Abstract
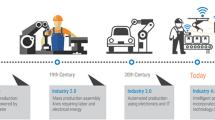
The Internet of Things (IoT) has a significant effect on the development of manufacturing technology. Therefore, according to the analysis of the challenges and opportunities faced by manufacturing industry, this study uses the assembly process of mechanical products as the research object and analyzes the characteristics of IoT-based manufacturing systems. To improve the interconnection, perception, efficiency, and intelligence of the assembly system, this study proposes the concept of IoT-enabled intelligent assembly system for mechanical products (IIASMP). The IIASMP framework, which is based on advanced techniques such as information and communication technology, sensor network, and radio-frequency identification, is then presented. Key technologies under this framework, including assembly resources identification, information interaction technology, multi-source data perception and fusion, intelligent assembly agent, and value-added data and dynamic self-adaptive optimization, are described. Finally, the current results of IIASMP are described in the case study. The proposed framework and methods aims to have an important reference value for applying the key technologies and be used widely in the intelligent manufacturing field.


















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aguilar-Ponce, R., Kumar, A., Tecpanecatl-Xihuitl, J. L., & Bayoumi, M. (2007). A network of sensor-based framework for automated visual surveillance. Journal of Network and Computer Applications, 30(3), 1244–1271.
Al-Habaibeh, A., & Parkin, R. (2003). An autonomous low-cost infrared system for the online monitoring of manufacturing processes using novelty detection. International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology, 22(3–4), 249–258.
Atlas, L. E., Bernard, G. D., & Narayanan, S. B. (1996). Applications of time-frequency analysis to signals from manufacturing and machine monitoring sensors. Proceedings of the IEEE, 84(9), 1319–1329.
Atzori, L., Iera, A., & Morabito, G. (2010). The internet of things: A survey. Computer Networks, 54(15), 2787–2805.
Bargelis, A., Hoehne, G., & Cesnulevicius, A. (2004). Intelligent functional model for costs minimization in hybrid manufacturing systems. Informatica, 15(1), 3–22.
Beach, R., Muhlemann, A. P., Price, D. H. R., Paterson, A., & Sharp, J. A. (2000). A review of manufacturing flexibility. European Journal of Operational Research, 122(1), 41–57.
Changfeng, Y., Dinghua, Z., Wenli, P., & Kun, B. (2006). Research on resources optimisation deployment model and algorithm for collaborative manufacturing process. International Journal of Production Research, 44(16), 3279–3301.
Chaves, L. W., & Nochta, Z. (2011). Breakthrough towards the internet of things. In D. C. Ranasinghe, Q. Z. Sheng & S. Zeadally (Eds.), Unique Radio Innovation For The 21st Century (pp. 25–38). Berlin: Springer. http://link.springer.com/chapter/10.1007/978-3-642-03462-6_2 .
Chen, R. S., & Tu, M. A. (2009). Development of an agent-based system for manufacturing control and coordination with ontology and RFID technology. Expert Systems with Applications, 36(4), 7581–7593.
Chen, K. Y. (2012). Cell controller design for RFID based flexible manufacturing systems. International Journal of Computer Integrated Manufacturing, 25(1), 35–50.
Chiu, S. W. (2008). An optimization problem of manufacturing systems with stochastic machine breakdown and rework process. Applied Stochastic Models in Business and Industry, 24(3), 203–219.
Choudhary, A. K., Harding, J. A., & Tiwari, M. K. (2009). Data mining in manufacturing: A review based on the kind of knowledge. Journal of Intelligent Manufacturing, 20(5), 501–521.
Chryssolouris, G., Mavrikios, D., Papakostas, N., Mourtzis, D., Michalos, G., & Georgoulias, K. (2009). Digital manufacturing: History, perspectives, and outlook. Proceedings of the Institution of Mechanical Engineers, Part B: Journal of Engineering Manufacture, 223(5), 451–462.
Cutting-Decelle, A. F., Young, R. I., Michel, J. J., Grangel, R., Le Cardinal, J., & Bourey, J. P. (2007). ISO 15531 MANDATE: A product-process-resource based approach for managing modularity in production management. Concurrent Engineering, 15(2), 217–235.
