Abstract
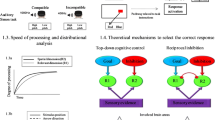
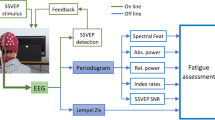
Even though it has long been felt that psychological state influences the performance of brain-computer interfaces (BCI), formal analysis to support this hypothesis has been scant. This study investigates the inter-relationship between motor imagery (MI) and mental fatigue using EEG: a. whether prolonged sequences of MI produce mental fatigue and b. whether mental fatigue affects MI EEG class separability. Eleven participants participated in the MI experiment, 5 of which quit in the middle because of experiencing high fatigue. The growth of fatigue was monitored using the Kernel Partial Least Square (KPLS) algorithm on the remaining 6 participants which shows that MI induces substantial mental fatigue. Statistical analysis of the effect of fatigue on motor imagery performance shows that high fatigue level significantly decreases MI EEG separability. Collectively, these results portray an MI-fatigue inter-connection, emphasizing the necessity of developing adaptive MI BCI by tracking mental fatigue.















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adel, T., Wong, A., Stashuk, D. (2015). A weakly supervised learning approach based on spectral graph-theoretic grouping. arXiv:150800507.
Blankertz, B., Losch, F., Krauledat, M., Dornhege, G., Curio, G., Müller, K.R. (2008). The Berlin brain-computer interface: accurate performance from first-session in BCI-naive subjects. IEEE Transactions on Biomedical Engineering, 55(10), 2452–2462.
Borghini, G., Vecchiato, G., Toppi, J., Astolfi, L., Maglione, A., Isabella, R., Caltagirone, C., Kong, W., Wei, D., Zhou, Z., Polidori, L., Vitiello, S., Babiloni, F. (2012). Assessment of mental fatigue during car driving by using high resolution EEG activity and neurophysiologic indices. In IEEE 34th annual international conference on the engineering in medicine and biology society (EMBC) (pp. 6442–6445).
Borghini, G., Astolfi, L., Vecchiato, G., Mattia, D., Babiloni, F. (2014). Measuring neurophysiological signals in aircraft pilots and car drivers for the assessment of mental workload, fatigue and drowsiness. Neuroscience & Biobehavioral Reviews, 44, 58–75.
Caldwell, J.A., Hall, K.K., Erickson, B.S. (2002). EEG data collected from helicopter pilots in flight are sufficiently sensitive to detect increased fatigue from sleep deprivation. The International Journal of Aviation Psychology, 12(1), 19–32.
Cao, T., Wan, F., Wong, C.M., da Cruz, J.N., Hu, Y. (2014). Objective evaluation of fatigue by EEG spectral analysis in steady-state visual evoked potential-based brain-computer interfaces. Biomedical Engineering Online, 13(1), 28.
Cella, M., & Chalder, T. (2010). Measuring fatigue in clinical and community settings. Journal of Psychosomatic Research, 69(1), 17–22.
Chai, R., Tran, Y., Naik, G.R., Nguyen, T.N., Ling, S.H., Craig, A., Nguyen, H.T. (2016). Classification of EEG based-mental fatigue using principal component analysis and Bayesian neural network. In IEEE 38th annual international conference on the engineering in medicine and biology society (EMBC) (pp. 4654–4657).
Chai, R., Ling, S.H., San, P.P., Naik, G.R., Nguyen, T.N., Tran, Y., Craig, A., Nguyen, H.T. (2017a). Improving EEG-based driver fatigue classification using sparse-deep belief networks. Frontiers in Neuroscience, 11.
Chai, R., Naik, G.R., Nguyen, T.N., Ling, S.H., Tran, Y., Craig, A., Nguyen, H.T. (2017b). Driver fatigue classification with independent component by entropy rate bound minimization analysis in an EEG-based system. IEEE Journal of Biomedical and Health Informatics, 21(3), 715–724.
