Abstract
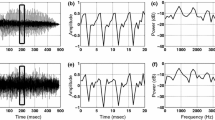
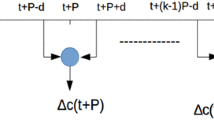
Automatic language identification (LID) system has extensively recognized in a real world multilanguage speech specific applications. The formation speech is relying on the vocal tract area which explores the excitation source information for LID task. In this paper, LID system utilizes sub segmental, segmental and supra segmental features from Linear Prediction residual of speech signal, represents various native language speech excitation source information. The glottal flow derivative of speech signal is obtained through iterative adaptive inverse filtering method. Moreover, the prosodic features of speech signal are extracted using short time Fourier transform due to its capability to process non-stationary signals. Finally, the deep neural network based Q-learning (DNNQL) algorithm has been employed for identification of the class label for a specific language. Experimental validation of the proposed approach is carried out using Indian language recorded database. Finally, the proposed LID system approach is performing well with 97.3% accuracy compared to other machine learning based approaches.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ambikairajah, E., Li, H., Wang, L., Yin, B., & Sethu, V. (2011). Language identification: A tutorial. IEEE Circuits and Systems Magazine, 11(2), 82–108.
Bouguelia, M. R., Nowaczyk, S., Santosh, K. C., & Verikas, A. (2018). Agreeing to disagree: Active learning with noisy labels without crowdsourcing. International Journal of Machine Learning and Cybernetics, 9(8), 1307–1319.
Dey, N., & Ashour, A. S. (2018a). Applied examples and applications of localization and tracking problem of multiple speech sources. In Direction of arrival estimation and localization of multi-speech sources (pp. 35–48). Cham: Springer.
Dey, N., & Ashour, A. S. (2018b). Sources localization and DOAE techniques of moving multiple sources. In Direction of arrival estimation and localization of multi-speech sources (pp. 23–34). Cham: Springer.
Dey, N., & Ashour, A. S. (2018c). Challenges and future perspectives in speech-sources direction of arrival estimation and localization. In Direction of arrival estimation and localization of multi-speech sources (pp. 49–52). Cham: Springer.
Diez, M., Varona, A., Penagarikano, M., Rodriguez-Fuentes, J. L., & Bordel, G. (2012) On the use of phone log-likelihood ratios as features in spoken language recognition. In Spoken language technology workshop (SLT), 2012 IEEE (pp. 274–279). IEEE.
Diez, M., Varona, A., Penagarikano, M., Rodriguez-Fuentes, J. L., & Bordel, G. (2013) Dimensionality reduction of phone log-likelihood ratio features for spoken language recognition. In INTERSPEECH (pp. 64–68).
Diez, M., Varona, A., Penagarikano, M., Rodriguez-Fuentes, J. L., & Bordel, G. (2014). On the projection of PLLRs for unbounded feature distributions in spoken language recognition. IEEE Signal Processing Letters, 21(9), 1073–1077.
Ferrer, L., Lei, Y., McLaren, M., & Scheffer, N. (2016). Study of senone-based deep neural network approaches for spoken language recognition. IEEE/ACM Transactions on Audio, Speech and Language Processing (TASLP), 24(1), 105–116.
Gamallo, P., Pichel, J. R., & Alegria, I. (2017). From language identification to language distance. Physica A: Statistical Mechanics and its Applications, 484, 152–162.
Gonzalez-Dominguez, J., Lopez-Moreno, I., Moreno, P. J., & Gonzalez-Rodriguez, J. (2015). Frame-by-frame language identification in short utterances using deep neural networks. Neural Networks, 64, 49–58.
Guijarrubia, V. G., & Torres, M. I. (2010). Text-and speech-based phonotactic models for spoken language identification of Basque and Spanish. Pattern Recognition Letters, 31(6), 523–532.
Jothilakshmi, S., Ramalingam, V., & Palanivel, S. (2012). A hierarchical language identification system for Indian languages. Digital Signal Processing, 22(3), 544–553.
Kockmann, M., & Burget, L. (2011). Application of speaker-and language identification state-of-the-art techniques for emotion recognition. Speech Communication, 53(9), 1172–1185.
Koolagudi, S., Rastogi, G., D., and Rao, K. S. (2012) Identification of language using mel-frequency cepstral coefficients (MFCC). Procedia Engineering, 38, 3391–3398.
Li, H., Ma, B., & Lee, K. A. (2013) Spoken language recognition: from fundamentals to practice. Proceedings of the IEEE, 101(5), 1136–1159.
