Abstract
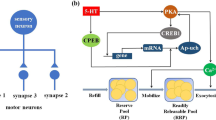
A model was developed to examine dynamical properties of regulatory motifs correlated with different temporal domains of memory. The model represents short-, intermediate-, and long-term phases of protein kinase A (PKA) activation, which appear related to corresponding phases of facilitation of the Aplysia sensorimotor synapse. The model also represents phosphorylation of the transcription factor CREB1 by PKA and consequent induction of the immediate-early gene Aplysia ubiquitin hydrolase (Ap-uch), which is essential for long-term synaptic facilitation (LTF). Simulations suggest mechanisms responsible for differing profiles of synaptic facilitation following massed vs. spaced exposures to 5-HT, and suggest a novel regulatory motif (gated positive feedback) is important for LTF. Simulations suggest zero-order ultrasensitivity may underlie a requirement of a threshold number of exposures to 5-HT for LTF induction. The model makes predictions for the dynamics of PKA activation and Ap-uch induction when MAP kinase is activated, or when repression of Ap-uch is relieved by inhibiting the transcription factor CREB2. This model may therefore be useful for understanding processes underlying memory formation in Aplysia and other systems.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agranoff BW, Davis RE, Brink, JJ,: (1965) Memory fixation in the goldfish. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 54: 788–793.
Alberts AS, Montminy M, Shenolikar S, Feramisco JR,: 1994 Expression of a peptide inhibitor of protein phosphatase 1 increases phosphorylation and activity of CREB in NIH 3T3 fibroblasts Mol. Cell. Biol. 14 4398–4407
Bacskai BJ, Hochner B, Mahaut-Smith M, Adams SR, Kaang B, Kandel ER, Tsien RY,: (1993) Spatially resolved dynamics of cAMP and protein kinase A subunits in Aplysia sensory neurons. Science 260: 222–226.
Bailey CH, Bartsch D, Kandel ER,: (1996) Toward a molecular definition of long-term memory storage. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 93: 13445–13552.
Barbas D, DesGroseillers L, Castellucci VF, Carew TJ, Marinesco S,: (2003) Multiple serotonergic mechanisms contributing to sensitization in Aplysia: Evidence of diverse serotonin receptor subtypes. Learn. Mem. 10: 373–386.
Barth AL, McKenna M, Glazewski S, Hill P, Impey S, Storm D, Fox K,: (2000) Upregulation of cAMP response element-mediated gene expression during experience-dependent plasticity in adult neocortex. J. Neurosci. 20: 4206–4216.
Bartsch D, Casadio A, Karl KA, Serodio P, Kandel ER,: (1998) CREB1 encodes a nuclear activator, a repressor, and a cytoplasmic modulator that form a regulatory unit critical for long-term facilitation. Cell 95: 211–223.
Bartsch D, Ghirardi M, Skehel PA, Karl KA, Herder SP, Chen M, Bailey CH, Kandel ER,: (1995) Aplysia CREB2 represses long-term facilitation: Relief of repression converts transient facilitation into long-term functional and structural change. Cell 83: 979–992.
Bergold PJ, Beushausen SA, Sacktor TC, Cheley S, Bayley H, Schwartz JH,: (1992) A regulatory subunit of the cAMP-dependent protein kinase down-regulated in Aplysia sensory neurons during long-term sensitization. Neuron 8: 387–397.
Byrne JH, Kandel ER,: (1996) Presynaptic facilitation revisited: State and time dependence. J. Neurosci. 16: 425–435.
Castellucci VF, Blumenfeld H, Goelet P, Kandel ER,: (1989) Inhibitor of protein synthesis blocks long-term behavioral sensitization in the isolated gill-withdrawal reflex of Aplysia. J. Neurobiol. 20: 1–9.
Chain DG, Casadio A, Schacher S, Hegde AN, Valbrun M, Yamamoto N, Goldberg AL, Bartsch D, Kandel ER, Schwartz JH,: (1999) Mechanisms for generating the autonomous cAMP-dependent protein kinase required for long-term facilitation in Aplysia. Neuron 22: 147–156.
