconsistency between D-S evidence theory and probability theory may lead to some limitations to existing measures. Deng et al proposed an improved total uncertainty measure which is directly based on D-S evidence theory. In their measure, the belief structures are transformed to belief interval which is constructed by the belief function and plausibility function of a proposition. Inspired by the previous research, a new total uncertainty measure (NTU) is proposed in this paper. The proposed measure is based on the Euclidean distance between the belief interval of the singleton subset and the most uncertain interval. It not only retains the properties and advantages of the previous measure, but also presents a higher sensitivity and greater extent to the change of evidences. Some numerical examples, practical applications and related analyses are used to verify the rationality and sensitivity of the proposed measure.
















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Fortino G, Galzarano S, Gravina R, Li W (2015) A framework for collaborative computing and multi-sensor data fusion in body sensor networks. Inform Fusion 22:50–70
Geng H, Liang Y, Yang F, Xu L, Pan Q (2017) Model-reduced fault detection for multi-rate sensor fusion with unknown inputs. Inform Fusion 33:1–14
Zhang L, Ding L, Wu X, Skibniewski MJ (2017) An improved Dempster-Shafer approach to construction safety risk perception. Knowl-Based Syst 132(sep.15):30–46
Nie R-X, Tian Z-P, Wang X-K, Wang J-Q, Wang T-L (2018) Risk evaluation by fmea of supercritical water gasification system using multi-granular linguistic distribution assessment. Knowl-Based Syst 162:185–201
Wu D, Tang Y (2020) An improved failure mode and effects analysis method based on uncertainty measure in the evidence theory. Qual Reliab Eng Int 36(5):1786–1807
Zhang H, Deng Y (2020) Weighted belief function of sensor data fusion in engine fault diagnosis. Soft Comput 24(3):2329–2339
Song Y, Fu Q, Wang Y-F, Wang X (2019) Divergence-based cross entropy and uncertainty measures of atanassov’s intuitionistic fuzzy sets with their application in decision making. Appl Soft Comput 84:105703
Deng X, Deng Y (2019) D-ahp method with different credibility of information. Soft Comput 23(2):683–691
Xu X, Zhang D, Bai Y, Chang L, Li J (2020) Evidence reasoning rule-based classifier with uncertainty quantification. Inf Sci 516:192–204
Xiao F, Zhang Z, Abawajy J (2019) Workflow scheduling in distributed systems under fuzzy environment. J Intell Fuzzy Syst 37(4):5323–5333
Bo W, Xiao F, Shi Y (2019) Synchronization in kuramoto oscillator networks with sampled-data updating law. IEEE Trans Cybern 50(6):2380–2388
Tang Y, Wu D, Liu Z (2021) A new approach for generation of generalized basic probability assignment in the evidence theory. Pattern Anal Applic 1–17
Behrouz M, Alimohammadi S (2018) Uncertainty analysis of flood control measures including epistemic and aleatory uncertainties: Probability theory and evidence theory. J Hydrol Eng 23(8):04018033
Liu B, Hu Y, Deng Y (2018) New failure mode and effects analysis based on d numbers downscaling method. Int J Comput Commun Control, 13(2)
Deng X, Jiang W (2019) Evaluating green supply chain management practices under fuzzy environment: a novel method based on d number theory. Int J Fuzzy Syst 21(5):1389–1402
Zadeh LA (2011) A note on z-numbers. Inf Sci 181(14):2923–2932
Liu Q, Ye T, Kang B (2019) Derive knowledge of z-number from the perspective of Dempster-Shafer evidence theory. Eng Appl Artif Intell 85:754–764
Seiti H, Hafezalkotob A (2019) Developing the r-topsis methodology for risk-based preventive maintenance planning: A case study in rolling mill company. Comput Indust Eng 128:622–636
Seiti H, Hafezalkotob A, Martínez L (2019) R-numbers, a new risk modeling associated with fuzzy numbers and its application to decision making. Inf Sci 483:206–231
Düntsch I, Gediga G (1998) Uncertainty measures of rough set prediction. Artif Intell 106 (1):109–137
Luo C, Li T, Yi Z, Fujita H (2016) Matrix approach to decision-theoretic rough sets for evolving data. Knowl-Based Syst 99:123–134
Xiao F (2019) A distance measure for intuitionistic fuzzy sets and its application to pattern classification problems. IEEE Trans Syst Man Cybern Syst