Charbonnier, S., Roy, R.N., Bonnet, S., Campagne, A. (2016). EEG index for control operators’ mental fatigue monitoring using interactions between brain regions. Expert Systems with Applications, 52, 91–98.
Cover, T.M., & Thomas, J.A. (2012). Elements of information theory. New York: Wiley.
Craig, A., Tran, Y., Wijesuriya, N., Nguyen, H. (2012). Regional brain wave activity changes associated with fatigue. Psychophysiology, 49(4), 574–582.
Davies, D.L., & Bouldin, D.W. (1979). A cluster separation measure. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence 1(2), 224–227.
Duda, R.O., Hart, P.E., Stork, D.G. (1973). Pattern classification. New York: Wiley.
Dunn, J.C. (1973). A fuzzy relative of the ISODATA process and its use in detecting compact well-separated clusters. Journal of Cybernetics, 3(3), 32–57.
Ekštein, K., & Pavelka, T. (2004). Entropy and entropy-based features in signal processing. In Proceedings of PhD workshop systems & control.
Ge, S., Wang, R., Yu, D. (2014). Classification of four-class motor imagery employing single-channel electroencephalography. PloS One, 9(6), e98,019.
Górski, P. (2014). Common spatial patterns in a few channel BCI interface. Journal of Theoretical and Applied Computer Science, 8(4), 56–63.
Hasan, B.A.S. (2010). Adaptive methods exploiting the time structure in EEG for self-paced brain-computer interfaces. PhD thesis, University of Essex.
Jackson, S.A., Thomas, P.R., Marsh, H.W., Smethurst, C.J. (2001). Relationships between flow, self-concept, psychological skills, and performance. Journal of Applied Sport Psychology, 13(2), 129–153.
Jap, B.T., Lal, S., Fischer, P., Bekiaris, E. (2009). Using EEG spectral components to assess algorithms for detecting fatigue. Expert Systems with Applications, 36(2), 2352–2359.
Jensen, O., Goel, P., Kopell, N., Pohja, M., Hari, R., Ermentrout, B. (2005). On the human sensorimotor-cortex beta rhythm: sources and modeling. Neuroimage, 26(2), 347–355.
Kar, S., Bhagat, M., Routray, A. (2010). EEG signal analysis for the assessment and quantification of driver’s fatigue. Transportation Research Part F: Traffic Psychology and Behaviour, 13(5), 297–306.
Lal, S.K., & Craig, A. (2002). Driver fatigue: electroencephalography and psychological assessment. Psychophysiology, 39(3), 313–321.
Lee, K.A., Hicks, G., Nino-Murcia, G. (1991). Validity and reliability of a scale to assess fatigue. Psychiatry Research, 36(3), 291–298.
Liu, J., Zhang, C., Zheng, C. (2010). EEG-based estimation of mental fatigue by using KPCA–HMM and complexity parameters. Biomedical Signal Processing and Control, 5(2), 124–130.
Löster, T. (2016). Determining the optimal number of clusters in cluster analysis. In The 10th international days of statistics and economics, Prague.
Lu, H., Plataniotis, K.N., Venetsanopoulos, A.N. (2009). Regularized common spatial patterns with generic learning for EEG signal classification. In IEEE annual international conference on engineering in medicine and biology society (pp. 6599–6602).
Mammone, N., & Morabito, F.C. (2014). Enhanced automatic wavelet independent component analysis for electroencephalographic artifact removal. Entropy, 16(12), 6553–6572.
Montgomery, L.D., Montgomery, R.W., Guisado, R. (1995). Rheoencephalographic and electroencephalographic measures of cognitive workload: analytical procedures. Biological Psychology, 40(1–2), 143–159.
Myrden, A., & Chau, T. (2015). Effects of user mental state on EEG-BCI performance. Frontiers in Human Neuroscience, 9, 308.