Chain DG, Hegde AN, Yamamoto N, Liu-Marsh B, Schwartz JH,: (1995) Persistent activation of cAMP-dependent protein kinase by regulated proteolysis suggests a neuron-specific function of the ubiquitin system in Aplysia. J. Neurosci. 15: 7592–7603.
Clark GA, Kandel ER,: (1993) Induction of long-term facilitation in Aplysia sensory neurons by local application of serotonin to remote synapses. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 90: 11411– 11415.
Cleary LJ, Lee WL, Byrne JH,: (1998) Cellular correlates of long-term sensitization in Aplysia. J. Neurosci. 18: 5988–5998.
Crow T, Siddiqi V, Dash PK,: (1997) Long-term enhancement but not short-term in Hermissenda is dependent upon mRNA synthesis. Neurobiol. Learn. Mem. 68: 340–347.
Crow T, Xue-Bain J, Siddiqi V,: (1999) Protein synthesis-dependent and mRNA synthesis-independent intermediate phase of memory in Hermissenda. J. Neurophysiol. 82: 495–500.
Dash PK, Hochner B, Kandel ER,: (1990) Injection of the cAMP-responsive element into the nucleus of Aplysia sensory neurons blocks long-term facilitation. Nature 345: 718–721.
Davis HP, Squire LR,: (1984) Protein synthesis and memory: A review. Psych. Bull. 96: 518–559.
DeZazzo J, Tully T,: (1995) Dissection of memory formation from behavioral pharmacology to molecular genetics. Trends Neurosci. 18: 212–218.
Dudai Y,: (1989) The Neurobiology of Memory: Concepts, Findings, Trends. Oxford Univ. Press, New York, NY.
Dyer JR, Manseau F, Castellucci VF, Sossin WS,: (2003) Serotonin persistently activates the extracellular signal-related kinase in sensory neurons of Aplysia independently of cAMP or protein kinase C. Neuroscience 116: 13–17.
Emptage NJ, Carew TJ,: (1993) Long-term synaptic facilitation in the absence of short-term facilitation in Aplysia neurons. Science 262: 253–256.
English JD, Sweatt JD,: (1997) A requirement for the mitogen-activated protein kinase cascade in hippocampal long term potentiation. J. Biol. Chem. 272: 19103–19106.
Ferrell JE,: (1996) Tripping the switch fantastic: How a protein kinase cascade can convert graded inputs into switch-like outputs. Trends Bioch. Sci. 21: 460–466.
Frost WN, Castelluci VF, Hawkins RD, Kandel ER,: (1985) Monosynaptic connections made by the sensory neurons of the gill- and siphon-withdrawal reflex in Aplysia participate in the storage of long-term memory for sensitization. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 82: 8266–8269.
Genoux D, Haditsch U, Knobloch M, Michalon A, Storm D, Mansuy IM,: (2002) Protein phosphatase 1 is a molecular constraint on learning and memory. Nature 418: 970–975.
Ghirardi M, Montarolo PG, Kandel ER,: (1995) A novel intermediate stage in the transition between short-term and long-term facilitation in the sensory to motor neuron synapse of Aplysia. Neuron 14: 413–420.
Glanzman DL, Mackey SL, Hawkins RD, Dyke AM, Lloyd PE, Kandel ER,: (1989) Depletion of serotonin in the nervous system of Aplysia reduces the behavioral enhancement of gill withdrawal as well as the heterosynaptic facilitation produced by tail shock. J. Neurosci. 9: 4200–4213.
Goldsmith JR, Byrne JH,: (1993) Bag cell extract inhibits tail-siphon withdrawal reflex, suppresses long-term but not short-term sensitization, and attenuates sensory-to-motor neuron synapses in Aplysia. J. Neurosci. 13: 1688–1700.
Goldbeter A, Koshland DE,: (1984) Ultrasensitivity in biochemical systems controlled by covalent modification; interplay between zero-order and multistep effects. J. Biol. Chem. 259: 14441–14447.
