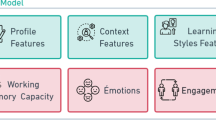
Abstract
The issues of accessibility, management, storage and organization of Learning Objects (LOs) in education systems are a high priority of the Thai Government. Incorporating personalized learning or learning styles in a learning object management system to improve the accessibility of LOs has been addressed continuously in the Thai education system. A proposed Learning Object Management Model (LOMM) is discussed in this paper which aims to adapt and optimize the learning process based on characteristics of the individual learners. This study aims to find the correlation between learning styles and LOs characteristics in the LOMM. Decision Tree and Apriori algorithms were used to generate a predictive model for the classification of learners. Development of the predictive model was based on survey results from 1,586 high school students in Nakhon Ratchasima province, Thailand. The diverse LOs characteristics were analyzed in order to find the correlation with learning styles of the learners. The classification model consists of 24 sub-models used to predict a learner’s class based on 8 groups of LOs characteristics. The best accuracy obtained in the study was 80.23%. Finally, for the next phase this approach has been designed to support the proposed LOMM and it is expected that it could be readily applied to other e-learning systems and digital repositories.


















Similar content being viewed by others
References
ADL. (2004). Scorm (2nd ed.). Retrieved November, 26, 2013, from http://www.adlnet.org.
Amira, R., & Jelas, Z. M. (2010). Teaching and learning styles in higher education institutions: Do they match? Procedia - Social and Behavioral Sciences, 7, 680–684.
Arch-int, N., & Arch-int, S. (2013). Semantic ontology mapping for interoperability of learning resource systems using a rule-based reasoning approach. Expert Systems with Applications, 40(18), 7428–7443.
Babadogan, C., & Kilic, G. (2012). Learning modalities of sixth grade students and the learning and teaching modalities of the english teachers at primary schools. Procedia - Social and Behavioral Sciences, 46, 2467–2471.
Baki, A., & Çakıroğlu, Ü. (2010). Learning objects in high school mathematics classrooms: Implementation and evaluation. Computers & Education, 55(4), 1459–1469.
Baykul, Y., Gürsel, M., Sulak, H., Ertekin, E., Yazıcı, E., Dülger, O., Aslan, Y., & Büyükkarcı, K. (2010). A validity and reliability study of grasha- riechmann student learning style scale. International Journal of Human and Social Sciences, 5(3), 177–184.
Boydak, A. (2001). Öğrenme stilleri. İstanbul: Beyaz yayınları.
Chang, Y.-C., Kao, W.-Y., Chu, C.-P., & Chiu, C.-H. (2009). A learning style classification mechanism for e-learning. Computers & Education, 53(2), 273–285.
Chen, C.-M. (2008). Intelligent web-based learning system with personalized learning path guidance. Computers & Education, 51(2), 787–814.
Chen, W., & Persen, R. (2012). Recommending collaboratively generated knowledge. Computer Science and Information Systems, 9(2), 871–892.
Dağ, F., & Geçer, A. (2009). Relations between online learning and learning styles. Procedia - Social and Behavioral Sciences, 1(1), 862–871.
DCMI. (1995). Dublin core metadata element set, version 1.1. Retrieved November, 26, 2013, from http://dublincore.org/documents/dces/.
de Boer, J., Kommers, P. A. M., & de Brock, B. (2011). Using learning styles and viewing styles in streaming video. Computers & Education, 56(3), 727–735.
Dinçol, S., Temel, S., Oskay, Ö. Ö., Erdoğan, Ü. I., & Yılmaz, A. (2011). The effect of matching learning styles with teaching styles on success. Procedia - Social and Behavioral Sciences, 15, 854–858.
DSpace. (2013). Top reasons to use dspace. Retrieved November, 26, 2013, from http://www.dspace.org/why-use.
Dunn, R., & Dunn, K. (1993). Teaching secondary students through their individual learning styles practical approaches for grades 7-12. Boston: Ailyn and Bacon.
Grasha, A. F., & Riechmann, S. W. (1974). A rational to developing and assessing the construct validity of a student learning styles scale instrument. Journal of Psychology, 87(2), 213–223.
