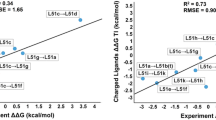
Abstract
Optimization of fragment size d-amino acid oxidase (DAAO) inhibitors was investigated using a combination of computational and experimental methods. Retrospective free energy perturbation (FEP) calculations were performed for benzo[d]isoxazole derivatives, a series of known inhibitors with two potential binding modes derived from X-ray structures of other DAAO inhibitors. The good agreement between experimental and computed binding free energies in only one of the hypothesized binding modes strongly support this bioactive conformation. Then, a series of 1-H-indazol-3-ol derivatives formerly not described as DAAO inhibitors was investigated. Binding geometries could be reliably identified by structural similarity to benzo[d]isoxazole and other well characterized series and FEP calculations were performed for several tautomers of the deprotonated and protonated compounds since all these forms are potentially present owing to the experimental pKa values of representative compounds in the series. Deprotonated compounds are proposed to be the most important bound species owing to the significantly better agreement between their calculated and measured affinities compared to the protonated forms. FEP calculations were also used for the prediction of the affinities of compounds not previously tested as DAAO inhibitors and for a comparative structure–activity relationship study of the benzo[d]isoxazole and indazole series. Selected indazole derivatives were synthesized and their measured binding affinity towards DAAO was in good agreement with FEP predictions.
Graphical Abstract














Similar content being viewed by others
References
Badner JA, Gershon ES (2002) Meta-analysis of whole-genome linkage scans of bipolar disorder and schizophrenia. Mol Psychiatry 7(4):405–411
Burnet PWJ, Eastwood SL, Bristow GC, Godlewska BR, Sikka P, Walker M, Harrison PJ (2008) d-amino acid oxidase activity and expression are increased in schizophrenia. Mol Psychiatry 13(7):658–660
Millan MJ (2005) N-methyl-d-aspartate receptors as a target for improved antipsychotic agents: novel insights and clinical perspectives. Psychopharmacology 179(1):30–53
Ferraris D, Duvall B, Ko Y-S, Thomas AG, Rojas C, Majer P, Hashimoto K, Tsukamoto T (2008) Synthesis and biological evaluation of d-amino acid oxidase inhibitors. J Med Chem 51(12):3357–3359
Wolosker H (2007) NMDA receptor regulation by d-serine: new findings and perspectives. Mol Neurobiol 36(2):152–164
Adage T, Trillat A-C, Quattropani A, Perrin D, Cavarec L, Shaw J, Guerassimenko O, Giachetti C, Gréco B, Chumakov I, Halazy S, Roach A, Zaratin P (2008) In vitro and in vivo pharmacological profile of AS057278, a selective d-amino acid oxidase inhibitor with potential anti-psychotic properties. Eur Neuropsychopharmacol 18(3):200–214
Lange JHM, Venhorst J, van Dongen MJP, Frankena J, Bassissi F, de Bruin NMWJ., den Besten C, de Beer SBA, Oostenbrink C, Markova N, Kruse CG (2011) Biophysical and physicochemical methods differentiate highly ligand-efficient human d-amino acid oxidase inhibitors. Eur J Med Chem 46(10):4808–4819
Sparey T, Abeywickrema P, Almond S, Brandon N, Byrne N, Campbell A, Hutson PH, Jacobson M, Jones B, Munshi S, Pascarella D, Pike A, Prasad GS, Sachs N, Sakatis M, Sardana V, Venkatraman S, Young MB (2008) The discovery of fused pyrrole carboxylic acids as novel, potent d-amino acid oxidase (DAO) inhibitors. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 18(11):3386–3391
Smith SM, Uslaner JM, Yao L, Mullins CM, Surles NO, Huszar SL, McNaughton CH, Pascarella DM, Kandebo M, Hinchliffe RM, Sparey T, Brandon NJ, Jones B, Venkatraman S, Young MB, Sachs N, Jacobson MA, Hutson PH (2009) The behavioral and neurochemical effects of a novel d-amino acid oxidase inhibitor compound 8 [4H-Thieno [3,2-B]pyrrole-5-carboxylic acid] and d-serine. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 328(3):921–930
Duplantier AJ, Becker SL, Bohanon MJ, Borzilleri KA, Chrunyk BA, Downs JT, Hu LY, El-Kattan A, James LC, Liu S, Lu J, Maklad N, Mansour MN, Mente S, Piotrowski MA, Sakya SM, Sheehan S, Steyn SJ, Strick CA, Williams VA, Zhang L (2009) Discovery, SAR, and pharmacokinetics of a novel 3-Hydroxyquinolin-2(1H)-one series of potent d-amino acid oxidase (DAAO) inhibitors. J Med Chem 52(11):3576–3585
