Abstract
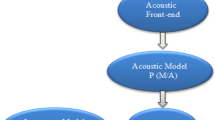
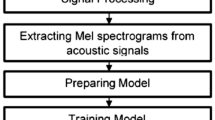
This paper describes the performance of Amazigh speech recognition via an interactive voice response in noisy conditions. The experiments were first conducted for the uncoded speech and then repeated for decoded speech in a noisy environment for different signal noise ratios (SNR). In this study, we analyze the effect of noise at different SNR levels on the ten first Amazigh digits which have collected from 22 Moroccan native speakers including both males and females. Our experiments results show that the degradation of accuracy was observed for all studied words by different degrees due to word components or the speech coding.








Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
Wavesurfer: http://sourceforge.net/projects/wavesurfer/
Sox Tool: http://sox.sourceforge.net/sox.html
References
Alsulaiman, M., Mahmood, A., & Muhammad, G. (2017). Speaker recognition based on Arabic phonemes. Speech Communication,86, 42–51.
Benahmed, Y., Selouani, S. A., O’Shaughnessy, D., & Abolhassani, A. H. (2011). Real-life speech-enabled system to enhance interaction with RFID networks in noisy environments. In 2011 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP) (pp. 1781–1784). IEEE.
Boukous, A. (2009). Phonologie de l’amazighe. Institut royal de la culture amazighe: Rabat.
Chaker, S. (1984). Textes en linguistique berbère: introduction au domaine berbère. Paris: Ed. du C.N.R.S.
Deng, L., Hinton, G., & Kingsbury, B. (2013). New types of deep neural network learning for speech recognition and related applications: An overview. In 2013 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (pp. 8599–8603). IEEE.
Espana-Bonet, C., & Fonollosa, J. A. (2016). Automatic speech recognition with deep neural networks for impaired speech. In International Conference on Advances in Speech and Language Technologies for Iberian Languages (pp. 97–107). Springer, Cham.
Feng, X., Zhang, Y., & Glass, J. (2014). Speech feature denoising and dereverberation via deep autoencoders for noisy reverberant speech recognition. In 2014 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP) (pp. 1759–1763). IEEE.
Fousek, P., Pollak, P. (2003). Additive noise and channel distortionrobust parameterization tool—Performance evaluation on Aurora 2&3. In Eurospeech (pp. 1785–1788).
Goel, S., Garg, V., Ranjan, P., Rao, S., & Bhattacharya, M. (2009). ASR system integration with asterisk for SIP or IAX softphone clients. In 2009 International Association of Computer Science and Information Technology-Spring Conference (pp. 100–104). IEEE.
Gong, Y. (1995). Speech recognition in noisy environments: A survey. Speech Communication,16, 261.
Hamidi, M., Satori, H., and Satori, K. (2016). Amazigh digits speech recognition on IVR server. Advances in Information Technology: Theory and Application 1(1).
Hamidi, M., Satori, H., & Satori, K. (2016b). Implementing a voice interface in VOIP network with IVR server using Amazigh digits. The International Journal of Multi-disciplinary Sciences,2, 38–43.
Hamidi, M., Satori, H., Zealouk, O., & Satori, K. (2019). Speech coding effect on Amazigh alphabet speech recognition performance. Journal of Advanced Research in Dynamical and Control Systems,11(2), 1392–1400.
Hamidi, M., Satori, H., Zealouk, O., Satori, K., & Laaidi, N. (2018). Interactive voice response server voice network administration using hidden markov model speech recognition system. In 2018 Second World Conference on Smart Trends in Systems, Security and Sustainability (WorldS4) (pp. 16–21). IEEE.
Handley, M., Schulzrinne, H., Schooler, H., et al. (1999). RFC 2543. SIP: Session Initiation Protocol
Hansen, J. H., Zhang, X., Akbacak, M., Yapanel, U. H., Pellom, B., Ward, W., & Angkititrakul, P. (2005). CU-MOVE: Advanced in-vehicle speech systems for route navigation. In DSP for in-vehicle and mobile systems (pp. 19–45). Springer, Boston, MA.
Huang, X., Acero, A., Hon, H. W., & Foreword By-Reddy, R. (2001). Spoken language processing: A guide to theory, algorithm, and system development. Upper Saddle River: Prentice hall.