Lopez-Moreno, I., Gonzalez-Dominguez, J., Martinez, D., Plchot, O., Gonzalez-Rodriguez, J., & Moreno, P. J. (2016). On the use of deep feed forward neural networks for automatic language identification. Computer Speech & Language, 40, 46–59.
Lu, X., Shen, P., Tsao, Y., & Kawai, H. (2017). Regularization of neural network model with distance metric learning for i-vector based spoken language identification. Computer Speech & Language, 44, 48–60.
Manchala, S., Prasad, V. K., & Janaki, V. (2014). GMM based language identification system using robust features. International Journal of Speech Technology, 17(2), 99–105.
Mary, L., & Yegnanarayana, B. (2008). Extraction and representation of prosodic features for language and speaker recognition. Speech Communication, 50(10), 782–796.
Masumura, R., Asami, T., Masataki, H., & Aono, Y. (2017) Parallel phonetically aware DNNs and LSTM-RNNS for frame-by-frame discriminative modeling of spoken language identification. In 2017 IEEE international conference on IEEE acoustics, speech and signal processing (ICASSP) (pp. 5260–5264).
Mounika, K. V., Achanta, S., Lakshmi, H. R., Gangashetty, S. V., & Vuppala, A. K. (2016) An investigation of deep neural network architectures for language recognition in Indian languages. In INTERSPEECH (pp. 2930–2933).
Mukherjee, H., Obaidullah, S. M., Santosh, K. C., Phadikar, S., & Roy, K. (2018). Line spectral frequency-based features and extreme learning machine for voice activity detection from audio signal. International Journal of Speech Technology. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10772-018-9525-6.
Orfanidou, E., Adam, R., Morgan, G., & McQueen, J. M. (2010). Recognition of signed and spoken language: Different sensory inputs, the same segmentation procedure. Journal of Memory and Language, 62(3), 272–283.
Roy, P., & Das, P. K. (2013). A hybrid VQ-GMM approach for identifying Indian languages. International Journal of Speech Technology, 16, 33–39.
Sadjadi, S. O., & Hansen, J. H. (2015). Mean Hilbert envelope coefficients (MHEC) for robust speaker and language identification. Speech Communication, 72, 138–148.
Sim, K. C., & Li, H. (2008). On acoustic diversification front-end for spoken language identification. IEEE Transactions on Audio, Speech, and Language Processing, 16(5), 1029–1037.
Sizov, A., Lee, K. A., & Kinnunen, T. (2017) Direct optimization of the detection cost for I-vector-based spoken language recognition. IEEE/ACM Transactions on Audio, Speech, and Language Processing, 25(3), 588–597.
Song, Y., Hong, X., Jiang, B., Cui, R., McLoughlin, I., & Dai, L. R. (2015), Deep bottleneck network based i-vector representation for language identification. In Sixteenth annual conference of the International Speech Communication Association.
Takçı, H., & Güngör, T. (2012). A high performance centroid-based classification approach for language identification. Pattern Recognition Letters, 33(16), 2077–2084.
Tanaka, T., Shinozaki, T., Watanabe, S., & Hori, T. (2016). Evolution strategy based neural network optimization and LSTM language model for robust speech recognition. Cit. on, 130.
Tong, R., Ma, B., Li, H., & Chng, E. S. (2009). A target-oriented phonotactic front-end for spoken language recognition. IEEE Transactions on Audio, Speech, and Language Processing, 17(7), 1335–1347.
Trabelsi, I., & Bouhlel, M. S. (2017) Feature selection for GUMI kernel-based SVM in speech emotion recognition. In Artificial intelligence: Concepts, methodologies, tools, and applications (pp. 941–953). IGI Global.
Wang, H., Leun, C.-C., Lee, T., Ma, B., & Li, H. (2013). Shifted-delta mlp features for spoken language recognition. IEEE Signal Processing Letters, 20(1), 15–18.
Zazo, R., Lozano-Diez, A., Gonzalez-Dominguez, J., Toledano, D. T., & Gonzalez-Rodriguez, J. (2016) Language identification in short utterances using long short-term memory (LSTM) recurrent neural networks. PloS ONE, 11(1), e0146917.
Zhu, D., Li, H., Ma, B., & Lee, C.-H. (2008). Optimizing the performance of spoken language recognition with discriminative training. IEEE Transactions on Audio, Speech, and Language Processing, 16(8), 1642–1653.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Das, H.S., Roy, P. Optimal prosodic feature extraction and classification in parametric excitation source information for Indian language identification using neural network based Q-learning algorithm. Int J Speech Technol 22, 67–77 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10772-018-09582-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10772-018-09582-6