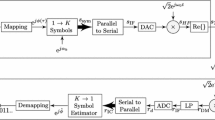
Estimation of channel and data characteristics by the receiver is important in adaptive wireless transmission protocols and in cognitive radio. This paper formulates the estimation problem with the help of an illustrative example from the IEEE 802.11a OFDM standard. The problem reduces to the estimation of the common component variance and mixing probabilities in a finite Gaussian mixture, with known values for component means. Using the known component means, μ1, ... , μ M , a set of non-linear transformations, \({\sinh \mu_i x}\) and \({\cosh \mu_i x}\) of the data (mixture random variable X) are used to develop convergent and computationally efficient estimators for both the noise variance and the vector of symbol probabilities. The estimation equations can be implemented recursively or with a batch processing algorithm. Asymptotic variances of the estimates and the Cramer–Rao minimum variance bounds are derived. The estimates converge to true unknowns even when the sequences of noise and data symbols are dependent sequences. The OFDM example is simulated with parameters corresponding to the highest acceptable error rate. For a time-varying channel model chosen from the literature, it is shown that our estimator receives considerably more than adequate amount of data during an average time interval of unchanging channel characteristics. Analytical results, numerical results and related issues are discussed.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
R. W. Brodersen, A. Wolisz, D. Cabric, S. M. Mishra, and D. Willkomm, Corvus: A cognitive radio approach for usage of virtual unlicensed spectrum. http://www.bwrc.eecs.berkeley.edu/Research/MCMA/CR_White_paper_final1.pdf, White Paper, July 2004
J. Mitola III, Software Radio – Cognitive Radio. http://www.ourworld.compuserve.com/homepages/jmitola
Pursley M. B., Wilkins C. S. (2000) Adaptive transmission for direct-sequence spread-spectrum communications over multipath channels. International Journal of Wireless Information Networks 7(2):69–77
Gass Jr. J. H., Pursley M. B., Russell H. B., Wysocarski J. S. (2001) An adaptive-transmission protocol for frequency-hop wireless communication Networks. Wireless Networks 7:487–495
McLachlan G., Krishnan T. (1997) The EM Algorithm and Extensions. Wiley Interscience, NY, USA
Silverman B. W. (1986) Density Estimation for Statistics and Data Analysis. Chapman & Hall, FL, USA
Everitt B. S., Hand D. J. (1981) Finite Mixture Distributions. Chapman & Hall, FL, USA
Dattatreya G. R., Fang X. (2003) Parameter estimation: known vector signals in unknown Gaussian noise. Pattern Recognition 36:2317–2332
Krishnamurthy V., Moore B. (1993) On-line estimation of hidden Markov model parameters based on Kullback–Leibler information measure. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing 41:557–573
Tugnait J. K., Tong L., Ding Z. (2000) Single-user channel estimation and equalization. IEEE Signal Processing Magazine 17:17–28
Wang X., Chen R. (2001) Blind turbo equalization in Gaussian and impulsive noise. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology 50:1092–1105
Monin A., Salut G. (2001) Minimum variance estimation of parameters constrained by bounds. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing 49:246–248
Pham D. S., Zoubir A. M. (2005) A sequential algorithm for robust parameter estimation. IEEE Signal Processing Letters 12:21–24
Farquharson M., O’Shea P., Ledwich G. (2005) A computationally efficient technique for estimating the parameters of polynomial-phase signals from noisy observation. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing 53:3337–3342
X. Deng, A. M. Haimovich, and J. Garcia-Frias, Decision Directed iterative channel estimation for MIMO systems. IEEE International Conference on Communications (ICC ’03), pp. 2326–2329, 2003
S. Jeong and R. M. Gray. A comparison of EM and GMVQ in estimating Gauss mixtures: application to probabilistic image retrieval. Proceedings of ICASSP 2005, Vol. 5, v/361–v/364, 2005
S. A. Vorobyov, Y. C. Eldar, A. Nemirovski, and A. B. Gershman, Probability-constrained approach to estimation of random Gaussian parameters. 1st IEEE International Workshop on Computational Advances in Multi-Sensor Adaptive Processing, pp. 101–104, 2005
Proakis J. G. (1995) Digital Communications. McGraw Hill, NY, USA
Tanenbaum A. S. (2003) Computer Networks. Prentice-Hall, NJ, USA
Papoulis A. (1984) Probability, Random Variables and Stochastic Processes. McGraw Hill, NY, USA
Lancaster P., Tismenetsky M. (1985) The Theory of Matrices: 2nd edition. Academic Press Inc., CA, USA
Serfling R. J. (1980) Approximation Theorems of Mathematical Statistics. John Wiley & Sons, NY, USA
Folland G. B. (1999) Real Analysis: Modern Techniques and Their Applications: 2nd Edition. John Wiley & Sons, NY, USA
Judge G. G., Hill R. C., Griffiths W. E., Lütkepohl H., Lee T. (1982) Introduction to the Theory and Practice of Econometrics. John Wiley & Sons, NY, USA
van Trees H. L. (1968) Detection, Estimation and Modulation Theory, Part 1. John Wiley & Sons, NY, USA
Dattatreya G. R., Kanal L. N. (1990) Asymptotically efficient estimation of prior probabilities in multiclass finite mixtures. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory 37(3):482–489
Davisson L. D., Schwartz S. C. (1970) Analysis of a decision-directed receiver with unknown priors. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory 16:270–276
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Singh, L.N., Dattatreya, G.R. Channel and Data Estimation for Ad Hoc Networks and Cognitive Radio. Int J Wireless Inf Networks 14, 17–31 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10776-006-0052-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10776-006-0052-z