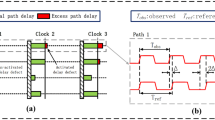
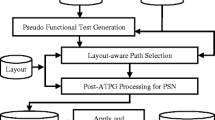
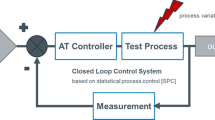
Abstract
In this study, a novel path clustering technique for adaptive path delay testing, where the test paths are altered according to the extracted device parameters, is proposed. The proposed algorithm is based on the k-means++ algorithm. By considering the probability function of the die-to-die systematic process variation, the proposed algorithm clusters path sets to minimize the total number of test paths. A figure of merit for clustering, which represents the expected number of test paths, is also proposed for quantitatively evaluating path clustering under different conditions. The proposed clustering method is evaluated numerically by applying it to the OpenCores benchmark circuit. Using our clustering technique, the average number of test paths in the adaptive test is reduced to less than 92 % compared with those in the conventional test. In addition, adaptive testing using the proposed technique can reduce the test patterns by 94.26 % while retaining the test quality.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arthur D, Vassilvitskii S (2007) K-means++: the advantages of careful seeding. In: Proceedings of ACM-SIAM symposium on discrete algorithms, pp 1027–1035
Benner S, Boroffice O (2001) Optimal production test times through adaptive test programming. In: Proceedings of IEEE international test conference, pp 908–915
Chan TB, Kahng AB (2012) Improved path clustering for adaptive path-delay testing. In: Proceedings of IEEE international symposium on quality electronic design, pp 13–20
Chang H, Sapatnekar S (2005) Statistical timing analysis under spatial correlations. IEEE Trans Comput Aided Des Integr Circuits Syst 24(9):1467–1482
Jiayong Le XL, Pileggi LT (2004) STAC statistical timing analysis with correlation. In: Proceedings of IEEE/ACM design automation conference, pp 343–348
Lin CJ, Reddy SM (1987) On delay fault testing in logic circuits. IEEE Trans Ind Electron 6:694–703
Madge R, Benware B, Ward M, Daasch R (2005) The value of statistical testing for quality, yield and test cost improvement. In: Proceedings of IEEE international test conference, pp 322–332
Mahfuzul IAKM, Tsuchiya A, Kobayashi K, Onodera H (2012) Variation-sensitive monitor circuits for estimation of global process parameter variation. IEEE Trans Semicond Manuf 25(4):571–580
Opencores. [Online], Available: http://www.opencores.org
Saxena S, Hess C, Karbasi H, Rossoni A, Tonello S, McNamara P, Lucherini S, Minehane S, Dolainsky C, Quarantelli M (2008) Variation in transistor performance and leakage in nanometer-scale technologies. IEEE Trans Electron Devices 55(1):131–144
Segura J, Keshavarzi A, Soden J, Hawkins C (2002) Parametric failures in CMOS ICs - a defect-based analysis. In: Proceedings of IEEE international test conference, pp 90–99
Semiconductor industry association: international technology roadmap for semiconductors, 2013 edition. [Online]. Available: http://www.itrs.net
Shintani M, Sato A (2012) A bayesian-based process parameter estimation using IDDQ current signature. In: Proceedings of IEEE VLSI test symposium, pp 86–91
Shintani M, Sato T (2014) Sensorless estimation of global device-parameter based on fmax testing. In: Proceedings of IEEE/ACM international conference on computer-aided design, pp 498–503
Shintani M, Uezono T, Takahashi T, Hatayama K, Aikyo T, Masu K, Sato T (2014) A variability-aware adaptive test flow for test quality improvement. IEEE Trans Comput Aided Des Integr Circuits Syst 33(7):1056–1066
Sivaraman M, Strojwas AJ (1996) Delay fault coverage A realistic metric and an estimation technique for distributed path delay faults. In: Proceedings of IEEE/ACM international conference on computer-aided design, pp 494–501
Smith GL (1985) Model for delay faults based upon paths. In: Proceedings of IEEE international test conference, pp 342–349
Synopsys Inc. (2013) Design compiler user guide version I-2013.12
Synopsys Inc. (2013) HSPICE user guide: basic simulation and analysis version I-2013.12
Synopsys Inc. (2013) PrimeTime fundamental user guide version H-2013.06
Synopsys Inc. (2013) TetraMAX ATPG user guide version I-2013.12
Takahashi T, Uezono T, Shintani M, Masu K, Sato T (2009) On-die parameter extraction from Path-Delay measurements. In: Proceedings of IEEE asian solid-state circuits conference, pp 101–104
Visweswariah C, Ravindran K, Kalafala K, Walker SG, Narayan S, Beece DK, Piaget J, Venkateswaran N, Hemmett JG (2004) First-order incremental block-based statistical timing analysis. In: Proceedings of IEEE/ACM design automation conference, pp 331–336
Zolotov V, Xiong J, Fatemi H, Visweswariah C (2008) Statistical path selection for at-speed test. In: Proceedings of IEEE/ACM international conference on computer-aided design, pp 624–631
Acknowledgments
This work has been partly supported by JSPS KAKENHI Grant No. 15K15960 and by VDEC, the University of Tokyo, in collaboration with Synopsys, Inc.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible Editor: K.-J. Lee
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shintani, M., Uezono, T., Hatayama, K. et al. Path Clustering for Test Pattern Reduction of Variation-Aware Adaptive Path Delay Testing. J Electron Test 32, 601–609 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10836-016-5614-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10836-016-5614-0