Abstract
Phishing is web based criminal activity of making innocent online users to reveal sensitive information into fake web sites. Such fake web sites lead to fraudulent charges against individuals and corporations. Phishers have a lot of methods to design and host phished web pages, so in reality there cannot be a single solution that can help us combat phishing. As technology advances, the phishing techniques being used are also getting advanced and hence it demands the anti-phishing techniques also to be upgraded and the new techniques are to be included along with the existing methods. But most of the anti-phishing techniques today do not satisfy these criteria.
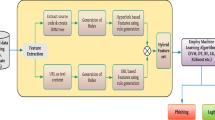
In this paper, we propose service oriented three-layer architecture model for detecting and identifying phishing web sites as it overcomes the shortcomings of existing anti-phishing solutions. This model enables us to separate the user interface layer from the anti-phishing components layer. This is done through web service middleware layer, which provides us with the freedom of building our own anti-phishing components layer in an efficient and flexible way, independent of other layers.
Anti-phishing components layer provides a set of reusable components to convert webpage into feature vectors using finest heuristic methods and external repositories of information. The feature vectors act as an input to trained support vector machine classifier to generate phishing label which determines whether a webpage is legitimate or a phishing page. This when experimented, displayed the significance and importance of three-layered architecture model along with combination of heuristics in detection of phishing webpage. This results in high accuracy of 99 % with less than 1 % of false positive rate.













Similar content being viewed by others
References
RSA Anti-Fraud Command Center: RSA monthly online fraud report, May 2012. http://www.rsa.com/solutions/consumer_authentication/intelreport/11713_Online_Fraud_report_0512.pdf, visited on June 2012
Wu, M., Miller, R.C., Garfinkel, S.L.: Do security toolbars actually prevent phishing attacks? In: CHI, April, pp. 601–610 (2006)
Cranor, L., Egelman, S., Hong, J., Zhang, Y.: Phinding phish: an evaluation of anti-phishing toolbars. Technical report, Carnegie Mellon University, November 2006, pp. 1–20
The Symantec Security Response team: Symantec report on attack kits and malicious websites, January 2011. http://www.symantec.com/content/en/us/enterprise/other_resources/b-symantec_report_on_attack_kits_and_malicious_websites_exec_summary_21169172_WP.en-us.pdf, visited on Feb 2012
Kumaraguru, P., Sheng, S., Acquisti, A., Cranor, L.F., Hong, J.: Teaching jOhnny not to fall for phish. ACM Trans. Internet Technol. 10(2), 7 (2010). doi:10.1145/1754393.1754396
Irani, D., Webb, S., Giffin, J., Pu, C.: Evolutionary study of phishing. In: Proceedings of the 3rd Anti-Phishing Working Group eCrime Researchers Summit, Atlanta, GA, pp. 1–8 (2008)
FDIC: putting an end to account-hijacking identity theft. http://www.fdic.gov/consumers/consumer/idtheftstudy/identity_theft.pdf, visited on Feb 2012
Symantec global intelligence network, state of spam and phishing report, February 2010. http://eval.symantec.com/mktginfo/enterprise/other_resources/b-state_of_spam_and_phishing_report_02-2010.en-us.pdf
Zhang, Y., Hong, J.I., Cranor, L.F.: CANTINA—a content-based approach to detecting phishing web sites. In: Proc. of the 16th International Conference on World Wide Web, Banff, Alberta, Canada, May 08–12, pp. 639–648 (2007)
He, M., Horng, S.-J., Fan, P., Khan, M.K., Run, R.-S., Lai, J.-L., Chen, R.-J., Sutanto, A.: An efficient phishing webpage detector. Expert Syst. Appl. Int. J. 38(10), 18–27 (2011)
Pan, Y., Ding, X.: Anomaly based web phishing page detection. In: Proc. of the 22nd Annual Computer Security Applications Conference (ACSAC’06), pp. 381–392 (2006)
Wang, Y., Agrawal, R., Choi, B.: Light weight anti-phishing with user white listing in a web browser. In: Proc. of the IEEE Region 5 Conference, Kansas City, pp. 1–4 (2008)
Han, W., Cao, Y., Bertino, E., Yong, J.: Using automated individual white-list to protect web digital identities. Expert Syst. Appl. (2012). doi:10.1016/j.eswp.2012.02.020
Sharifi, M., Siadati, S.: A phishing sites blacklist generator. In: Proc. of International Conference on Computer Systems and Applications, AICCSA, Doha, Qatar, pp. 840–843 (2008)
Chandrasekaran, M., Chinchani, R., Upadhyaya, S.: PHONEY: mimicking user response to detect phishing attacks. In: Proc. of Intl. Symposium on World of Wireless, Mobile and Multimedia Networks, Niagara-Falls, NY, June 2006, pp. 668–672 (2006)