Grasha, A. F., & Yangarber-Hicks, N. (2000). Integrating teaching styles and learning styles with instructional technology. College Teaching, 48(1), 2–10.
Honigsfeld, A., & Dunn, R. (2006). Learning-style characteristics of adult learners. The Delta Kappa Gamma Bulletin, Winter, 2006, 14–31.
IEEE. (2002). Final 1484.12.1 lom draft standarddocument Retrieved November, 26, 2013, from http://ltsc.ieee.org/wg12/20020612-Final-LOM-Draft.html.
IMS. (2001). Ims learning resource meta-data information model Retrieved November, 26, 2013, from http://www.imsproject.org/.
Jovanović, J., Devedžić, V., Gašević, D., Hatala, M., Eap, T., Richards, G., & Brooks, C. (2007). Using semantic web technologies to analyze learning content. IEEE Internet Computing, 11(5), 45–53.
Kay, R. H., & Knaack, L. (2008). A formative analysis of individual differences in the effectiveness of learning objects in secondary school. Computers & Education, 51(3), 1304–1320.
Keefe, J.W. (1987). Learning style: Theory and practice. Reston, Virginia: National association of secondary school principals.
Klašnja-Milićević, A., Vesin, B., Ivanović, M., & Budimac, Z. (2011). E-learning personalization based on hybrid recommendation strategy and learning style identification. Computers & Education, 56(3), 885–899.
Knight, C., Gašević, D., & Richards, G. (2005). Ontologies to integrate learning design and learning content. Journal of Interactive Media in Education, 7, 1–24.
Lee, Y.-J. (2012). Developing an efficient computational method that estimates the ability of students in a web-based learning environment. Computers & Education, 58(1), 579–589.
Lin, C. F., Yeh, Y.-C., Hung, Y. H., & Chang, R. I. (2013). Data mining for providing a personalized learning path in creativity: An application of decision trees. Computers & Education, 68, 199–210.
Lu, H., Jia, L., Gong, S.-H., & Clark, B. (2007). The relationship of kolb learning styles, online learning behaviors and learning outcomes. Educational Technology & Society, 10(4), 187–196.
Maneenil, S., Srisa-ard, B., & Chookhampaeng, C. (2010). Causal factors influencing critical thinking of students in different learning styles. Journal of Education, Mahasarakham University, 4(4), 88–95.
Marković, S., & Jovanović, N. (2012). Learning style as a factor which affects the quality of E-Learning. Artificial Intelligence Review, 38(4), 303–312.
Martin, M.O., Mullis, I., Foy, P., & Stanco, G.M. (2012). TIMSS 2011 International Results in Science. Retrieved Febuary, 21, 2014, from http://timssandpirls.bc.edu/timss2011/international-results-science.html.
Miao, D., Duan, Q., Zhang, H., & Jiao, N. (2009). Rough set based hybrid algorithm for text classification. Expert Systems with Applications., 36(5), 9168–9174.
Ministry of Education. (2010). National education act of b.E.2542.
Montogomery, S.M., Groat, L.N. (1998). Student learning styles and their implications for teaching. The Center for Research on Learning and Teaching.
Moodle. (2013). Moodle sites. Retrieved November, 26, 2013, from http://moodle.org/sites/index.php?country=TH.
Ocepek, U., Bosnić, Z., Nančovska Šerbec, I., & Rugelj, J. (2013). Exploring the relation between learning style models and preferred multimedia types. Computers & Education, 69, 343–355.
Özpolat, E., & Akar, G. B. (2009). Automatic detection of learning styles for an e-learning system. Computers & Education, 53(2), 355–367.
Pashler, H., McDaniel, M., Rohrer, D., & Bjork, R. (2009). Learning styles-concepts and evidence. Psychological Science in the Public Interest, 9(3), 105–119.
Poisson M., (2000). Final report of the international workshop on the reform in the teaching of science and technology at primary and secondary level in ASIA: Comparative references to Europe. Retrieved Febuary, 21, 2014, from http://www.ibe.unesco.org/fileadmin/user_upload/archive/curriculum/China/Pdf/beijingrep.pdf.
Quinlan, J. R. (1986). Induction of decision trees. Machine Learning, 1, 81–106.
