Abstract
In this paper, we consider a networked multi-robot system operating in an obstacle populated planar workspace under a single leader-multiple followers architecture. We propose a distributed reconfiguration strategy of the set of connectivity and formation specifications that assures convergence to the desired point, while guaranteeing global connectivity. In particular, we construct a low-level distributed navigation functions based controller that encodes the goals and safety requirements of the system. However, owing to topological obstructions, stable critical points other than the desired one may appear. In such case, we employ a high-level distributed discrete procedure which attempts to solve a distributed constraint satisfaction problem on a local Voronoi partition, providing the necessary reconfiguration for the system to progress towards its goal. Eventually, we show that the system either converges to the desired point or attains a tree configuration with respect to the formation topology, in which case the system switches to a novel controller based on the prescribed performance control technique, that eventually guarantees convergence. Finally, multiple simulation studies clarify and verify the approach.










Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
More general types of obstacles can be considered by appropriately transforming them into disks [see Loizou (2014)].
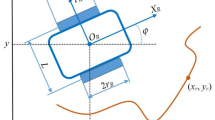
The same approach holds for convex obstacles in general, where \(x_k\) can be any arbitrary point in the interior of the obstacle.
The formation graph \(\mathcal {G}_f\) is considered piecewise constant.
Definitions of switches:
$$\begin{aligned}&\sigma _\epsilon (z) \triangleq {\left\{ \begin{array}{ll}-\frac{1}{\epsilon ^2}z^2+\frac{2}{\epsilon }z,&{} z<\epsilon \\ 1,&{} z\ge \epsilon \end{array}\right. },\\&\sigma _{\epsilon ,R}(z) \triangleq {\left\{ \begin{array}{ll}1, &{}z\le R-\epsilon \\ \frac{2}{\epsilon ^3}z^3+\frac{-6R+3\epsilon }{\epsilon ^3}z^2 + \frac{6R^2-6R\epsilon }{e^3}z + \frac{-2R^3+3R^2\epsilon }{\epsilon ^3}, &{}R-\epsilon<z<R\\ 0, &{}z\ge R \end{array}\right. }\end{aligned}$$Agents can agree that the system has reached an equilibrium through a consensus procedure (Olfati-Saber et al. 2007).
This a valid assumption given that both \(\theta _i\) and \(d_i\) are initially known, thus rendering proper initialization trivial.
References
Ajorlou, A., & Aghdam, A. G. (2013). Connectivity preservation in nonholonomic multi-agent systems: A bounded distributed control strategy. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 58(9), 2366–2371.
Arslan, O., Guralnik, D. P., & Koditschek, D. E. (2016). Coordinated robot navigation via hierarchical clustering. IEEE Transactions of Robotics, 32(2), 352–371.
Ayanian, N., Kumar, V., & Koditschek, D. (2011). Synthesis of controllers to create, maintain, and reconfigure robot formations with communication constraints. Berlin: Springer.
Bechlioulis, C. P., & Rovithakis, G. A. (2008). Robust adaptive control of feedback linearizable mimo nonlinear systems with prescribed performance. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 53(9), 2090–2099.
Bullo, F., Cortes, J., & Martinez, S. (2009). Distributed control of robotic networks: A mathematical approach to motion coordination algorithms. Princeton, NJ: Princeton University Press.
Chaimowicz, L., & Kumar, V. (2007). Aerial shepherds: Coordination among uavs and swarms of robots. Tokyo: Springer.
Cheng, T. H., Kan, Z., Rosenfeld, J. A., & Dixon, W. E. (2014). Decentralized formation control with connectivity maintenance and collision avoidance under limited and intermittent sensing. In 2014 American control conference, pp. 3201–3206.
Couzin, I. D., Krause, J., Franks, N. R., & Levin, S. A. (2005). Effective leadership and decision-making in animal groups on the move. Nature, 433(7025), 513–516.
Dimarogonas, D., Loizou, S., & Kyriakopoulos, K. (2006a). Multirobot navigation functions ii: Towards decentralization. Stochastic Hybrid Systems, 337, 209–253.
Dimarogonas, D. V., & Frazzoli, E. (Dec 2010). Analysis of decentralized potential field based multi-agent navigation via primal-dual lyapunov theory. In 49th IEEE conference on decision and control (CDC), pp. 1215–1220.
Dimarogonas, D. V., & Johansson, K. H. (2010). Bounded control of network connectivity in multi-agent systems. IET Control Theory Applications, 4(8), 1330–1338.
Dimarogonas, D. V., & Kyriakopoulos, K. J. (Dec 2005). Formation control and collision avoidance for multi-agent systems and a connection between formation infeasibility and flocking behavior. In Proceedings of the 44th IEEE conference on decision and control, pp. 84–89.
Dimarogonas, D. V., Loizou, S. G., Kyriakopoulos, K. J., & Zavlanos, M. M. (2006b). A feedback stabilization and collision avoidance scheme for multiple independent non-point agents. Automatica, 42(2), 229–243.
Esposito, J. M., & Dunbar, T. W. (May 2006). Maintaining wireless connectivity constraints for swarms in the presence of obstacles. In Proceedings 2006 IEEE international conference on robotics and automation, 2006. ICRA 2006, pp. 946–951.
Gennaro, M. C. D., & Jadbabaie, A. (Dec 2006). Decentralized control of connectivity for multi-agent systems. In Proceedings of the 45th IEEE conference on decision and control, pp. 3628–3633.
Guruprasad, K. R., & Dasgupta, P. (Oct 2012). Distributed voronoi partitioning for multi-robot systems with limited range sensors. In 2012 IEEE/RSJ international conference on intelligent robots and systems, pp. 3546–3552.
