Abstract
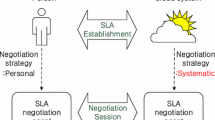
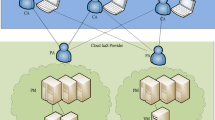
Since participants in a Cloud may be independent bodies, some mechanisms are necessary for resolving the different preferences to establish a service-level agreement (SLA) for Cloud service reservations. Whereas there are some mechanisms for supporting SLA negotiation, there is little or no negotiation support involving price, time slot, and QoS issues concurrently for a Cloud service reservation. For the concurrent price, timeslot, and QoS negotiation, a tradeoff algorithm to generate and evaluate a proposal which consists of price, timeslot, and QoS proposals is necessary. The contribution of this work is designing a multi-issue negotiation mechanism to facilitate 1) concurrent price, time slot, and QoS negotiations including the design of QoS utility functions and 2) adaptive and similarity-based trade-off proposals for price, time slots, and level of QoS issues. The tradeoff algorithm referred to as “adaptive burst mode” is especially designed to increase negotiation speed, total utility, and to reduce computational load for evaluating proposals by adaptively generating concurrent set of proposals. The empirical results obtained from simulations carried out using an agent-based testbed suggest that using the negotiation mechanism, (i) a consumer and a provider agent have a mutually satisfying agreement on price, time slot, and QoS issues in terms of the aggregated utility and (ii) the fastest negotiation speed with (iii) comparatively lower number of evaluated proposals in a negotiation.















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Brandic, I., Music, D., & Dustdar, S. (2009). Service mediation and negotiation bootstrapping as first achievements towards self-adaptable grid and cloud services. In Proc. Grids meet Autonomic Computing Workshop 2009 (GMAC 2009), In conjunction with the 6th International Conference on Autonomic Computing and Communications, Barcelona, Spain, June 2009.
Buyya, R., Yeo, C. S., Venugopal, S., Broberg, J., & Brandic, I. (2009). Cloud computing and emerging IT platforms: Vision, hype, and reality for delivering computing as the 5th utility. Future Generation Computer Systems, 25(6), 599–616.
Czajkowski, K., Foster, I., Kesselman, C., Sander, V., & Tuecke, S. (2002). SNAP: A protocol for negotiating service level agreements and coordinating resource management in distributed systems. in Proc. 8th Workshop on Job Scheduling Strategies for Parallel Processing, Edinburgh Scotland, July 2002.
Foster, I., Kesselman, C., Lee, C., Lindell, B., Nahrstedt, K., & Roy, A. (1999). A distributed resource management architecture that supports advance reservations and co-allocation. in Proc. 7th International Workshop on Quality of Service (IWQoS’99), London, UK. IEEE CS Press, LA, USA, Mar. 1999.
Foster, I., Roy, A., & Sander, V. (2000). A quality of service architecture that combines resource reservation and application adaptation. In proc. 8th International Workshop on Quality of Service, 2000.
Gimpel, H., Ludwig, H., Dan, A., & Kearney, R. (2003). PANDA: Specifying policies for automated negotiations of service contracts. in Proc. ICSOC, vol. 2910, LNCS, New York, 2003, pp. 287–302.
Goiri, Í., Guitart, J., & Torres, J. (2012). Economic model of a Cloud provider operating in a federated Cloud. Information Systems Frontiers, 14(4), 827–843.
Hassan, M.M., Hossain, M.S., Sarkar, A.M.J., & Huh, E.-N. (2012). Cooperative game-based distributed resource allocation in horizontal dynamic cloud federation platform. Information Systems Frontiers, Online First. June. 2012.
Jafarpour, N., & Khayyambashi, M. R. (2010). QoS-aware Selection of Web Service Compositions using Harmony Search Algorithm. Journal of Digital Information Management, 8(3), 160–166.
Lang, F. (2005). Developing dynamic strategies for multi-issue automated contracting in the agent based commercial grid. in Proc. IEEE Int. Symp. Cluster Comput. Grid (CCGrid05), Workshop Agent-Based Grid Econ, Cardiff, U.K, pp. 342–349, May 2005.
