Abstract
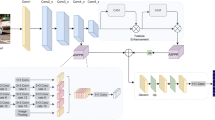
Multi-person pose estimation is a fundamental yet challenging task in computer vision. Although great success has been made in this field due to the rapid development of deep learning, complex situations (e.g., extreme poses, occlusions, overlapped persons, and crowded scenes) are still not well solved. To further mitigate these issues, we propose a novel Content-aware Feature Enhancement Network (CFENet), which consists of three effective modules: Feature Aggregation and Selection Module (FASM), Feature Fusion Module (FFM) and Dense Upsampling Convolution (DUC) module. The FASM includes Feature Aggregation Module (FAM) and Information Selection Module (ISM). The FAM constructs the hierarchical multi-scale feature aggregations in a granular level to capture more accurate fine-grained representations. The ISM makes the aggregated representations more distinguished, which adaptively highlights the discriminative human part representations both in the spatial location and channel context. Then, we perform FFM which effectively fuses high-resolution spatial features and low-resolution semantic features to obtain more reliable context information for well-estimated joints. Finally, we adopt DUC module to generate more precise prediction, which can recover missing joint details that are usually unavailable in common upsampling process. Comprehensive experiments demonstrate that the proposed approach outperforms most of the popular methods and achieves a competitive performance with the state-of-the-art methods over three benchmark datasets: the recent big dataset CrowdPose, the COCO keypoint detection dataset and the MPII Human Pose dataset. Our code will be released upon acceptance.













Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andriluka M, Pishchulin L, Gehler PV, Schiele B (2014) 2d human pose estimation: New benchmark and state of the art analysis. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp 3686–3693
Bodla N, Singh B, Chellappa R, Davis LS (2017) Soft-nms improving object detection with one line of code. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, pp 5562–5570
Buitelaar P, Wood I, Negi S, Arcan M, Mccrae JP, Abele A, Robin C, Andryushechkin V, Sagha H, Schmitt M (2018) Mixedemotions: an open-source toolbox for multi-modal emotion analysis. IEEE Trans Multimed 20(9):2454–2465
Cao Z, Simon T, Wei S, Sheikh Y (2017) Realtime multi-person 2d pose estimation using part affinity fields. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp 1302–1310
Chen L, Papandreou G, Kokkinos I, Murphy KP, Yuille AL (2018a) Deeplab: Semantic image segmentation with deep convolutional nets, atrous convolution, and fully connected crfs. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 40(4):834–848
Chen Y, Shen C, Wei X, Liu L, Yang J (2017) Adversarial posenet: A structure-aware convolutional network for human pose estimation. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, pp 1221–1230
Chen Y, Wang Z, Peng Y, Zhang Z, Yu G, Sun J (2018b) Cascaded pyramid network for multi-person pose estimation. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp 7103–7112
Chou C, Chien J, Chen H (2018) Self adversarial training for human pose estimation. In: Proceedings of the Asia Pacific Signal and Information Processing Association Annual Summit and Conference, pp 17–30
Chu X, Yang W, Ouyang W, Ma C, Yuille AL, Wang X (2017) Multi-context attention for human pose estimation. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp 5669–5678
Dong L, Chen X, Wang R, Zhang Q, Izquierdo E (2018) Adore: an adaptive holons representation framework for human pose estimation. IEEE Trans Circ Syst Video Technol 28(10):2803–2813
Fang H, Xie S, Tai Y, Lu C (2017) Rmpe: Regional multi-person pose estimation. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, pp 2353–2362
Gao S, Cheng M, Zhao K, Zhang X, Yang M, Torr PHS (2019) Res2net: a new multi-scale backbone architecture. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell:1–1
