Abstract
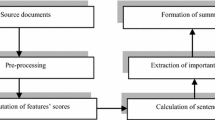
The goal of abstractive summarization of multi-documents is to automatically produce a condensed version of the document text and maintain the significant information. Most of the graph-based extractive methods represent sentence as bag of words and utilize content similarity measure, which might fail to detect semantically equivalent redundant sentences. On other hand, graph based abstractive method depends on domain expert to build a semantic graph from manually created ontology, which requires time and effort. This work presents a semantic graph approach with improved ranking algorithm for abstractive summarization of multi-documents. The semantic graph is built from the source documents in a manner that the graph nodes denote the predicate argument structures (PASs)—the semantic structure of sentence, which is automatically identified by using semantic role labeling; while graph edges represent similarity weight, which is computed from PASs semantic similarity. In order to reflect the impact of both document and document set on PASs, the edge of semantic graph is further augmented with PAS-to-document and PAS-to-document set relationships. The important graph nodes (PASs) are ranked using the improved graph ranking algorithm. The redundant PASs are reduced by using maximal marginal relevance for re-ranking the PASs and finally summary sentences are generated from the top ranked PASs using language generation. Experiment of this research is accomplished using DUC-2002, a standard dataset for document summarization. Experimental findings signify that the proposed approach shows superior performance than other summarization approaches.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Fattah, M.A., Ren, F.: GA, MR, FFNN, PNN and GMM based models for automatic text summarization. Comput. Speech Lang. 23(1), 126–144 (2009)
Barzilay, R., McKeown, K.R.: Sentence fusion for multidocument news summarization. Comput. Linguist. 31(3), 297–328 (2005)
Das, D., Martins, A.F.: A survey on automatic text summarization. Lit. Surv. Lang. Stat. II course at CMU 4, 192–195 (2007)
Ye, S., Chua, T.-S., Kan, M.-Y., Qiu, L.: Document concept lattice for text understanding and summarization. Inf. Process. Manag. 43(6), 1643–1662 (2007)
Luhn, H.P.: The automatic creation of literature abstracts. IBM J. Res. Dev. 2(2), 159–165 (1958)
Kupiec, J., Pedersen, J., Chen, F.: A trainable document summarizer. In: Proceedings of the 18th Annual International ACM SIGIR Conference on Research and Development in Information Retrieval, Washington, USA, 9–13 July 1995, pp. 68-73. ACM (1995)
Knight, K., Marcu, D.: Statistics-based summarization-step one: Sentence compression. In: Proceedings of the National Conference on Artificial Intelligence 2000, pp. 703–710. AAAI Press, Menlo Park (1999)
Larsen, B.: A trainable summarizer with knowledge acquired from robust NLP techniques. Adv. Autom. Text Summ. 71 (1999)
Fattah, M.A.: A hybrid machine learning model for multi-document summarization. Appl. Intell. 40(4), 592–600 (2014)
Erkan, G., Radev, D.R.: LexPageRank: prestige in multi-document text summarization. In: EMNLP 2004, pp. 365–371 (2004)
Erkan, G., Radev, D.R.: LexRank: graph-based lexical centrality as salience in text summarization. J. Artif. Intell. Res. (JAIR) 22(1), 457–479 (2004)
Mihalcea, R., Tarau, P.: A language independent algorithm for single and multiple document summarization (2005)
Wan, X., Yang, J.: Improved affinity graph based multi-document summarization. In: Proceedings of the Human Language Technology Conference of the NAACL, Companion Volume: Short Papers, New York City, USA, June 2006, pp. 181–184. ACL (2006)
Barzilay, R., McKeown, K.R., Elhadad, M.: Information fusion in the context of multi-document summarization. In: Proceedings of the 37th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics on Computational Linguistics, College Park, Maryland, 20–26 June 1999, pp. 550–557. ACL (1999)
Tanaka, H., Kinoshita, A., Kobayakawa, T., Kumano, T., Kato, N.: Syntax-driven sentence revision for broadcast news summarization. In: Proceedings of the 2009 Workshop on Language Generation and Summarisation, Suntec, Singapore, 6 August 2009, pp. 39–47. ACL (2009)