Cao Z, Ding W, Wang Y-K, Hussain FK, Al-Jumaily A, Lin C-T (2020) Effects of repetitive ssveps on eeg complexity using multiscale inherent fuzzy entropy. Neurocomputing 389:198–206
Yang J-B, Xu D-L (2013) Evidential reasoning rule for evidence combination. Artif Intell 205:1–29
Fu C, Hou B, Chang W, Feng N, Yang S (2020) Comparison of evidential reasoning algorithm with linear combination in decision making. Int J Fuzzy Syst 22(2):686–711
Dempster AP (2008) Upper and lower probabilities induced by a multivalued mapping. In: Classic works of the Dempster-Shafer theory of belief functions. Springer, pp 57–72
Shafer G (1976) A mathematical theory of evidence, vol 42. Princeton University Press, Princeton
Deng X, Jiang W (2020) On the negation of a dempster–shafer belief structure based on maximum uncertainty allocation. Inf Sci 516:346–352
Xiao F (2020) A new divergence measure for belief functions in d–s evidence theory for multisensor data fusion. Inf Sci 514:462–483
Jing M, Tang Y (2021) A new base basic probability assignment approach for conflict data fusion in the evidence theory. Appl Intell 51(2):1056–1068
Su X, Mahadevan S, Han W, Deng Y (2016) Combining dependent bodies of evidence. Appl Intell 44(3):634–644
Deng X, Qi L, Deng Y, Mahadevan S (2016) An improved method to construct basic probability assignment based on the confusion matrix for classification problem. Inf Sci 340:250–261
Deng X, Jiang W, Wang Z (2019) Zero-sum polymatrix games with link uncertainty: A Dempster-Shafer theory solution. Appl Math Comput 340:101–112
Mo H, Deng Y (2019) Identifying node importance based on evidence theory in complex networks. Physica A: Stat Mechan Appl 529:121538
Shannon CE (2001) A mathematical theory of communication. ACM SIGMOBILE mobile computing and communications review 5(1):3–55
Pal NR, Bezdek JC, Hemasinha R (1992) Uncertainty measures for evidential reasoning i: A review. Int J Approx Reason 7(3-4):165–183
Pal NR, Bezdek JC, Hemasinha R (1993) Uncertainty measures for evidential reasoning II: A new measure of total uncertainty. Int J Approx Reason 8(1):1–16
Abellán J, Bossé É (2020) Critique of recent uncertainty measures developed under the evidence theory and belief intervals. IEEE Trans Syst Man Cybern Syst 50(3):1186–1192
Yager RR (1983) Entropy and specificity in a mathematical theory of evidence. Int J Gen Syst 9(4):249–260
Yager RR (2018) Interval valued entropies for dempster–shafer structures. Knowl-Based Syst 161:390–397
Jiroušek R, Shenoy PP (2018) A new definition of entropy of belief functions in the dempster–shafer theory. Int J Approx Reason 92:49–65
Körner R, Näther W (1995) On the specificity of evidences. Fuzzy Sets Syst 71(2):183–196
Jiang W (2018) A correlation coefficient for belief functions. Int J Approx Reason 103:94–106
Jiroušek R, Shenoy PP (2020) On properties of a new decomposable entropy of Dempster-Shafer belief functions. Int J Approx Reason 119:260–279
Hohle U (1982) Entropy with respect to plausibility measures. In: Proc of 12th IEEE Int Symp on multiple valued logic, Paris 1982
Dubois D, Prade H (1987) Properties of measures of information in evidence and possibility theories. Fuzzy Sets Syst 24(2):161–182
Klir GJ, Wierman MJ (1999) Uncertainty formalizations. In: Uncertainty-based information. Springer, pp 7–41
Klir GJ, Parviz B (1992) A note on the measure of discord. In: Uncertainty in artificial intelligence. Elsevier, pp 138–141
Dubois D, Prade H (1985) A note on measures of specificity for fuzzy sets. Int J General Syst 10(4):279–283
Hartley RVL (1928) Transmission of information 1. Bell Syst Technic J 7(3):535–563
Harmanec D, Klir GJ (1994) Measuring total uncertainty in dempster-shafer theory: A novel approach. Int J Gen Syst 22(4):405–419
Jousselme A-L, Liu C, Grenier D, Bossé É (2006) Measuring ambiguity in the evidence theory. IEEE Trans Syst Man Cybern-Part A Syst Humans 36(5):890–903
Maeda Y, Nguyen HT, Ichihashi H (1993) Maximum entropy algorithms for uncertainty measures. Int J Uncert Fuzziness Knowl-Based Syst 1(01):69–93
Klir GJ, Ramer A (1990) Uncertainty in the dempster-shafer theory: A critical re-examination. Int J Gen Syst 18(2):155–166