Iutzeler, F., Ciblat, P., & Jakubowicz, J. (2012). Analysis of max-consensus algorithms in wireless channels. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 60(11), 6103–6107.
Jadbabaie, A., Lin, J., & Morse, A. S. (2003). Coordination of groups of mobile autonomous agents using nearest neighbor rules. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 48(6), 988–1001.
Kan, Z., Dani, A. P., Shea, J. M., & Dixon, W. E. (Dec 2011). Ensuring network connectivity for nonholonomic robots during rendezvous. In 2011 50th IEEE conference on decision and control and European control conference, pp. 2369–2374.
Kan, Z., Dani, A. P., Shea, J. M., & Dixon, W. E. (2012). Network connectivity preserving formation stabilization and obstacle avoidance via a decentralized controller. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 57(7), 1827–1832.
Khatib, O. (1986). Real-time obstacle avoidance for manipulators and mobile robots. The International Journal of Robotics Research, 5(1), 90–98.
Koditschek, D., & Rimon, E. (1990). Robot navigation functions on manifolds with boundary. Advances in Applied Mathematics, 11(4), 412–442.
Lee, C. Y. (1961). An algorithm for path connections and its applications. IRE Transactions on Electronic Computers, EC–10(3), 346–365.
Li, X., Sun, D., & Yang, J. (2013). Preserving multirobot connectivity in rendezvous tasks in the presence of obstacles with bounded control input. IEEE Transactions on Control Systems Technology, 21(6), 2306–2314.
Loizou, S. (July 2014). The multi-agent navigation transformation: Tuning-free multi-robot navigation. In Proceedings of robotics: Science and systems, Berkeley, USA.
Munkres, J. R. (1975). Topology: A first course. Upper Saddle River: Prentice Hall.
Ogren, P. (2004). Split and join of vehicle formations doing obstacle avoidance. In Proceedings of robotics and automation. 2004 IEEE international Conference on ICRA’04 (Vol. 2. pp. 1951–1955), IEEE.
Olfati-Saber, R., Fax, J. A., & Murray, R. M. (2007). Consensus and cooperation in networked multi-agent systems. Proceedings of the IEEE, 95(1), 215–233.
Ren, W., & Beard, R. W. (2005). Consensus seeking in multiagent systems under dynamically changing interaction topologies. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 50(5), 655–661.
Sabattini, L., Secchi, C., & Chopra, N. (May 2012). Decentralized connectivity maintenance for networked lagrangian dynamical systems. In 2012 IEEE international conference on robotics and automation, pp. 2433–2438.
Tanner, H. G., Loizou, S. G., & Kyriakopoulos, K. J. (2003). Nonholonomic navigation and control of cooperating mobile manipulators. IEEE Transactions on Robotics and Automation, 19(1), 53–64.
Tardioli, D., Mosteo, A., Riazuelo, L., Villarroel, J., & Montano, L. (2010). Enforcing network connectivity in robot team missions. The International Journal of Robotics Research, 29(4), 460–480.
Urcola, P., Lzaro, M. T., Castellanos, J. A., & Montano, L. (2017). Cooperative minimum expected length planning for robot formations in stochastic maps. Robotics and Autonomous Systems, 87, 38–50.
Urcola, P., & Montano, L. (Oct 2009). Cooperative robot team navigation strategies based on an environment model. In 2009 IEEE/RSJ international conference on intelligent robots and systems, pp. 4577–4583.
Vrohidis, C., Bechlioulis, C. P., & Kyriakopoulos, K. J. (2017). Safe decentralized and reconfigurable multi-agent control with guaranteed convergence. In 2017 IEEE international conference on robotics and automation, Marina Bay Sands Convention Centre, Singapore.
Wahbi, M. (2013). Algorithms and ordering heuristics for distributed constraint satisfaction problems., Focus series New York: Wiley.
Wen, G., Duan, Z., Su, H., Chen, G., & Yu, W. (2012). A connectivity-preserving flocking algorithm for multi-agent dynamical systems with bounded potential function. IET Control Theory Applications, 6(6), 813–821.
Yokoo, M., Durfee, E. H., Ishida, T., & Kuwabara, K. (1998). The distributed constraint satisfaction problem: Formalization and algorithms. IEEE Transactions on Knowledge and Data Engineering, 10(5), 673–685.
Yokoo, M., Ishida, T., Durfee, E. H., & Kuwabara, K. (Jun 1992). Distributed constraint satisfaction for formalizing distributed problem solving. In Proceedings of the 12th international conference on distributed computing systems, 1992, pp. 614–621.
Yoo, A., Chow, E., Henderson, K., McLendon, W., Hendrickson, B., & Catalyurek, U. (2005). A scalable distributed parallel breadth-first search algorithm on bluegene/l. In Proceedings of the 2005 ACM/IEEE conference on supercomputing, ser. SC ’05. Washington, DC, USA: IEEE Computer Society, pp. 25–30.
Zavlanos, M. M., Egerstedt, M. B., & Pappas, G. J. (2011). Graph-theoretic connectivity control of mobile robot networks. Proceedings of the IEEE, 99(9), 1525–1540.
Zavlanos, M. M., & Pappas, G. J. (2008). Distributed connectivity control of mobile networks. IEEE Transactions on Robotics, 24(6), 1416–1428.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This is one of several papers published in Autonomous Robots comprising the Special Issue on Online Decision Making in Multi-Robot Coordination.
This work was supported by the EU funded project Co4Robots: Achieving Complex Collaborative Missions via Decentralized Control and Coordination of Interacting Rob‘ots, H2020-ICT-731869, 2017–2019.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Vrohidis, C., Vlantis, P., Bechlioulis, C.P. et al. Reconfigurable multi-robot coordination with guaranteed convergence in obstacle cluttered environments under local communication. Auton Robot 42, 853–873 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10514-017-9660-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10514-017-9660-y