Abstract
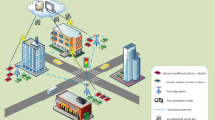
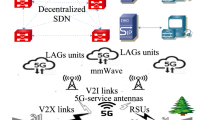
In this study, a secure and coordinated blockchain based energy trading system for Electric Vehicles (EVs) is presented. The major goals of this study are to provide secure and efficient energy trading between EVs and Charging Stations (CSs), and to ensure efficient coordination between EVs. In this study, a consortium blockchain based energy trading algorithm is presented that handles the essential energy requests, discards the redundant requests and calculates the distance between EVs and CSs. Moreover, Matching Pool (M-Pool) and Pairing Pool (P-Pool) are used to store energy and payment requests. Furthermore, a blockchain based mechanism is proposed for ensuring efficient coordination between EVs at the unsignalized crossroads and intersections. The scheme involves efficient communication between EVs and the timely sharing of important messages. In the proposed work, EVs are authenticated using a Registration Authority (RA) before they become part of a Vehicular Energy Network (VEN). The increase in the number of EVs results in an increase in the number of messages leading to data redundancy issue. To solve the issue, message filtration is performed. The delays incurred in the VEN are also mathematically formulated in this study. In addition, the range anxiety issue is discussed in the proposed work. Besides, a Local Aggregator (LAG) is used as an energy broker to manage energy trading events and transaction validation. To promote the users to take part in the proposed network, they are provided with incentives. The proposed model is tested against selfish mining attack and the security analysis is performed through Oyente tool. The simulation results show that the proposed study excels in providing a secure, efficient and coordinated energy trading and data sharing system for EVs. The results show that due to proper coordination, the risk factor is reduced by almost 25–30%. Moreover, almost 40–50% reduction in time is observed when storing less redundant data.


















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Dorahaki, S., Dashti, R., Shaker, H.R.: Optimal energy management in the smart microgrid considering the electrical energy storage system and the demand-side energy efficiency program. J. Energy Storage 28, 101229 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.est.2020.101229
Shahidehpour, M., Li, Z., Ganji, M.: Smart cities for a sustainable urbanization: Illuminating the need for establishing smart urban infrastructures. IEEE Electrif. Mag. 6(2), 16–33 (2018)
Hassija, V., Chamola, V., Garg, S., Krishna, D.N.G., Kaddoum, G., Jayakody, D.N.K.: A blockchain-based framework for lightweight data sharing and energy trading in V2G network. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 69(6), 5799–5812 (2020)
Zhou, Z., Tan, L., Xu, G.: October. Blockchain and edge computing based vehicle-to-grid energy trading in energy Internet. In: 2018 2nd IEEE Conference on Energy Internet and Energy System Integration (EI2) (pp. 1-5). IEEE (2018)
Zhang, D., Yu, F.R., Yang, R.: Blockchain-based distributed software-defined vehicular networks: A dueling deep \({Q}\)-learning approach. IEEE Trans. Cogn. Commun. Netw. 5(4), 1086–1100 (2019)
Wang, D., Zhang, X.: Secure data sharing and customized services for intelligent transportation based on a consortium blockchain. IEEE Access 8, 56045–56059 (2020)
Dwivedi, S.K., Amin, R., Vollala, S., Chaudhry, R.: Blockchain-based secured event-information sharing protocol in internet of vehicles for smart cities. Comput. Electr. Eng. 86, 106719 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compeleceng.2020.106719