Papadelis, C., Kourtidou-Papadeli, C., Bamidis, P.D., Chouvarda, I., Koufogiannis, D., Bekiaris, E., Maglaveras, N. (2006). Indicators of sleepiness in an ambulatory EEG study of night driving. In IEEE 28th annual international conference on engineering in medicine and biology society (pp. 6201–6204).
Petrovic, S. (2006). A comparison between the silhouette index and the davies-bouldin index in labelling ids clusters. In Proceedings of the 11th Nordic workshop of secure IT systems (pp. 53– 64).
Pomer-Escher, A., Tello, R., Castillo, J., Bastos-Filho, T. (2014). Analysis of mental fatigue in motor imagery and emotional stimulation based on EEG. In XXIV Congresso Brasileiro de Engenharia Biomedica-CBEB.
Ramoser, H., Muller-Gerking, J., Pfurtscheller, G. (2000). Optimal spatial filtering of single trial EEG during imagined hand movement. IEEE Transactions on Rehabilitation Engineering, 8(4), 441–446.
Romero, P., & Calvillo-Gámez, E. (2013). An embodied view of flow. Interacting with Computers, 26(6), 513–527.
Rosipal, R., & Trejo, L.J. (2001). Kernel partial least squares regression in reproducing kernel hilbert space. Journal of Machine Learning Research, 2, 97–123.
Roy, R.N., Charbonnier, S., Bonnet, S. (2014). Detection of mental fatigue using an active BCI inspired signal processing chain. IFAC Proceedings Volumes, 47(3), 2963–2968.
Rozand, V., Lebon, F., Stapley, P.J., Papaxanthis, C., Lepers, R. (2016). A prolonged motor imagery session alter imagined and actual movement durations: potential implications for neurorehabilitation. Behavioural Brain Research, 297, 67–75.
Talukdar, U., & Hazarika, S.M. (2016). Estimation of mental fatigue during EEG based motor imagery. In International conference on intelligent human computer interaction (pp. 122–132). Berlin: Springer.
Talukdar, U., & Hazarika, S.M. (2017). Designing optimal spatio-temporal filter for single trial EEG based BCI. In 3rd international conference on advances in robotics (AIR). ACM.
Talukdar, U., Hazarika, S.M., Gan, J.Q. (2018). A Kernel Partial least square based feature selection method. Pattern Recognition, 83, 91–106.
Trejo, L.J., Kubitz, K., Rosipal, R., Kochavi, R.L., Montgomery, L.D. (2015). EEG-based estimation and classification of mental fatigue. Psychology, 6(05), 572.
Zhang, Y., Chen, Y., Bressler, S.L., Ding, M. (2008). Response preparation and inhibition: the role of the cortical sensorimotor beta rhythm. Neuroscience, 156(1), 238–246.
Zhao, C., Zheng, C., Zhao, M., Tu, Y., Liu, J. (2011). Multivariate autoregressive models and kernel learning algorithms for classifying driving mental fatigue based on electroencephalographic. Expert Systems with Applications, 38(3), 1859–1865.
Zhou, M. (2016). Hybrid feature selection method based on fisher score and genetic algorithm. Journal of Mathematical Sciences: Advances and Applications, 37, 51–78.
Acknowledgements
Financial support from MHRD as Centre of Excellence on Machine Learning Research and Big Data Analysis is gratefully acknowledged. Assistance received from DST-UKEIRI Project: DST/INT/UK/P-91/2014 is also acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Action Editor: Sridevi Sarma
Appendix A
Appendix A
1.1 A.1 Visual Analogue Scale- Fatigue
1.2 A.2 Chalder Fatigue Scale
1.3 A.3 Fatigue Scale (FS) at the end of each run
1.4 A.4 Plot of the trends of KPLS scores and subjective scores for runs 1–8
1.5 A.5 Plot of the trends of KPLS scores and subjective scores for runs 2–7
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Talukdar, U., Hazarika, S.M. & Gan, J.Q. Motor imagery and mental fatigue: inter-relationship and EEG based estimation. J Comput Neurosci 46, 55–76 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10827-018-0701-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10827-018-0701-0