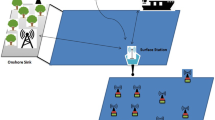
Abstract
Advances in the development of underwater full duplex sensors have meant they can now provide solutions to underwater acoustic sensor networks (UASN) that suffer from narrow bandwidth and long end-to-end transmission delay. In this paper, a full machine learning-based duplex medium access control (MAC) protocol for single hop underwater acoustic sensor networks is proposed to enhance the performance on throughput, delay and fairness access. The proposed protocol is designed in different access schemes for uplink and downlink transmission according to their main uses, respectively. The access scheme of the downlink is contention free to ensure that command information can be delivered to sensor nodes with a low collision rate. A hybrid scheme is utilized in the uplink to maximize the network throughput to meet transmission requirements of monitoring data collected by sensor nodes. In this way, transmission resources can be used more efficiently and fairer. In addition, as a unique characteristic of underwater acoustic communication, propagation time in the transmission is taken into consideration in the design of the MAC protocol. Simulation results and analysis exhibited that the proposed protocol performs significantly better than state-of-the-art MAC protocols for UASN on network throughput, end-to-end delay and transmission fairness. Underwater acoustic sensor networks (UASN), machine learning medium access control (MAC) protocol, full duplex transmission, network throughput, and end-to-end delay.
Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The data used to support the finding of this study are included in the article.
Abbreviations
- UASN:
-
Underwater acoustic sensor networks
- MAC:
-
Medium access control
- UAV:
-
Unmanned Aerial vehicle
- WSN:
-
Wireless Sensor Network
- SIC:
-
Self-interference cancellation
- AP :
-
Access Point
- TDMA:
-
Time division multiple access
- ALOHA:
-
Additive Links On-line Hawaii Area
- CSMA:
-
Carrier sense multiple access
- CSMA/CA:
-
Carrier sense multiple access with collision avoid
- DTMAC:
-
Delay Tolerant MAC protocol
- VI-ALOHA:
-
Variable Interval ALOHA
- CDMA:
-
Code division multiple access
- FDMA:
-
Frequency division multiple access
- RISM:
-
Receiver initiated spectrum management
- HCFMA:
-
Hybrid Collision-Free Medium Access
- UPMAC:
-
Underwater Practical MAC
- WT:
-
Wake up to transmit
- DIFS:
-
Distributed inter-frame spacing
- TD:
-
Transmission delay
- DTP:
-
Data transmission period
- SIFS:
-
Short inter-frame spacing
- U-DTP:
-
The uplink data transmission period
- D-DTP:
-
Downlink data transmission period
- CP:
-
Contending period
- CFP:
-
Contend free period
- CW:
-
Contending window
- DT:
-
Data transmission
- NS:
-
Next Subset
- FI :
-
Fairness index
- SNR:
-
Signal noise ratio
- PL:
-
Propagation loss
References
Jiang, S.: State-of-the-art Medium Access Control (MAC) protocols for underwater acoustic networks: a survey based on a mac reference model. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutor. 20(1), 96–131 (2018)
Gorma, W., et al.: CFDAMA-SRR: a MAC protocol for underwater acoustic sensor networks. IEEE Access 7, 60721–60735 (2019)
Su, Y., Zhou, Z., Jin, Z., Yang, Q.: A joint relay selection and power allocation MAC protocol for underwater acoustic sensor network. IEEE Access 8, 65197–65210 (2020)
Qu, F., Yang, H., Yu, G., Yang, L.: In-band full-duplex communications for underwater acoustic networks. IEEE Netw. 31(5), 59–65 (2017)
Kiran, R., Mehta, N.B., Thomas, J.: Design and network topology-specific renewal-theoretic analysis of a MAC protocol for asymmetric full-duplex WLANs. IEEE Trans. Commun. 67(12), 8532–8544 (Dec.2019)
Ahn, H., Lee, J., Kim, C., Suh, Y.: Frequency domain coordination MAC protocol for full-duplex wireless networks. IEEE Commun. Lett. 23(3), 518–521 (2019)