Fette, I., Sadeh, N., Tomasic, A.: Learning to detect phishing emails. In: Proc. of the 16th Intl. Conf. on World Wide Web, Banff, Alberta, Canada, May 2007, pp. 649–656 (2007)
Dhamija, R., Tygar, J.: The battle against phishing: dynamic security skins. In: Proc. of the Symposium on Usable Privacy and Security, Pittsburgh, USA, July 2005, pp. 77–88 (2005)
Liu, W., Deng, X., Huang, G., Fu, A.Y.: An anti-phishing strategy based on visual similarity assessment. IEEE Internet Comput. 10(2), 58–65 (2006)
Chou, N., Ledesma, R., Teraguchi, Y., Boneh, D., Mitchell, J.: Client-side defense against web-based identify theft. In: Proc. of the 11th Annual Network and Distributed System Security Symposium, NDSS’04, San Diego, CA, February 2004, vol. 380 (2004)
Xiang, G., Hong, J., Rose, C.P., Cranor, L.: CANTINA+: a feature-rich machine learning framework for detecting phishing web sites. ACM Trans. Inf. Syst. Secur. 14(2), 21 (2011). doi:10.1145/2019599.2019606
Xiang, G., Hong, J.I.: A hybrid phish detection approach by identity discovery and keywords retrieval. In: Proceedings of the 18th International Conference on World Wide Web, pp. 571–580. ACM Press, New York (2009)
Florencio, D., Herley, C.: Microsoft research; evaluating a trial deployment of password re-use for phishing prevention. In: APWG eCrime Researchers Summit, Pittsburgh, PA, USA, October 4–5, 2007, pp. 26–36 (2007)
Joshi, Y., Saklikar, S., Das, D., Saha, S.: PhishGuard: a browser plug-in for protection from phishing. In: Proc. of the 2nd International Conference on Internet Multimedia Services Architecture and Applications, Bangalore, India, pp. 1–6 (2008)
Yue, C., Wang, H.: BogusBiter: a transparent protection against phishing attacks. ACM Trans. Internet Technol. 10(2), 6 (2010). doi:10.1145/1754393.1754395
Wenyin, L., Fang, N., Quan, X., Qiu, B., Liu, G.: Discovering phishing target based on semantic link network. Future Gener. Comput. Syst. 26(3) (2010)
Shahriar, H., Zulkernine, M.: Trustworthiness testing of phishing websites: a behavior model-based approach. Future Gener. Comput. Syst. (2011). doi:10.1016/j.feture.2011.02.001
Peltz, C.: Web services orchestration and choreography. Computer, 46–52 (2003)
Wood, J., Brodlie, K., Seo, J., Duke, D., Walton, J.: A web services architecture for visualization. In: Proc. of the IEEE International Conference on eScience, pp. 1–7 (2008)
SOAP 1.1: simple object access protocol (SOAP) 1.1, W3C, Note 08 May 2000. http://www.w3.org/TR/2000/NOTE-SOAP-20000508, visited on Feb 2012
Lau, K.-K., Tran, C.M.: Composite web services. In: Pautasso, C., Gschwind, T. (eds.) Emerging Web Services Technology, vol. 2, pp. 77–95. Birkhauser, Basel (2008)
Dao, T.: Term frequency-inverse document frequency implementation in C#, the code project, C# programming. http://www.codeproject.com/csharp/tfidf.asp, visited on Nov 2011
Davies, M.: (2011) Word frequency data from the Corpus of Contemporary American English (COCA). Downloaded from http://www.wordfrequency.info on December 18, 2011
Sobek, M.: A survey of Google’s pagerank. Available at http://pr.efactory.de/
Bian, K., Park, J.-M., Hsiao, M.S., Belanger, F., Hiller, J.: Evaluation of online resources in assisting phishing detection. In: Ninth Annual International Symposium on Applications and the Internet, 20–24 July 2009, pp. 30–36 (2009)
Netcraft: Governments hosted 146 new phishing sites in July, July 2011. http://news.netcraft.com/archives/2011/08/19/governments-hosted-146-new-phishing-sites-in-july.html, visited on Feb 2012
Ronda, T., Saroiu, S., Wolman, A.: Itrustpage: a user-assisted anti-phishing tool. In: Proc. of the 3rd ACM SIGOPS/EuroSys European Conference on Computer Systems 2008, pp. 261–272. ACM, New York (2008)
Kumaraguru, P., Cranshaw, J., Acquisti, A., Cranor, L., Hong, J., Blair, M.A., Pham, T.: School of phish: a real-world evaluation of anti-phishing training. In: Symposium on Usable Privacy and Security, Mountain View, CA. USA July 15–17, 2009
Anti-phishing act of 2005. http://www.govtrack.us/congress/bills/109/hr1099/text, visited on June 2012
Barrett, M., Levy, D.: A practical approach to managing phishing. Paypal Whitepaper, April 2008
Maeda, T., Nomura, Y., Hara, H.: Security and reliability for web services. Fujitsu Sci. Tech. J. 39(2), 214–223 (2003)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gowtham, R., Krishnamurthi, I. PhishTackle—a web services architecture for anti-phishing. Cluster Comput 17, 1051–1068 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10586-013-0320-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10586-013-0320-5