Quinlan, J. R. (1993). C.45: Programs for machine learning. San Francisco, CA: Morgan Kaufmann.
Raza, M. A., & Shah, A. F. (2011). Impact of favourite subject towards the scientific aptitude of the students at elementary level. Pakistan Journal of Social Sciences (PJSS), 31(1), 135–143.
Reiff, J. C. (1992). Learning styles. Washington, DC: National Education Association.
Tan, P.-N., Michael, S., Kumar, V. (2005). “Chapter 6. Association analysis - basic concepts and algorithms”. Introduction to data mining: Addison-Wesley.
TCU. (2013). Tcu globe gateway. Retrieved November, 26, 2013, from http://globe.thaicyberu.go.th/.
Thonthai, T. (2009). Learning styles of graduate diploma students in teaching profession at princess of Naradhiwas University. Princess of Naradhiwas University Journal, 1(3), 145–157.
TKC. (2013). Thailand knowledge center. Retrieved November, 26, 2013, from http://www.tkc.go.th/.
Tseng, J. C. R., Chu, H.-C., Hwang, G.-J., & Tsai, C.-C. (2008). Development of an adaptive learning system with two sources of personalization information. Computers & Education, 51(2), 776–786.
ULCC. (2003). Unesco thesaurus: Hierarchical list. Retrieved November, 26, 2013, from http://www2.ulcc.ac.uk/unesco/thesaurus.htm.
Verbert, K., Klerkx, J., Meire, M., Najjar, J., Duval, E. (2004). Towards a global component architecture for learning objects: An ontology based approach. Paper presented at the OTM 2004 Workshop on Ontologies, Semantics and E-Learning, Agia Napa, Cyprus.
Verbert, K., Jovanović, J., Duval, E., Gašević, D., & Meire, M. (2006). Ontology-based learning content repurposing: The alocom framework. International Journal on E-Learning, 5(1), 67–74.
Vesin, B., Ivanovic, M., Klasnja-Milicevic, A., & Budimac, Z. (2013). Ontology-based architecture with recommendation strategy in java tutoring system. Computer Science and Information Systems, 10(1), 237–261.
W3C. (2009). Skos simple knowledge organization system reference. Retrieved November, 26, 2013, from http://www.w3.org/TR/2009/REC-skos-reference-20090818/.
Wanapu, S., Fung, C.-C., Kajornrit, J., Niwattanakul, S., & Chamnongsri, N. (2014a). Improving performance of decision trees for recommendation systems by features grouping method. Recent Advances in Information and Communication Technology Advances in Intelligent Systems and Computing, 265, 223–232.
Wanapu, S., Fung, C.-C., Kajornrit, J., Niwattanakul, S., & Chamnongsri, N. (2014b). Selecting feature grouping and decision tree to improve results from the learning object management model (LOMM). JCIT: Journal of Convergence Information Technology, 9(3), 131–142.
Wang, M., Jia, H., Sugumaran, V., Ran, W., & Liao, J. (2011). A web-based learning system for software test professionals. IEEE Transactions on Education, 54(2), 263–272.
Wiley, D.A. (2000). A learning object design and sequencing theory. (Doctor of Philosophy), Brigham Young University, Provo, Utah-Brigham Young University. Retrieved from http://opencontent.org/docs/dissertation.pdf.
Zhang, Y., & Zhao, Y. (2003). Classification in multidimensional parameter space: Methods and examples. Publications of the Astronomical Society of the Pacific, 115(August 2003), 1006–1018.
Zhao, Y., & Zhang, Y. (2008). Comparison of decision tree methods for finding active objects. Advances in Space Research, 41(12), 1955–1959.
Acknowledgments
I would like to thank the Office of the Higher Education Commission, Thailand for providing the grant under the Higher Education Research Promotion and National Research University. I would also like to express my gratitude to Assistant Professor Dr. Issra Pramoolsook at the School of Foreign Languages, Suranaree University of Technology, for his assistance in correcting grammatical errors and English usage throughout this research paper.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wanapu, S., Fung, C.C., Kerdprasop, N. et al. An investigation on the correlation of learner styles and learning objects characteristics in a proposed Learning Objects Management Model (LOMM). Educ Inf Technol 21, 1113–1134 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10639-014-9371-3
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10639-014-9371-3