Greenberg SM, Castellucci VF, Bayley H, Schwartz JH,: (1987) A molecular mechanism for long-term sensitization in Aplysia. Nature 329: 62–65.
Guzowski JF, McGaugh JL,: (1997) Antisense oligodeoxyri- bonucleotide-mediated disruption of hippocampal cAMP response element binding protein levels impairs consolidation of memory for water maze training. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 94: 2693–2698.
Hegde AN, Goldberg AL, Schwartz JH,: (1993) Regulatory subunits of cAMP-dependent protein kinase are degraded after conjugation to ubiquitin: A molecular mechanism underlying long-term synaptic plasticity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 90: 7436–7440.
Hegde AN, Inokuchi K, Pei W, Casadio A, Ghirardi M, Chain DG, Martin KC, Kandel ER, Schwartz JH,: (1997) Ubiquitin C-terminal hydrolase is an immediate-early gene essential for long-term facilitation in Aplysia. Cell 89: 115–126.
Herberg FW, Taylor SS, Dostmann WR,: (1996) Active site mutations define the pathway for the cooperative activation of cAMP-dependent protein kinase. Biochemistry 35: 2934–2942.
Huang CF, Ferrell JE,: (1996) Ultrasensitivity in the mitogen-activated protein kinase cascade. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 93: 10078–10083.
Huang YS, Jung MY, Sarkissian M, Richter JD,: (2002) N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor signaling results in Aurora kinase-catalyzed CPEB phosphorylation and α -CaMKII mRNA polyadenylation at synapses. EMBO J. 21: 2139–2148.
Huang YY, Martin KC, Kandel ER,: (2000) Both protein kinase A and mitogen-activated protein kinase are required in the amygdala for the macromolecular synthesis-dependent late phase of long-term potentiation. J. Neurosci. 20: 6317–6325.
Ichinose M, Byrne JH,: (1991) Role of protein phosphatases in the modulation of neuronal membrane currents. Brain Res. 549: 146–150.
Josselyn SA, Shi C, Carlezon WA, Neve RL, Nestler EJ, Davis M,: (2001) Long-term memory is facilitated by cAMP response element-binding protein overexpression in the amygdala. J. Neurosci. 21: 2404–2412.
Kida S, Josselyn SA, de Ortiz SP, Kogan JH, Chevere I, Masushige S, Silva AJ,: (2002) CREB required for the stability of new and reactivated fear memories. Nat. Neurosci. 5: 348– 355.
Leloup JC, Goldbeter A,: (1998) A model for circadian rhythms in Drosophila incorporating the formation of a complex between the PER and TIM proteins. J. Biol. Rhythms. 13: 70–87.
Levenson J, Byrne JH, Eskin A,: (1999) Levels of serotonin in the hemolymph of Aplysia are modulated by light/dark cycles and sensitization training. J. Neurosci. 19: 8094–8103.
Lin CH, Lee CC, Gean PW,: (2003) Involvement of a calcineurin cascade in amygdala depotentiation and quenching of fear memory. Mol. Pharmacol. 63: 44–52.
Levenson J, Endo S, Kategaya LS, Fernandez RI, Brabham DG, Chin J, Byrne JH, Eskin A,: (2000) Long-term regulation of neuronal high-affinity glutamate and glutamine uptake in Aplysia. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 97: 12858–12863.
Liu J, Hu JY, Schacher S, Schwartz JH,: (2004) The two regulatory subunits of Aplysia cAMP-dependent protein kinase mediate distinct functions in producing synaptic plasticity. J. Neurosci. 24: 2465–2474.
Liu J, Schwartz JH,: (2003) The cytoplasmic polyadenylation element binding protein and polyadenylation of messenger RNA in Aplysia neurons. Brain Res. 959: 68–76.
Lonze BE, Ginty DD,: (2002) Function and regulation of CREB family transcription factors in the nervous system. Neuron 35: 605– 623.