Klir GJ, Smith RM (1999) Recent developments in generalized information theory. Int J Fuzzy Syst 1(1):1–13
Pearl J (1990) Reasoning with belief functions: An analysis of compatibility. Int J Approx Reason 4(5-6):363–389
Yi Y, Han D (2016) A new distance-based total uncertainty measure in the theory of belief functions. Knowl-Based Syst 94:114–123
Deng X, Xiao F, Deng Y (2017) An improved distance-based total uncertainty measure in belief function theory. Appl Intell 46(4):898–915
Su Z-G, Denoeux T (2018) Bpec: Belief-peaks evidential clustering. IEEE Trans Fuzzy Syst 27(1):111–123
Su Z-G, Denoeux T, Hao Y-S, Zhao M (2018) Evidential k-nn classification with enhanced performance via optimizing a class of parametric conjunctive t-rules. Knowl-Based Syst 142:7–16
Wu D, Liu Z, Tang Y (2020) A new classification method based on the negation of a basic probability assignment in the evidence theory. Eng Appl Artif Intell 96:103985
Liu Z-G, Pan Q, Dezert J, Mercier G (2017) Hybrid classification system for uncertain data. IEEE Trans Syst Man Cybern 47(10):2783–2790
Yi Y, Han D, Dezert J (2016) A new non-specificity measure in evidence theory based on belief intervals. Chin J Aeronaut 29(3):704–713
Abellán J, Masegosa A (2008) Requirements for total uncertainty measures in dempster–shafer theory of evidence. Int J Gen Syst 37(6):733–747
Han D, Dezert J, Yang Y (2016) Belief interval-based distance measures in the theory of belief functions. IEEE Trans Syst Man Cybern Syst 48(6):833–850
Irpino A, Verde R (2008) Dynamic clustering of interval data using a wasserstein-based distance. Pattern Recogn Lett 29(11):1648–1658
Deng X (2018) Analyzing the monotonicity of belief interval based uncertainty measures in belief function theory. Int J Intell Syst 33(9):1869–1879
Abellan J (2011) Combining nonspecificity measures in dempster–shafer theory of evidence. Int J Gen Syst 40(6):611–622
Abellán J, Masegosa A (2008) Requirements for total uncertainty measures in dempster–shafer theory of evidence. Int J Gen Syst 37(6):733–747
Klir GJ, Wierman MJ (2013) Uncertainty-based information: elements of generalized information theory, volume 15 Physica
Papoulis A, Saunders H (1989) Probability random variables and stochastic processes
Quost B, Denaeux T, Masson M (2005) Pairwise classifier combination in the transferable belief model. In: 2005 7th international conference on information fusion, vol 1. IEEE, pp 8–pp
Walley P (2000) Towards a unified theory of imprecise probability. Int J Approx Reason 24 (2-3):125–148
Augustin Thomas, Hable Robert (2010) On the impact of robust statistics on imprecise probability models: A review. Struct Saf 32(6):358–365
Yu X, Zou P, Li M (2012) Dempster-shafer theory as an applied approach to scenario forecasting based on imprecise probability. In: IEEE 12th international conference on computer and information technology. IEEE, p 2012
Tsallis C (2009) Introduction to nonextensive statistical mechanics: Approaching a complex world. Springer Science & Business Media, New York
Yong D, WenKang S, ZhenFu Z, Qi L (2004) Combining belief functions based on distance of evidence. Decis Support Syst 38(3):489–493
Murphy CK (2000) Combining belief functions when evidence conflicts. Decis Support Syst 29 (1):1–9
Kang B-Y, Li Y, Deng Y, Zhang Y-J, Deng X-Y (2012) Determination of basic probability assignment based on interval numbers and its application. Dianzi Xuebao(Acta Electronica Sinica) 40(6):1092–1096
Smets P (2005) Decision making in the tbm: The necessity of the pignistic transformation. Int J Approx Reason 38(2):133– 147
Duda RO, Hart PE, Stork DG (2012) Pattern classification. Wiley, New York
Masson M-H, Denoeux T (2008) Ecm: An evidential version of the fuzzy c-means algorithm. Pattern Recogn 41(4):1384– 1397
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
The work is partially supported by National Key Research and Development Project of China (Grant No. 2019YFB2102602).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, R., Chen, Z., Li, H. et al. A new distance-based total uncertainty measure in Dempster-Shafer evidence theory. Appl Intell 52, 1209–1237 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10489-021-02378-3
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10489-021-02378-3