Junqua, J. C., & Haton, J. P. (2012). Robustness in automatic speech recognition: fundamentals and applications (Vol. 341). New York: Springer.
Karapantazis, S., & Pavlidou, F. N. (2009). VoIP: A comprehensive survey on a promising technology. Computer Networks,53(12), 2050–2090.
Kim, H. K., & Rose, R. C. (2003). Cepstrum-domain acoustic feature compensation based on decomposition of speech and noise for ASR in noisy environments. IEEE Transactions on Speech and Audio Processing,11(5), 435–446.
Kumar, A., and Thorenoor, S. G. (2011). Analysis of IP Network for different Quality of Service. In International Symposium on Computing, Communication, and Control (ISCCC), Proc. of CSIT (Vol. 1).
Li, J., Deng, L., Gong, Y., & Haeb-Umbach, R. (2014). An overview of noise-robust automatic speech recognition. IEEE/ACM Transactions on Audio, Speech, and Language Processing,22, 745–777.
Ouakrim, O. (1995). Fonética y fonología del Bereber. Survey: University of Autònoma de Barcelona.
Passricha, V., & Aggarwal, R. K. (2018). Convolutional neural networks for raw speech recognition. From natural to artificial intelligence: Algorithms and applications, 21
Popović, B., Ostrogonac, S., Pakoci, E., Jakovljević, N., & Delić, V. (2015). Deep neural network based continuous speech recognition for Serbian using the Kaldi toolkit. In International Conference on Speech and Computer (pp. 186–192). Springer, Cham.
Rabiner, L. R. (1989). A tutorial on hidden Markov models and selected applications in speech recognition. Proceedings of the IEEE,77(2), 257–286.
Rajnoha, J., & Pollák, P. (2011). ASR systems in noisy environment: Analysis and solutions for increasing noise robustness. Radioengineering,20(1), 74–83.
Ridouane, R. (2003) Suites de consonnes en berbère: phonétique et phonologie. PhD diss. Université de la Sorbonne nouvelle-Paris III.
Sakka, Z., Techini, E., & Bouhlel, M. (2017). Using geometric spectral subtraction approach for feature extraction for DSR front-end Arabic system. International Journal of Speech Technology,20(3), 645–650.
Satori, H., & Elhaoussi, F. (2014). Investigation Amazigh speech recognition using CMU tools. International Journal of Speech Technology,17(3), 235–243.
Satori, H., Zealouk, O., Satori, K., & ElHaoussi, F. (2017). Voice comparison between smokers and non-smokers using HMM speech recognition system. International Journal of Speech Technology,20(4), 771–777.
Selouani, S.A., Abolhassani, A.H., and O’Shaughnessy, D. (2007). Speech enhancement using PCA and variance of the reconstruction error in distributed speech recognition. In IEEE ASRU Workshop, Kyoto (pp. 19–23).
Shah, S. A. A., ul Asar, A., & Shaukat, S. (2009). Neural Network Solution for Secure Interactive Voice Response. World Applied Sciences Journal,6(9), 1264–1269.
Shariah, M. A. A., Ainon, R. N., Zainuddin, R., & Khalifa, O. O. (2007). Human computer interaction using isolated-words speech recognition technology. In 2007 International Conference on Intelligent and Advanced Systems (pp. 1173–1178). IEEE.
Zealouk, O., Satori, H., Hamidi, M., Laaidi, N., & Satori, K. (2018a). Vocal parameters analysis of smoker using Amazigh language. International Journal of Speech Technology,21(1), 85–91.
Zealouk, O., Satori, H., Hamidi, M., & Satori, K. (2018b). Voice pathology assessment based on automatic speech recognition using Amazigh digits. In Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Smart Digital Environment (pp. 100–105). ACM.
Zealouk, O., Satori, H., Hamidi, M., & Satori, K. (2018c). Speech recognition for moroccan dialects: Feature extraction and classification methods. Journal of Advanced Research in Dynamical and Control Systems,11(2), 1401–1408.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hamidi, M., Satori, H., Zealouk, O. et al. Amazigh digits through interactive speech recognition system in noisy environment. Int J Speech Technol 23, 101–109 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10772-019-09661-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10772-019-09661-2