Centelles, D., Soriano, A., Martí, J.V., Sanz, P.J.: Underwater multirobot cooperative intervention MAC protocol. IEEE Access 8, 60867–60876 (2020)
Beniwal, M., Singh, R.P., Sangwan, A.: A localization scheme for underwater sensor networks without time synchronization. Wirel. Pers. Commun. 88(3), 537–552 (2016)
Chen, K.Y., Ma, M.D., Cheng, E., Yuan, F., Su, W.: A survey on MAC protocols for underwater wireless sensor networks. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutor. 16(3), 1433–1447 (2014)
Liu, J., Wang, J.: A MACA-based collision avoidance MAC protocol for underwater acoustic sensor networks. In: Proc. IEEE/OES China Ocean Acoust. (COA), Harbin, China, pp. 1–4 (2016)
Pu, L., et al.: Comparing underwater MAC protocols in real sea experiments. Comput. Commun. 56, 47–59 (2014)
Deng, M., Chen, H., Xie, L.: DCO-MAC: a hybrid MAC protocol for data collection in underwater acoustic sensor networks. Sensors 18(7), 2300 (2018)
Li, C., et al.: DTMAC: A delay tolerant MAC protocol for underwater wireless sensor networks. IEEE Sensors J. 16(11), 4137–4146 (Jun.2016)
Su, X., Chan, S., Bandai, M.: A cross-layer MAC protocol for underwater acoustic sensor networks. IEEE Sensors J. 16(11), 4083–4090 (Jun.2016)
Chen, K., Cheng, E., Yuan, F., Su, W., Ma, M.: The influence of MAC protocol on a non-synchronous localization scheme in large-scale UWSNs. IEEE Access 6, 16386–16394 (2018)
Liu, E., He, R., Chen, X., Yu, C.: Deep reinforcement learning based optical and acoustic dual channel multiple access in heterogeneous underwater sensor networks. Sensors 22, 1628 (2022)
Ng, H.-H., Soh, W.-S., Motani, M.: Saturation throughput analysis of the slotted BiC-MAC protocol for underwater acoustic networks. IEEE Trans. Wirel. Commun. 14(7), 3948–3960 (2015)
Lmai, S., Chitre, M., Laot, C., Houcke, S.: Throughput-efficient super-TDMA MAC transmission schedules in ad hoc linear underwater acoustic networks. IEEE J. Ocean. Eng. 42(1), 156–174 (Jan.2017)
Luo, Y., et al.: Receiver-initiated spectrum management for underwater cognitive acoustic network. IEEE Trans. Mob. Comput. 16(1), 198–212 (2017)
Yang, M., Gao, M.S., Foh, C.H., Cai, J.F.: Hybrid collision-free medium access (HCFMA) protocol for underwater acoustic networks: design and performance evaluation. IEEE J. Ocean. Eng. 40(2), 292–302 (2015)
Zhu, M., et al.: UPMAC: a localized load-adaptive MAC protocol for underwater acoustic networks. IEEE Sensors J. 16(11), 4110–4118 (2016)
Alim, A., Watanabe, T.: Full duplex medium access control protocol for asymmetric traffic. In: Proc. IEEE VTC-Fall, Montreal, QC, Canada, pp. 1–6 (2016)
Lee, J., Ahn, H., Kim, C.: An OFDMA two-symbol coordination MAC protocol for full-duplex wireless networks. In: Proc. ICOIN, Da Nang, Vietnam, pp. 344–348 (2017)
Funding
This work is supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China under Grant No.62001384, the Xi’an Key Laboratory of Intelligent Perception and Cultural Inheritance under Grant No. 2019219614SYS011CG033, and also supported by the Natural Science Basic Research Plan in Shaanxi Province of China under Grant No. 2020JQ-605, It is also founded by the China Postdoctoral Science Foundation under Grant No.2020M683694XB. Fundamental Research Funds for the Provincial Universities of Zhejiang, Grant No. GK219909299001-024.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest regarding the publication of this paper.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, W., Li, J., Wan, Y. et al. Machine Learning-Based Performance-Efficient MAC Protocol for Single Hop Underwater Acoustic Sensor Networks. J Grid Computing 20, 41 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10723-022-09636-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10723-022-09636-9