Abstract
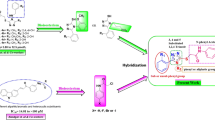
Here, we report our results from quantitative structure–activity relationship studies on tyrosinase inhibitors. Interactions between benzoic acid derivatives and tyrosinase active sites were also studied using a molecular docking method. These studies indicated that one possible mechanism for the interaction between benzoic acid derivatives and the tyrosinase active site is the formation of a hydrogen-bond between the hydroxyl (aOH) and carbonyl oxygen atoms of Tyr98, which stabilized the position of Tyr98 and prevented Tyr98 from participating in the interaction between tyrosinase and ORF378. Tyrosinase, also known as phenoloxidase, is a key enzyme in animals, plants and insects that is responsible for catalyzing the hydroxylation of tyrosine into o-diphenols and the oxidation of o-diphenols into o-quinones. In the present study, the bioactivities of 48 derivatives of benzaldehyde, benzoic acid, and cinnamic acid compounds were used to construct three-dimensional quantitative structure–activity relationship (3D-QSAR) models using comparative molecular field (CoMFA) and comparative molecular similarity indices (CoMSIA) analyses. After superimposition using common substructure-based alignments, robust and predictive 3D-QSAR models were obtained from CoMFA (q 2 = 0.855, r 2 = 0.978) and CoMSIA (q 2 = 0.841, r 2 = 0.946), with 6 optimum components. Chemical descriptors, including electronic (Hammett σ), hydrophobic (π), and steric (MR) parameters, hydrogen bond acceptor (H-acc), and indicator variable (I), were used to construct a 2D-QSAR model. The results of this QSAR indicated that π, MR, and H-acc account for 34.9, 31.6, and 26.7% of the calculated biological variance, respectively. The molecular interactions between ligand and target were studied using a flexible docking method (FlexX). The best scored candidates were docked flexibly, and the interaction between the benzoic acid derivatives and the tyrosinase active site was elucidated in detail. We believe that the QSAR models built here provide important information necessary for the design of novel tyrosinase inhibitors.










Similar content being viewed by others
Literature Cited
Sánchez-Ferrer A, Rodríguez-López JN, García-Cánovas F, García-Carmona F (1995) Biochim Biophys Acta 1247:1
Chase MR, Raina K, Bruno J, Sugumaran M (2000) Insect Biochem Molec 30:953
Chen QX, Liu XD, Huang H (2003) Biochemistry-Moscow 68:644
Xu Y, Stokes AH, Freeman WM, Kumer SC, Vogt BA, Vrana KET (1997) Mol Brain Res 45:159
Oetting WS (2000) Pigm Cell Res 13:320
Ashida M, Brey P (1995) Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 92:10698
Fitzpatrick TB, Eisen AZ, Wolff K, Freedberg IM, Austen KF (1983) Dermatology in general medicine. New York, NY
Maeda K, Fukuda M (1991) J Soc Cosmet Chem 42:361
Wang SD, Luo WC, Gao XX (2004) Agr Sci China 3:923
Wang SD, Luo WC, Xu SJ, Ding Q (2005) Pestic Biochem Phys 82:52
Wang SD, Luo WC, Xiao T, Xue CB (2005) Biopestic Int 1:82
Wang XY, Liu CY, Zhang JD, Luo WC (2005) Insect Sci 12:231
Xue CB, Luo WC, Chen QX, Wang Q, Ke LN (2006) Insect Sci 13:251
Xue CB, Zhang L, Luo WC, Xie XY, Jiang L, Xiao T (2007) Bioorg Med Chem 15:2006
Cramer RD III, Patterson DE, Bunce JD (1988) J Amer Chem Soc 110:5959
Klebe G, Abraham U, Mietzner T (1994) J Med Chem 37:4130
Chen QX, Song KK, Wang Q, Huang H (2003) J Enzym Inhib Med Ch 18:491
Huang H, Liu XD, Chen QX (2003) J Xiamen Univer 42:97
Huang XH, Chen QX, Wang Q, Song KK, Wang J, Li S, Guan X (2006) Food Chem 94:1
Zhang JP, Chen QX, Song KK, Xie JJ (2006) Food Chem 95:579
Chen QX, Song KK, Qiu L, Liu XD, Huang H, Guo HY (2005) Food Chem 91:269
Shi Y, Chen QX, Wang Q, Song KK, Qiu L (2005) Food Chem 92:707
Wold S, Albano C, Dunn WJ III, Edlund U, Esbensen K, Geladi P, Hellberg S, Johanson E, Lindberg W, Sjostrom M (1984) NATO ASI Ser Ser C 138:17
Wold S, Rhue A, Wold H, Dunn WJI (1984) SIAM J Sci Stat Comput 5:735
Clark M, Cramer RD III (1993) Quant Struct-Act Relat 12:137
Li RL (2004) In structure activity relationships of drug. The Medicine Science and Technology Press, Beijing, BJ
Rarey M, Kramer B, Lengauer T, Kleb G (1996) J Mol Biol 261:470
Rarey M, Kramer B, Lengauer T (1997) J Comput Aid Mol Des 11:369
Yang GF, Jiang XH, Yang HZ (2002) Pest Manag Sci 58:1063
Yang GF, Liu HY, Yang HZ (1999) Pestic Sci 55:1143
Yang GF, Jiang XH, Ding Y, Yang HZ (2002) Acta Chim Sinica 60:134
Yang GF, Huang XQ (2006) Curr Pharm Design 12:4601
Wei DG, Yang GF, Wan J, Zhan CG (2005) J Agric Food Chem 53:1604
Li W, Kubo I (2004) Bioorg Med Chem 12:701
Acknowledgement
The present investigation was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of P. R. China (Grant NO. 30571237) and Research Fund for the Doctoral Program of Higher Education of China (NO. 20070434006).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xue, CB., Luo, WC., Ding, Q. et al. Quantitative structure–activity relationship studies of mushroom tyrosinase inhibitors. J Comput Aided Mol Des 22, 299–309 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10822-008-9187-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10822-008-9187-6