Berry JF, Ferraris DV, Duvall B, Hin N, Rais R, Alt J, Thomas AG, Rojas C, Hashimoto K, Slusher BS, Tsukamoto T (2012) Synthesis and SAR of 1-hydroxy-1H-Benzo[d]imidazol-2(3H)-ones as inhibitors of d-amino acid oxidase. ACS Med Chem Lett 3(10):839–843
Hopkins SC, Heffernan MLR, Saraswat LD, Bowen CA, Melnick L, Hardy LW, Orsini MA, Allen MS, Koch P, Spear KL, Foglesong RJ, Soukri M, Chytil M, Fang QK, Jones SW, Varney MA, Panatier A, Oliet SHR, Pollegioni L, Piubelli L, Molla G, Nardini M, Large TH (2013) Structural, kinetic, and pharmacodynamic mechanisms of d-amino acid oxidase inhibition by small molecules. J Med Chem 56(9):3710–3724
Abel R, Mondal S, Masse C, Greenwood J, Harriman G, Ashwell MA, Bhat S, Wester R, Frye L, Kapeller R, Friesner RA (2017) Accelerating drug discovery through tight integration of expert molecular design and predictive scoring. Curr Opin Struct Biol 43:38–44
Wang L, Wu Y, Deng Y, Kim B, Pierce L, Krilov G, Lupyan D, Robinson S, Dahlgren MK, Greenwood J, Romero DL, Masse C, Knight JL, Steinbrecher T, Beuming T, Damm W, Harder E, Sherman W, Brewer M, Wester R, Murcko M, Frye L, Farid R, Lin T, Mobley DL, Jorgensen WL, Berne BJ, Friesner RA, Abel R (2015) Accurate and reliable prediction of relative ligand binding potency in prospective drug discovery by way of a modern free-energy calculation protocol and force field. J Am Chem Soc 137(7):2695–2703
Harder E, Damm W, Maple J, Wu C, Reboul M, Xiang JY, Wang L, Lupyan D, Dahlgren MK, Knight JL, Kaus JW, Cerutti DS, Krilov G, Jorgensen WL, Abel R, Friesner RA (2016) OPLS3: a force field providing broad coverage of drug-like small molecules and proteins. J Chem Theory Comput 12(1):281–296
Kuhn B, Tichý M, Wang L, Robinson S, Martin RE, Kuglstatter A, Benz J, Giroud M, Schirmeister T, Abel R, Diederich F, Hert J (2017) Prospective evaluation of free energy calculations for the prioritization of cathepsin L inhibitors. J Med Chem 60(6):2485–2497
Steinbrecher TB, Dahlgren M, Cappel D, Lin T, Wang L, Krilov G, Abel R, Friesner R, Sherman W (2015) Accurate binding free energy predictions in fragment optimization. J Chem Inf Model 55(11):2411–2420
Fang QK, Hopkins S, Jones S (2005) Espacenet - Bibliographic Data
FEP+, Schrödinger LLC (2017) New York, NY
Schrödinger Suite 2017–2 Protein Preparation Wizard, Epik, Prime, Schrödinger LLC (2017) New York, NY
Berman HM, Westbrook J, Feng Z, Gilliland G, Bhat TN, Weissig H, Shindyalov IN, Bourne PE (2000) The Protein Data Bank Nucleic Acids Research, 28(1):235–242
Glide, Schrödinger LLC (2017) New York, NY
Götz AW, Clark MA, Walker RC (2014) An extensible interface for QM/MM molecular dynamics simulations with AMBER. J Comput Chem 35(2):95–108
Hégely B, Bogár F, Ferenczy GG, Kállay M (2015) A QM/MM program using frozen localized orbitals and the Huzinaga equation. Theor Chem Acc 134(11):132
Song Z, Ogaya T, Ishii K, Ichiba H, Iizuka H, Fukushima T (2010) Utilization of kynurenic acid produced from d-Kynurenine in an in vitro assay of d-amino acid oxidase activity. J Heal Sci 56(3):341–346
Ku HH (1966) Notes on the use of propagation of error formulas. J Res 70c(4):263–273
Wang L, Deng Y, Knight JL, Wu Y, Kim B, Sherman W, Shelley JC, Lin T, Abel R (2013) Modeling local structural rearrangements using FEP/REST: application to relative binding affinity predictions of CDK2 inhibitors. J Chem Theory Comput 9(2):1282–1293
Brown SP, Muchmore SW, Hajduk PJ (2009) Healthy skepticism: assessing realistic model performance. Drug Discov Today 14(7–8):420–427
Ferenczy GG, Keserű GM (2016) On the enthalpic preference of fragment binding. Med Chem Commun 7(2):332–337
Freire E (2008) Do enthalpy and entropy distinguish first in class from best in class?. Drug Discovery Today 13(19–20):869–874
Ferenczy GG, Keserű GM (2015) The impact of binding thermodynamics on medicinal chemistry optimizations. Future Med Chem 7(10):1285–1303
Acknowledgements
Financial support by the National Brain Research Program (project KTIA NAP_13) and by the Hungarian Science Foundation OTKA (project K111862) is gratefully acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Orgován, Z., Ferenczy, G.G., Steinbrecher, T. et al. Validation of tautomeric and protomeric binding modes by free energy calculations. A case study for the structure based optimization of d-amino acid oxidase inhibitors. J Comput Aided Mol Des 32, 331–345 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10822-018-0097-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10822-018-0097-y