Marinesco S, Carew TJ,: (2002) Serotonin release evoked by tail nerve stimulation in the CNS of Aplysia: Characterization and relationship to heterosynaptic plasticity. J. Neurosci. 22: 2299– 2312.
Martin KC, Casadio A, Zhu H, Yaping E, Rose JC, Chen M, Bailey CH, Kandel ER,: (1997a) Synapse-specific, long-term facilitation of Aplysia sensory to motor synapses: A function for local protein synthesis in memory storage. Cell 91: 927– 938.
Martin SJ, Grimwood PD, Morris RG,: (2000) Synaptic plasticity and memory: An evaluation of the hypothesis. Annu. Rev. Neurosci. 23: 649–711.
Martin KC, Michael D, Rose JC, Barad M, Casadio A, Zhu H, Kandel ER,: (1997b) MAP kinase translocates into the nucleus of the presynaptic cell and is required for long-term facilitation in Aplysia. Neuron. 18: 899–912.
Martin SJ, Morris RG,: (2002) New life in an old idea: The synaptic plasticity and memory hypothesis revisited. Hippocampus 12: 609–636.
Matsushita M, Tomizawa K, Moriwaki A, Li ST,: (2001) A high-efficiency protein transduction system demonstrating the role of PKA in long-lasting long-term potentiation. J. Neurosci. 21: 6000–6007.
Mauelshagen J, Parker GR, Carew TJ,: (1996) Dynamics of induction and expression of long-term synaptic facilitation in Aplysia. J. Neurosci. 16: 7099–7108.
Mauelshagen J, Parker GR, Carew TJ,: (1998) Differential induction of long-term synaptic facilitation by spaced and massed applications of serotonin at sensory neuron synapses of Aplysia californica. Learn. Mem. 5: 246–256.
Mayford M, Kandel ER,: (1999) Genetic approaches to memory storage. Trends Genet. 15: 463–470.
McGaugh JL,: (2000) Memory—A century of consolidation. Science 287: 248–251.
Michael D, Martin KC, Seger R, Ning M, Baston R, Kandel ER,: (1998) Repeated pulses of serotonin required for long-term facilitation activate mitogen-activated protein kinase in sensory neurons of Aplysia. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 95: 1864– 1869.
Montarolo PG, Goelet P, Castellucci VF, Morgan J, Kandel ER, Schacher S,: (1986) A critical period for macromolecular synthesis in long-term heterosynaptic facilitation in Aplysia. Science 234: 1249–1253.
Müller U, Carew TJ,: (1998) Serotonin induces temporally and mechanistically distinct phases of persistent PKA activity in Aplysia sensory neurons. Neuron. 21: 1423–1434.
Ocorr KA, Byrne JH,: (1985) Membrane responses and changes in cAMP levels in Aplysia sensory neurons produced by serotonin, tryptamine, FMRFamide and small cardioactive peptide B: (SCPB). Neurosci. Lett. 55: 113–118.
Pinsker H, Carew TJ, Hening W, Kandel ER,: (1973) Long-term sensitization of a defensive withdrawal reflex in Aplysia californica. Science 182: 1039–1042.
Pittenger C, Huang YY, Paletzki RF, Bourtchouladze R, Scanlin H, Vronskaya S, Kandel ER,: (2002) Reversible inhibition of CREB/ATF transcription factors in region CA1 of the dorsal hippocampus disrupts hippocampus-dependent spatial memory. Neuron 34: 447–462.
Purcell AL, Sharma SK, Bagnall MW, Sutton, MA, Carew TJ,: (2003) Activation of a tyrosine kinase-MAPK cascade enhances the induction of long-term synaptic facilitation and long-term memory in Aplysia. Neuron. 37: 473–484.
Rosenzweig MR, Bennett EL, Colombo PJ, Lee DW, Serrano PA,: (1993) Short-term, intermediate-term, and long-term memories. Behav. Brain Res. 57: 193–198.