Aujla, G.S., Jindal, A., Kumar, N.: EVaaS: Electric vehicle-as-a-service for energy trading in SDN-enabled smart transportation system. Comput. Netw. 143, 247–262 (2018)
Emissions and Charging Costs-electric-cars. https://www.ucsusa.org/clean-vehicles/electric-vehicles/emissions-and-charging-costs-electric-cars accessed 7 July 2020
IHS Markit Forecasts Global EV Sales To Rise By 70% In 2021. 2021. IHS Markit. https://ihsmarkit.com/research-analysis/ihs-markit-forecasts-global-ev-sales-to-rise-by-70-percent.html. accessed 31 Jan 2021
Zhu, H., Yuen, K.V., Mihaylova, L., Leung, H.: Overview of environment perception for intelligent vehicles. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 18(10), 2584–2601 (2017)
Koufakis, A.M., Rigas, E.S., Bassiliades, N., Ramchurn, S.D.: Towards an optimal EV charging scheduling scheme with V2G and V2V energy transfer. In: 2016 IEEE International Conference on Smart Grid Communications (SmartGridComm) (pp. 302–307). IEEE (2016)
Qian, B., Zhou, H., Lyu, F., Li, J., Ma, T., Hou, F.: Toward collision-free and efficient coordination for automated vehicles at unsignalized intersection. IEEE Internet Things J. 6(6), 10408–10420 (2019)
Chen, R., Liu, X., Miao, L., Yang, P.: Electric vehicle tour planning considering range anxiety. Sustainability 12(9), 3685 (2020). https://doi.org/10.3390/su12093685
Ping, J., Yan, Z., Chen, S., Yao, L., Qian, M.: Coordinating EV charging via blockchain. J. Modern Power Syst. Clean Energy 8(3), 573–581 (2020)
Dorri, A., Steger, M., Kanhere, S.S., Jurdak, R.: Blockchain: A distributed solution to automotive security and privacy. IEEE Commun. Mag. 55(12), 119–125 (2017)
Chin, W.L., Li, W., Chen, H.H.: Energy big data security threats in IoT-based smart grid communications. IEEE Commun. Mag. 55(10), 70–75 (2017)
Chen, X., Zhang, X.: Secure electricity trading and incentive contract model for electric vehicle based on energy blockchain. IEEE Access 7, 178763–178778 (2019)
Wang, Y., Su, Z., Zhang, N.: BSIS: Blockchain-based secure incentive scheme for energy delivery in vehicular energy network. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inf. 15(6), 3620–3631 (2019)
Jindal, A., Aujla, G.S., Kumar, N.: SURVIVOR: A blockchain based edge-as-a-service framework for secure energy trading in SDN-enabled vehicle-to-grid environment. Comput. Netw. 153, 36–48 (2019)
Chaudhary, R., Jindal, A., Aujla, G.S., Aggarwal, S., Kumar, N., Choo, K.K.R.: BEST: Blockchain-based secure energy trading in SDN-enabled intelligent transportation system. Comput. Secur. 85, 288–299 (2019)
Javed, M.U., Javaid, N., Aldegheishem, A., Alrajeh, N., Tahir, M., Ramzan, M.: Scheduling charging of electric vehicles in a secured manner by emphasizing cost minimization using blockchain technology and IPFS. Sustainability 12(12), 5151 (2020). https://doi.org/10.3390/su12125151
Wang, H., Wang, Q., He, D., Li, Q., Liu, Z.: BBARS: Blockchain-based anonymous rewarding scheme for V2G networks. IEEE Internet Things J. 6(2), 3676–3687 (2019)
Liu, H., Zhang, Y., Zheng, S., Li, Y.: Electric vehicle power trading mechanism based on blockchain and smart contract in V2G network. IEEE Access 7, 160546–160558 (2019)
Ali, M.S., Vecchio, M., Pincheira, M., Dolui, K., Antonelli, F., Rehmani, M.H.: Applications of blockchains in the Internet of Things: A comprehensive survey. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutor. 21(2), 1676–1717 (2018)
Li, Y., Hu, B.: An iterative two-layer optimization charging and discharging trading scheme for electric vehicle using consortium blockchain. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 11(3), 2627–2637 (2019)
Nakamoto, S., Bitcoin: A peer-to-peer electronic cash system. https://bitcoin.org/bitcoin.pdf accessed 13 Aug 2020