He K, Gkioxari G, Dollar P, Girshick RB (2017) Mask r-cnn. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, pp 2980–2988
He K, Zhang X, Ren S, Sun J (2016) Deep residual learning for image recognition. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp 770–778
Hou Q, Cheng M, Hu X, Borji A, Tu Z, Torr PHS (2017) Deeply supervised salient object detection with short connections. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp 815–828
Hu J, Shen L, Sun G (2018) Squeeze-and-excitation networks. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp 7132–7141
Insafutdinov E, Pishchulin L, Andres B, Andriluka M, Schiele B (2016) Deepercut: a deeper, stronger, and faster multi-person pose estimation model. Eur Conf Comput Vis:34–50
Ke L, Chang M, Qi H, Lyu S (2018) Multi-scale structure-aware network for human pose estimation. Eur Conf Comput Vis:731–746
Kingma DP, Ba J (2014) Adam: A method for stochastic optimization. Computer Science
Kocabas M, Karagoz S, Akbas E (2018) Multiposenet: Fast multi-person pose estimation using pose residual network. Eur Conf Comput Vis:437–453
Li J, Wang C, Zhu H, Mao Y, Fang H, Lu C (2019a) Crowdpose: Efficient crowded scenes pose estimation and a new benchmark. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition
Li W, Wang Z, Yin B, Peng Q, Su J (2019b) Rethinking on multi-stage networks for human pose estimation. arXiv:190100148
Lin T, Dollar P, Girshick RB, He K, Hariharan B, Belongie SJ (2017) Feature pyramid networks for object detection. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp 936–944
Lin T, Maire M, Belongie SJ, Hays J, Perona P, Ramanan D, Dollar P, Zitnick CL (2014) Microsoft coco: Common objects in context. Eur Conf Comput Vis:740–755
Liu S, Li Y, Hua G (2019) Human pose estimation in video via structured space learning and halfway temporal evaluation. IEEE Trans Circ Syst Video Technol:2029–2038
Liu W, Anguelov D, Erhan D, Szegedy C, Reed SE, Fu C, Berg AC (2016) Ssd: Single shot multibox detector. Eur Conf Comput Vis:21–37
Long J, Shelhamer E, Darrell T (2015) Fully convolutional networks for semantic segmentation. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp 3431–3440
Lowe DG (2004) Distinctive image features from scale-invariant keypoints. Int J Comput Vis 60 (2):91–110
Luvizon DC, Tabia H, Picard D (2017) Human pose regression by combining indirect part detection and contextual information. Computers & Graphics
Marcosramiro A, Pizarro D, Marronromera M, Gaticaperez D (2015) Let your body speak: Communicative cue extraction on natural interaction using rgbd data. IEEE Trans Multimed 17(10):1721–1732
Martinezgonzalez A, Villamizar M, Canevet O, Odobez J (2019) Efficient convolutional neural networks for depth-based multi-person pose estimation. IEEE Trans Circ Syst Video Technol:1–1
MS-COCO, 2017 Coco keypoint leaderboard. http://cocodataset.org/
Newell A, Huang Z, Deng J (2017) Associative embedding: End-to-end learning for joint detection and grouping. In: Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, pp 2277–2287
Newell A, Yang K, Deng J (2016) Stacked hourglass networks for human pose estimation. Eur Conf Comput Vis:483–499
Nie X, Feng J, Zhang J, Yan S (2019) Single-stage multi-person pose machines. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, pp 6951–6960
Ning G, Zhang Z, He Z (2018) Knowledge-guided deep fractal neural networks for human pose estimation. IEEE Trans Multimed:1246–1259
Noh H, Hong S, Han B (2015) Learning deconvolution network for semantic segmentation. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, pp 1520–1528
Papandreou G, Zhu T, Kanazawa N, Toshev A, Tompson J, Bregler C, Murphy KP (2017) Towards accurate multi-person pose estimation in the wild. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp 3711–3719
Park J, Woo S, Lee J, Kweon IS (2018) Bam: Bottleneck attention module. arXiv:180706514
Facebook (2017) Pytorch. https://pytorch.org/
Pishchulin L, Insafutdinov E, Tang S, Andres B, Andriluka M, Gehler PV, Schiele B (2016) Deepcut: Joint subset partition and labeling for multi person pose estimation. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp 4929–4937