Sangha S, Scheibenstock A, McComb C, Lukowiak K,: (2003) Intermediate and long-term memories of associative learning are differentially affected by transcription versus translation blockers in Lymnaea. J. Exp. Biol. 206: 1605–1613.
Scholz KP, Byrne JH,: (1987) Long-term sensitization in Aplysia: Biophysical correlates in tail sensory neurons. Science 235: 685–687.
Sharma SK, Bagnall MW, Sutton MA, Carew TJ,: (2003b) Inhibition of calcineurin facilitates the induction of memory for sensitization in Aplysia: Requirement of mitogen-activated protein kinase. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 100: 4861–4866.
Sharma SK, Sherff CM, Shobe J, Bagnall MW, Sutton MA, Carew TJ,: (2003a) Differential role of mitogen-activated protein kinase in three distinct phases of memory for sensitization in Aplysia. J. Neurosci. 23: 3899–3907.
Sherff CM, Carew TJ,: (2004) Parallel somatic and synaptic processing in the induction of intermediate-term and long-term synaptic facilitation in Aplysia. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 101: 7463–7468.
Si K, Giustetto M, Etkin A, Hsu R, Janisiewicz AM, Miniaci MC, Kim JH, Zhu H, Kandel ER,: (2003) A neuronal isoform of CPEB regulates local protein synthesis and stabilizes synapse-specific long-term facilitation in Aplysia. Cell 115: 893–904.
Sutton MA, Carew TJ,: (2000) Parallel molecular pathways mediate expression of distinct forms of intermediate-term facilitation at tail sensory–motor synapses in Aplysia. Neuron. 26: 219– 231.
Sutton MA, Ide J, Masters SE, Carew TJ,: (2002) Interaction between amount and pattern of training in the induction of intermediate- and long-term memory for sensitization in Aplysia. Learn. Mem. 9: 29–40.
Sutton MA, Masters SE, Bagnall MW, Carew TJ,: (2001) Molecular mechanisms underlying a unique intermediate phase of memory in Aplysia. Neuron. 31: 143–154.
Theis M, Si K, Kandel ER,: (2003) Two previously undescribed members of the mouse CPEB family of genes and their inducible expression in the principal cell layers of the hippocampus. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 100: 9602–9607.
Tully T, Preat T, Boynton SC, Del Vecchio M,: (1994) Genetic dissection of consolidated memory in Drosophila. Cell. 79: 35– 47.
Wainwright ML, Byrne JH, Cleary LJ,: (2004) Dissociation of morphological and physiological changes associated with long-term memory in Aplysia. J. Neurophysiol. 92: 2628– 2632.
Wainwright ML, Zhang H, Byrne JH, Cleary LJ,: (2002) Localized neuronal outgrowth induced by long-term sensitization training in Aplysia. J. Neurosci. 22: 4132–4141.
Walters ET,: (1987a) Site-specific sensitization of defensive reflexes in Aplysia: A simple model of long-term hyperalgesia. J. Neurosci. 7: 400–407.
Walters ET,: (1987b) Multiple sensory neuronal correlates of site-specific sensitization in Aplysia. J. Neurosci. 7: 408–417.
Wright WG, McCance EF, Carew TJ,: (1996) Developmental emergence of long-term memory for sensitization in Aplysia. Neurobiol. Learn Mem. 65: 261–268.
Wu X, Spiro C, Owen WG, McMurray CT,: (1998) cAMP response element binding protein monomers cooperatively assemble to form dimers on DNA. J. Biol. Chem. 273: 20820– 20827.
Zhang F, Endo S, Cleary LJ, Eskin A, Byrne JH,: (1997) Role of transforming growth factor-β in long-term synaptic facilitation in Aplysia. Science 275: 1318–1320.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pettigrew, D.B., Smolen, P., Baxter, D.A. et al. Dynamic Properties of Regulatory Motifs Associated with Induction of Three Temporal Domains of Memory in Aplysia. J Comput Neurosci 18, 163–181 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10827-005-6557-0
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10827-005-6557-0