Wang, S., Taha, A.F., Wang, J., Kvaternik, K., Hahn, A.: Energy crowdsourcing and peer-to-peer energy trading in blockchain-enabled smart grids. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. Syst. 49(8), 1612–1623 (2019)
Sun, G., Dai, M., Zhang, F., Yu, H., Du, X., Guizani, M.: Blockchain-enhanced high-confidence energy sharing in internet of electric vehicles. IEEE Internet Things J. 7(9), 7868–7882 (2020)
Gai, K., Wu, Y., Zhu, L., Xu, L., Zhang, Y.: Permissioned blockchain and edge computing empowered privacy-preserving smart grid networks. IEEE Internet Things J. 6(5), 7992–8004 (2019)
Khalid, R., Javaid, N., Almogren, A., Javed, M.U., Javaid, S., Zuair, M.: A blockchain-based load balancing in decentralized hybrid P2P energy trading market in smart grid. IEEE Access 8, 47047–47062 (2020)
Yahaya, A.S., Javaid, N., Javed, M.U., Shafiq, M., Khan, W.Z., Aalsalem, M.Y.: Blockchain-based energy trading and load balancing using contract theory and reputation in a smart community. IEEE Access 8, 222168–222186 (2020)
Zhu, L., Wu, Y., Gai, K., Choo, K.K.R.: Controllable and trustworthy blockchain-based cloud data management. Future Gener. Comput. Syst. 91, 527–535 (2019)
Xu, H., Zhang, L., Liu, Y., Cao, B.: Raft based wireless blockchain networks in the presence of malicious jamming. IEEE Wirel. Commun. Lett. 9(6), 817–821 (2020)
Cui, Z., Fei, X.U.E., Zhang, S., Cai, X., Cao, Y., Zhang, W., Chen, J.: A hybrid Blockchain based identity authentication scheme for multi-WSN. IEEE Trans. Serv. Comput. 13(2), 241–251 (2020)
Kang, J., Yu, R., Huang, X., Wu, M., Maharjan, S., Xie, S., Zhang, Y.: Blockchain for secure and efficient data sharing in vehicular edge computing and networks. IEEE Internet Things J. 6(3), 4660–4670 (2018)
Liu, X., Huang, H., Xiao, F., Ma, Z.: A blockchain-based trust management with conditional privacy-preserving announcement scheme for VANETs. IEEE Internet Things J. 7(5), 4101–4112 (2019)
Khalid, A., Iftikhar, M.S., Almogren, A., Khalid, R., Afzal, M.K., Javaid, N.: A blockchain based incentive provisioning scheme for traffic event validation and information storage in VANETs. Inf. Process. Manag. 58(2), 102464 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ipm.2020.102464
Sadiq, A., Javed, M.U., Khalid, R., Almogren, A., Shafiq, M., Javaid, N.: Blockchain based Data and Energy Trading in Internet of Electric Vehicles. IEEE Access 9, 7000–7020 (2020)
Lei, K., Du, M., Huang, J., Jin, T.: Groupchain: Towards a scalable public blockchain in fog computing of IoT services computing. IEEE Trans. Serv. Comput. 13(2), 252–262 (2020)
Sultana, T., Almogren, A., Akbar, M., Zuair, M., Ullah, I., Javaid, N.: Data sharing system integrating access control mechanism using blockchain based smart contracts for IoT devices. Appl. Sci. 10(2), 488 (2020). https://doi.org/10.3390/app10020488
Li, H., Pei, L., Liao, D., Wang, X., Xu, D., Sun, J.: BDDT: Use blockchain to facilitate IoT data transactions. Clust. Comput. 1, 1–15 (2020)
Han, S., Xu, S., Meng, W., He, L.: Channel-correlation-enabled transmission optimization for MISO wiretap channels. IEEE Trans. Wirel. 20, 858–870 (2020)
Zhou, Z., Wang, B., Guo, Y., Zhang, Y.: Blockchain and computational intelligence inspired incentive-compatible demand response in internet of electric vehicles. IEEE Trans. Emerg. Topics Comput. Intell. 3(3), 205–216 (2019)
James, J.Q., Lam, A.Y., Tan, S.C.: October. Energy exchange coordination of off-grid charging stations with vehicular energy network. In: 2017 IEEE International Conference on Smart Grid Communications (SmartGridComm) (pp. 375–380). IEEE (2017)
Atallah, R., Khabbaz, M., Assi, C.: Energy harvesting in vehicular networks: A contemporary survey. IEEE Wirel. Commun. 23(2), 70–77 (2016)
Zhou, Z., Xiong, F., Xu, C., He, Y., Mumtaz, S.: Energy-efficient vehicular heterogeneous networks for green cities. IEEE Trans. Ind Inf. 14(4), 1522–1531 (2017)