Genest, P.-E., Lapalme, G.: Framework for abstractive summarization using text-to-text generation. In: Proceedings of the workshop on monolingual text-to-text generation, Oregon, USA, 24 June 2011, pp. 64–73. ACL (2011)
Harabagiu, S.M., Lacatusu, F.: Generating single and multi-document summaries with gistexter. In: Document Understanding Conferences, Pennsylvania, USA, 11–12 July 2002, pp. 40–45. NIST (2002)
Genest, P.-E., Lapalme, G.: Fully abstractive approach to guided summarization. In: Proceedings of the 50th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics: Short Papers-Volume 2, Jeju Island, Korea, 8–14 July 2012, pp. 354–358. ACL (2012)
Lee, C.-S., Jian, Z.-W., Huang, L.-K.: A fuzzy ontology and its application to news summarization. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. Part B: Cybern. 35(5), 859–880 (2005)
Greenbacker, C.F.: Towards a framework for abstractive summarization of multimodal documents. ACL HLT 2011, 75 (2011)
Moawad, I.F., Aref, M.: Semantic graph reduction approach for abstractive text summarization. In: 7th International Conference on Computer Engineering andSystems (ICCES), 2012, pp. 132–138. IEEE (2012)
Page, L., Brin, S., Motwani, R., Winograd, T.: The PageRank citation ranking: bringing order to the web. (1999)
Mani, I., Bloedorn, E.: Summarizing similarities and differences among related documents. Inf. Retr. 1(1–2), 35–67 (1999)
Zhang, J., Sun, L., Zhou, Q.: A cue-based hub-authority approach for multi-document text summarization. In: Proceedings of 2005 IEEE International Conference on Natural Language Processing and Knowledge Engineering, IEEE NLP-KE’05, 2005, pp. 642–645. IEEE (2005)
Wei, F., Li, W., Lu, Q., He, Y.: A document-sensitive graph model for multi-document summarization. Knowl. Inf. Syst. 22(2), 245–259 (2010)
Ge, S.S., Zhang, Z., He, H.: Weighted graph model based sentence clustering and ranking for document summarization. In: 4th International Conference on Interaction Sciences (ICIS), 2011, pp. 90–95. IEEE (2011)
Nguyen-Hoang, T.-A., Nguyen, K., Tran, Q.-V.: TSGVi: a graph-based summarization system for Vietnamese documents. J. Ambient Intell. Humaniz. Comput. 3(4), 305–313 (2012)
Cheung, J.C.K., Penn, G.: Towards Robust Abstractive Multi-Document Summarization: A Caseframe Analysis of Centrality and Domain. In: ACL (1), pp. 1233–1242 (2013)
Glavaš, G., Šnajder, J.: Event graphs for information retrieval and multi-document summarization. Expert Syst. Appl. 41(15), 6904–6916 (2014)
Liu, F., Flanigan, J., Thomson, S., Sadeh, N., Smith, N.A.: Toward abstractive summarization using semantic representations. In: Proceedings of the 2015 Conference of the North American Chapter of the Association for Computational Linguistics: Human Language Technologies, Denver, Colorado, 1–5 June 2015, pp. 1077–1086. ACL (2015)
Bing, L., Li, P., Liao, Y., Lam, W., Guo, W., Passonneau, R.J.: Abstractive multi-document summarization via phrase selection and merging. In: Proceedings of the 53rd Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics and the 7th International Joint Conference on Natural Language Processing, Beijing, China, 26–31 July 2015, pp. 1587–1597. ACL (2015)
Boudin, F., Mougard, H., Favre, B.: Concept-based summarization using integer linear programming: from concept pruning to multiple optimal solutions. In: Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing (EMNLP) 2015, Lisbon, Portugal, 17–21 September 2015, pp. 1914–1918. ACL (2015)
Belkebir, R., Guessoum, A.: Concept generalization and fusion for abstractive sentence generation. Expert Syst. Appl. 53, 43–56 (2016)
Gambhir, M., Gupta, V.: Recent automatic text summarization techniques: a survey. Artif. Intell. Rev. 47(1), 1–66 (2017)
Cuomo, S., De Michele, P., Piccialli, F., Galletti, A., Jung, J.E.: IoT-based collaborative reputation system for associating visitors and artworks in a cultural scenario. Expert Syst. Appl. 79, 101–111 (2017)
Farina, R., Cuomo, S., De Michele, P., Piccialli, F.: A smart GPU implementation of an elliptic kernel for an ocean global circulation model. Appl. Math. Sci. 7(61–64), 3007–3021 (2013)
Piccialli, F., Cuomo, S., De Michele, P.: A regularized mri image reconstruction based on hessian penalty term on CPU/GPU systems. Proc. Comput. Sci. 18, 2643–2646 (2013)