Ren S, He K, Girshick RB, Sun J (2015) Faster r-cnn: towards real-time object detection with region proposal networks. In: Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, pp 91–99
Ronneberger O, Fischer P, Brox T (2015) U-net: Convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation. Med Image Comput Comput Assist Intervent:234–241
Russakovsky O, Deng J, Su H, Krause J, Satheesh S, Ma S, Huang Z, Karpathy A, Khosla A, Bernstein MS et al (2015) Imagenet large scale visual recognition challenge. Int J Comput Vis 115(3):211–252
Mahshid M, Reza S (2019) A motion-aware convLSTM network for action recognition. Appl Intell:1–7
Su K, Yu D, Xu Z, Geng X, Wang C (2019) Multi-person pose estimation with enhanced channel-wise and spatial information. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp 5674–5682
Sun K, Lan C, Xing J, Zeng W, Liu D, Wang J (2017) Human pose estimation using global and local normalization. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, pp 5600–5608
Sun K, Xiao B, Liu D, Wang J (2019) Deep high-resolution representation learning for human pose estimation. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp 5693–5703
Sun X, Xiao B, Wei F, Liang S, Wei Y (2018) Integral human pose regression. Eur Conf Comput Vis:536–553
Szegedy C, Liu W, Jia Y, Sermanet P, Reed SE, Anguelov D, Erhan D, Vanhoucke V, Rabinovich A (2015) Going deeper with convolutions. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp 1–9
Tang W, Yu P, Wu Y (2018a) Deeply learned compositional models for human pose estimation. Eur Conf Comput Vis:197–214
Tang Z, Peng X, Geng S, Wu L, Zhang S, Metaxas DN (2018b) Quantized densely connected u-nets for efficient landmark localization. Eur Conf Comput Vis:348–364
Wang P, Chen P, Yuan Y, Liu D, Huang Z, Hou X, Cottrell GW (2018) Understanding convolution for semantic segmentation. Workshop Appl Comput Vis:1451–1460
Wei S, Ramakrishna V, Kanade T, Sheikh Y (2016) Convolutional pose machines. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp 4724–4732
Xiao B, Wu H, Wei Y (2018) Simple baselines for human pose estimation and tracking. Eur Conf Comput Vis:472–487
Xiao Y, Lu H, Sun C (2015) Pose estimation based on pose cluster and candidates recombination. IEEE Trans Cir Syst Video Technol 25(6):935–943
Yang B, Ma AJ, Yuen PC (2019) Body parts synthesis for cross-quality pose estimation. IEEE Trans Circ Syst Video Technol 29(2):461–474
Yang W, Li S, Ouyang W, Li H, Wang X (2017) Learning feature pyramids for human pose estimation. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, pp 1290–1299
Zeiler MD, Fergus R (2014) Visualizing and understanding convolutional networks. Eur Conf Comput Vis:818–833
Zhang X, Ding M, Fan G (2017) Video-based human walking estimation using joint gait and pose manifolds. IEEE Trans Circ Syst Video Technol 27(7):1540–1554
Zhang Z, Zhang X, Peng C, Xue X, Sun J (2018) Exfuse: Enhancing feature fusion for semantic segmentation. Eur Conf Comput Vis:273–288
Dinh D, Lim M, Thang N, Lee S, Kim T (2014) Real-time 3D human pose recovery from a single depth image using principal direction analysis. Appl Intell 41(2):473–486
Wang J, Chen K, Xu R, Liu Z, Joy C, Lin D (2019) CARAFE: Content-Aware ReAssembly of FEatures. Int Conf Comput Vis:3007–2016
Lin X, Zou Q, Xu X, Huang Y, Tian Y (2020) Motion-Aware Feature enhancement network for video prediction. IEEE Trans Circ Syst Video Technol PP(99):1–1
Acknowledgements
This research is supported by National Nature Science Foundation of China under Grants (No.61473031), the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (2019JBM019).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xu, X., Zou, Q. & Lin, X. CFENet: Content-aware feature enhancement network for multi-person pose estimation. Appl Intell 52, 215–236 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10489-021-02383-6
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10489-021-02383-6