Li, Z., Kang, J., Yu, R., Ye, D., Deng, Q., Zhang, Y.: Consortium blockchain for secure energy trading in industrial internet of things. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inf. 14(8), 3690–3700 (2017)
Aggarwal, S., Chaudhary, R., Aujla, G.S., Jindal, A., Dua, A., Kumar, N.: June. Energychain: Enabling energy trading for smart homes using blockchains in smart grid ecosystem. In: Proceedings of the 1st ACM MobiHoc Workshop on Networking and Cybersecurity for Smart Cities (pp. 1–6) (2018)
Martinez-Rendon, C., Camarmas-Alonso, D., Carretero, J., Gonzalez-Compean, J.L.: On the continuous contract verification using blockchain and real-time data. Clust. Comput. 1, 1–23 (2021)
Aloqaily, M., Boukerche, A., Bouachir, O., Khalid, F., Jangsher, S.: An energy trade framework using smart contracts: Overview and challenges. IEEE Netw. 34(4), 119–125 (2020)
Ali, F., Bouachir, O., Ozkasap, O., Aloqaily, M.: SynergyChain: Blockchain-assisted Adaptive Cyberphysical P2P Energy Trading. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inf. (2020)
Ali, F.S., Aloqaily, M., Alfandi, O., Ozkasap, O.: Cyberphysical blockchain-enabled peer-to-peer energy trading. Computer 53(9), 56–65 (2020)
Gao, F., Zhu, L., Shen, M., Sharif, K., Wan, Z., Ren, K.: A blockchain-based privacy-preserving payment mechanism for vehicle-to-grid networks. IEEE Netw. 32(6), 184–192 (2018)
Ghofrani, M., Arabali, A., Etezadi-Amoli, M., Fadali, M.S.: Smart scheduling and cost-benefit analysis of grid-enabled electric vehicles for wind power integration. IEEE Trans. Smart grid 5(5), 2306–2313 (2014)
Rehman, M., Javaid, N., Awais, M., Imran, M., Naseer, N.: December. Cloud based secure service providing for IoTs using blockchain. In: 2019 IEEE Global Communications Conference (GLOBECOM) (pp. 1–7). IEEE (2019)
Zou, S., Ma, Z., Liu, X., Hiskens, I.: An efficient game for coordinating electric vehicle charging. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 62(5), 2374–2389 (2016)
Liu, C., Chai, K.K., Zhang, X., Lau, E.T., Chen, Y.: Adaptive blockchain-based electric vehicle participation scheme in smart grid platform. IEEE Access 6, 25657–25665 (2018)
Mohammadi, J., Hug, G., Kar, S.: A fully distributed cooperative charging approach for plug-in electric vehicles. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 9(4), 3507–3518 (2016)
Amini, M.H., Moghaddam, M.P., Karabasoglu, O.: Simultaneous allocation of electric vehicles’ parking lots and distributed renewable resources in smart power distribution networks. Sustain. Cities Soc. 28, 332–342 (2017)
Rowan, S., Clear, M., Huggard, M., Mc Goldrick, C.: Securing vehicle to vehicle data sharing using blockchain through visible light and acoustic side-channels. arXiv:1704.02553 (2017)
Huang, X., Xu, C., Wang, P., Liu, H.: LNSC: A security model for electric vehicle and charging pile management based on blockchain ecosystem. IEEE Access 6, 13565–13574 (2018)
Gabay, D., Akkaya, K., Cebe, M.: Privacy-preserving authentication scheme for connected electric vehicles using blockchain and zero knowledge proofs. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 69(6), 5760–5772 (2020)
Pu, Y., Xiang, T., Hu, C., Alrawais, A., Yan, H.: An efficient blockchain based privacy preserving scheme for vehicular social networks. Inf. Sci. 308–324 (2020)
Khalid, U., Asim, M., Baker, T., Hung, P.C., Tariq, M.A., Rafferty, L.: A decentralized lightweight blockchain-based authentication mechanism for IoT systems. Clust. Comput. 1–21 (2020)
Elkhalil, A., Zhang, J., Elhabob, R.: An efficient heterogeneous blockchain-based online/offline signcryption systems for internet of vehicles. Clust. Comput. pp. 1–18 (2021)
Fayazi, S.A., Vahidi, A.: Mixed-integer linear programming for optimal scheduling of autonomous vehicle intersection crossing. IEEE Trans. Intell. Veh. 3(3), 287–299 (2018)