Lawley, R., Luck, M., Decker, K., Payne, T. R., & Moreau, L. (2003). Automated negotiation between publishers and consumers of grid notifications. Parallel Processing Letters, 13(4), 537–548.
Maximilien, E. M., & Singh, M. P. (2004). A framework and ontology for dynamic Web services selection. IEEE Internet Computing Magazine, 8(5), 84–93.
Menasce, D. A. (2002). Qos issues in web services. IEEE Internet Computing, 6(6), 72–75.
Netto, M.A., Bubendorfer, K., & Buyya, R. (2007). SLA-based advance reservations with flexible and adaptive time QoS parameters. in Proc. 5th international conference on Service-Oriented Computing, Vienna, Austria, Sep. 2007.
Papazoglou, M. P., Traverso, P., Dustdar, S., & Leymann, F. (2007). Service-oriented computing: State of the art and research challenges. Computer, 40(11), 38–45.
Paschke, A., Dietrich, J., & Kuhla, K. (2005). A logic based SLA management framework. in Proc. Semantic Web and Policy Workshop (SWPW), 4th Semantic Web Conference(ISWC 2005), Galway, Ireland, 2005.
Rubinstein, A. (1982). Perfect equilibrium in a bargaining model. Econometrica, 50(1), 97–109.
Sim, K. M. (2005). Equilibria, Prudent Compromises, and the "Waiting" Game. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics - Part B: Cybernetics, 35(4), 712–724.
Sim, K. M. (2006). G-commerce, market-driven G-negotiation agents and Grid resource management. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics - Part B: Cybernetics, 36(6), 1381–1394.
Sim, K. M. (2010a). Grid resource negotiation: survey and new directions. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics - Part C: Applications and Reviews, 40(3), 245–257.
Sim, K. M. (2010b). Towards complex negotiation for cloud economy. In proc. the 5th International Conference on Grid and Pervasive Computing (GPC 2010), LNCS 6104, pp. 395–406, 2010. May 10–13, Hualian, Taiwan.
Sim, K. M. (2012). Agent-based cloud computing. IEEE Transactions on Services Computing, 5(4), 564–577.
Sim, K. M. (2013). Complex and Concurrent Negotiations for Multiple Interrelated e-Markets. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, 43(1), 230–245.
Sim, K. M., & Shi, B. (2010). Concurrent Negotiation and Coordination for Grid Resource Coallocation. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics - Part B, 40(3), 753–766.
Son, S., & Sim, K.M. (2010). An adaptive tradeoff algorithm for multi-issue SLA negotiation. in Proc. The 2010 Conference on Grid and Distributed Computing. Grid and Distributed Computing, Control and Automation. Communications in Computer and Information Science (CCIS), vol. 121, pp. 32–41, 2010.
Son, S., & Sim, K.M. (2011). A negotiation mechanism that facilitates the price-timeslot-qos negotiation for establishing SLAs of cloud service reservation. In Proc. Int. Conf. on Networked Digital Technologies (NDT 2011), Communications in Computer and Information Science (CCIS), vol. 136, pp. 432–446, 2011.
Son, S., & Sim, K. M. (2012). A price and time slot negotiation mechanism for cloud service reservations. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics - Part B: Cybernetics, 42(3), 713–728. doi:10.1109/TSMCB.2011.2174355.
Venugopal, S., Chu, X., & Buyya, R. (2008). A negotiation mechanism for advance resource reservation using the alternate offers protocol. In proc. 16th Int. Workshop on Quality of Service (IWQoS 2008), Twente, The Netherlands. June 2008.
Yan, J., Kowalczyk, R., Lin, J., Chhetri, M. B., Goh, S. K., & Zhang, J. (2007). Autonomous service level agreement negotiation for service composition provision. Future Generation Computer Systems, 23(6), 748–759.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Korea Research Foundation Grant funded by the Korean Government (MEST) (KRF-2009-220-D00092) and the DASAN International Faculty Fund (project code: 140316). The authors would like to thank the Guest Editors and the anonymous referees for their comments and suggestions.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Son, S., Sim, K.M. Adaptive and similarity-based tradeoff algorithms in a price-timeslot-QoS negotiation system to establish cloud SLAs. Inf Syst Front 17, 565–589 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10796-013-9432-y
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10796-013-9432-y