Chianese, A., Marulli, F., Moscato, V., Piccialli, F.: A “smart” multimedia guide for indoor contextual navigation in cultural heritage applications. In: International Conference on Indoor Positioning and Indoor Navigation (IPIN), 2013, pp. 1–6. IEEE (2013)
Chianese, A., Piccialli, F.: SmaCH: a framework for smart cultural heritage spaces. In: 10th International Conference on Signal-Image Technology and Internet-Based Systems (SITIS), 2014, pp. 477–484. IEEE (2014)
Collobert, R., Weston, J., Bottou, L., Karlen, M., Kavukcuoglu, K., Kuksa, P.: Natural language processing (almost) from scratch. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 12, 2493–2537 (2011)
Barnickel, T., Weston, J., Collobert, R., Mewes, H.-W., Stümpflen, V.: Large scale application of neural network based semantic role labeling for automated relation extraction from biomedical texts. PLoS ONE 4(7), e6393 (2009)
Gatt, A., Reiter, E.: SimpleNLG: a realisation engine for practical applications. In: Proceedings of the 12th European Workshop on Natural Language Generation, Athens, Greece, 30–31 March 2009, pp. 90–93. ACL (2009)
Porter, M.F.: Snowball: a language for stemming algorithms (2001)
Jiang, J.J., Conrath, D.W.: Semantic similarity based on corpus statistics and lexical taxonomy. Preprint arXiv:cmp-lg/9709008 (1997)
Miller, G.A.: WordNet: a lexical database for English. Commun. ACM 38(11), 39–41 (1995)
Suanmali, L., Salim, N., Binwahlan, M.S.: Fuzzy logic based method for improving text summarization. Int. J. Comput. Sci. Inf. Secur. 2(1), 65–70 (2009)
Srinivas, M., Patnaik, L.M.: Genetic algorithms: a survey. Computer 27(6), 17–26 (1994)
Panda, S., Padhy, N.P.: Comparison of particle swarm optimization and genetic algorithm for FACTS-based controller design. Appl. Soft Comput. 8(4), 1418–1427 (2008)
Lin, C.-Y.: Rouge: a package for automatic evaluation of summaries. In: Proceedings of the ACL-04 workshop ontext summarization branches out, Barcelona, Spain, 25–26 July 2004, pp. 74–81. ACL (2004)
Brin, S., Page, L.: The anatomy of a large-scale hypertextual Web search engine. Comput. Netw. ISDN Syst. 30(1), 107–117 (1998)
Kleinberg, J.M.: Authoritative sources in a hyperlinked environment. J. ACM 46(5), 604–632 (1999)
Mihalcea, R., Tarau, P.: A language independent algorithm for single and multiple document summarization. http://digital.library.unt.edu/ark:/67531/metadc30965/ (2005)
Carbonell, J., Goldstein, J.: The use of MMR, diversity-based reranking for reordering documents and producing summaries. In: Proceedings of the 21st Annual International ACM SIGIR Conference on Research and Development in Information Retrieval, Melbourne, Australia, 24–28 August 1998, pp. 335–336. ACM (1998)
Jaccard, Paul: Étude comparative de la distribution florale dans une portion des Alpes et des Jura. Bulletin de la Société Vaudoise des Sciences Naturelles 37, 547–579 (1901)
Mihalcea, R., Corley, C., Strapparava, C.: Corpus-based and knowledge-based measures of text semantic similarity. In: AAAI 2006, pp. 775–780 (2006)
Nenkova, A., Passonneau, R.: Evaluating content selection in summarization: the pyramid method. In: 2004. NAACL-HLT (2004)
Over, P., Liggett, W.: Introduction to DUC: an intrinsic evaluation of generic news text summarization systems. http://www-nlpir.nist.gov/projects/duc/pubs/2002slides/overview.02.pdf (2002)
Acknowledgements
This research is supported by Higher Education Commission (HEC), Pakistan and Department of Computer Science, Islamia College, Peshawar, Pakistan. This research is also supported by Next-Generation Information Computing Development Program through the National Research Foundation (NRF) funded by the Korean Government (MSIT) (2017M3C4A7066010). This work is also supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) grant funded by the Korea Government (MSIP) (NRF2016R1A2A1A05005459).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Khan, A., Salim, N., Farman, H. et al. Abstractive Text Summarization based on Improved Semantic Graph Approach. Int J Parallel Prog 46, 992–1016 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10766-018-0560-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10766-018-0560-3