Lin, P., Liu, J., Jin, P.J., Ran, B.: Autonomous vehicle-intersection coordination method in a connected vehicle environment. IEEE Intell. Transpl. Syst. Mag. 9(4), 37–47 (2017)
Dai, P., Liu, K., Zhuge, Q., Sha, E.H.M., Lee, V.C.S., Son, S.H.: Quality-of-experience-oriented autonomous intersection control in vehicular networks. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 17(7), 1956–1967 (2016)
Hult, R., Zanon, M., Gros, S., Wymeersch, H., Falcone, P.: Optimisation based coordination of connected, automated vehicles at intersections. Veh. Syst. Dyn. 58(5), 726–747 (2020)
Gope, P., Sikdar, B.: An efficient privacy-preserving authentication scheme for energy internet based vehicle-to-grid communication. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 10(6), 6607–6618 (2019)
Luo, B., Li, X., Weng, J., Guo, J., Ma, J.: Blockchain enabled trust based location privacy protection scheme in VANET. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 69(2), 2034–2048 (2019)
What are the different types of network delay? https://www.educative.io/edpresso/what-are-the-different-types-of-network-delay accessed 15 July 2020
Network Delays and Losses https://www.d.umn.edu/~gshute/net/delays-losses.xhtml accessed 15 July 2020
30 states allow kWh pricing, but non-Tesla EV drivers mostly miss benefits https://electrek.co/2019/08/12/kWh-pricing-ev-drivers-miss-benefits/ accessed 17 Sept 2020
Sayeed, S., Marco-Gisbert, H., Caira, T.: Smart contract: Attacks and protections. IEEE Access 8, 24416–24427 (2020)
Yang, H., Yuan, J., Yao, H., Yao, Q., Yu, A., Zhang, J.: Blockchain-based hierarchical trust networking for JointCloud. IEEE Internet Things J. 7(3), 1667–1677 (2019)
Eyal, I., Sirer, E.G.: March. Majority is not enough: Bitcoin mining is vulnerable. In: International conference on financial cryptography and data security (pp. 436–454). Springer, Berlin (2014)
Chicarino, V., Albuquerque, C., Jesus, E., Rocha, A.: On the detection of selfish mining and stalker attacks in blockchain networks. Ann. Telecommun. 1–10 (2020)
Grunspan, C., Pérez-Marco, R.: On profitability of selfish mining. arXiv:1805.08281 (2018)
Ethereum Smart Contract Best Practices, Known Attacks. https://consensys.github.io/smart-contract-best-practices/known_attacks/ accessed 5 July 2020
How to use Oyente, a smart contract security analyzer—Solidity Tutorial. https://medium.com/haloblock/how-to-use-oyente-a-smart-contract-security-analyzer accessed 6 July 2020
Known Attacks - Ethereum Smart Contract Best Practices. https://consensys.github.io/smart-contract-best-practices/known_attacks/ accessed 6 July 2020
A Postmortem On The Parity Multi-Sig Library Self-Destruct. Blockchain Infrastructure For The Decentralised Web. https://www.parity.io/a-postmortem-on-the-parity-multi-sig-library-self-destruct/ accessed 6 July 2020
Hackernoon.com. Smart contract security: part 1 reentrancy attack. https://hackernoon.com/smart-contract-security-part-1-reentrancyattacks-ddb3b2429302 accessed 6 July 2020
Shahid, A., Almogren, A., Javaid, N., Al-Zahrani, F.A., Zuair, M., Alam, M.: Blockchain-based agri-food supply chain: A complete solution. IEEE Access 8, 69230–69243 (2020)
Wang, X., He, J., Xie, Z., Zhao, G., Cheung, S.C.: ContractGuard: Defend ethereum smart contracts with embedded intrusion detection. IEEE Trans. Serv. Comput. 13(2), 314–328 (2019)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Javed, M.U., Javaid, N., Malik, M.W. et al. Blockchain based secure, efficient and coordinated energy trading and data sharing between electric vehicles. Cluster Comput 25, 1839–1867 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10586-021-03435-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10586-021-03435-9