Dai, Q., Zhong, R., Huang, G. Q., Qu, T., Zhang, T., & Luo, T. (2012). Radio frequency identification-enabled real-time manufacturing execution system: A case study in an automotive part manufacturer. International Journal of Computer Integrated Manufacturing, 25(1), 51–65.
Deshpande, S., & Cagan, J. (2004). An agent based optimization approach to manufacturing process planning. Journal of Mechanical Design, 126(1), 46–55.
Drath, R., Luder, A., Peschke, J., & Hundt, L. (2008). AutomationML-the glue for seamless automation engineering. In IEEE international conference on emerging technologies and factory automation, 2008. ETFA 2008. (pp. 616–623). doi:10.1109/ETFA.2008.4638461.
Edinbarough, I., Balderas, R., & Bose, S. (2005). A vision and robot based online inspection monitoring system for electronic manufacturing. Computers in Industry, 56(8–9), 986–996.
Giusto, D., Lera, A., Morabito, G., & Atzori, L. (2010). The Internet of Things. Berlin: Springer.
Golnabi, H., & Asadpour, A. (2007). Design and application of industrial machine vision systems. Robotics and Computer-Integrated Manufacturing, 23(6), 630–637.
Guo, Q., & Zhang, M. (2008). Research on intelligent manufacturing system based on multi-agent. In C. Xiong, H. Liu, Y. Huang & Y. Xiong (Eds.), Intelligent Robotics and Applications (pp. 829–838). Berlin: Springer. http://link.springer.com/chapter/10.1007/978-3-540-88518-4_89.
Guo, Q., & Zhang, M. (2009). A novel approach for multi-agent-based intelligent manufacturing system. Information Sciences, 179(18), 3079–3090.
Huang, C. Y. (2002). Distributed manufacturing execution systems: A workflow perspective. Journal of Intelligent Manufacturing, 13(6), 485–497.
Jain, A., Jain, P. K., Chan, F. T., & Singh, S. (2013). A review on manufacturing flexibility. International Journal of Production Research, 51(19), 5946–5970.
Jardim-Goncalves, R., Sarraipa, J., Agostinho, C., & Panetto, H. (2011). Knowledge framework for intelligent manufacturing systems. Journal of Intelligent Manufacturing, 22(5), 725–735.
Jiang, C. Y., Wang, J. B., & Jiang, J. J. (2006). Research on analyzing and coding technology of manufacturing information resource based on granularity-structure. In C. Jiang, G. Liu, D. Zhang & X. Xu (Eds.), Materials science forum (Vol. 532, pp. 1080–1083). Pune: Trans Tech Publications. http://www.scientific.net/MSF.532-533.1080.
Kletti, J. (2007). Manufacturing execution systems-MES. Berlin: Springer.
Kumar, P., Barua, P., & Gaindhar, J. (2000). Quality optimization (multi-characteristics) through Taguchi’s technique and utility concept. Quality and Reliability Engineering International, 16(6), 475–485.
Lee, C. S., Jiang, C. C., & Hsieh, T. C. (2006). A genetic fuzzy agent using ontology model for meeting scheduling system. Information Sciences, 176(9), 1131–1155.
Liu, W., Zheng, L., Sun, D., Liao, X., Zhao, M., Su, J., et al. (2012). RFID-enabled real-time production management system for Loncin motorcycle assembly line. International Journal of Computer Integrated Manufacturing, 25(1), 86–99.
Luck, M., & d’Inverno, M. (2001). A conceptual framework for agent definition and development. The Computer Journal, 44(1), 1–20.
Madejski, J. (2007). Survey of the agent-based approach to intelligent manufacturing. Journal of Achievements in Materials and Manufacturing Engineering, 21(1), 67–70.
Makris, S., Michalos, G., & Chryssolouris, G. (2012). RFID driven robotic assembly for random mix manufacturing. Robotics and Computer-Integrated Manufacturing, 28(3), 359–365.
McFarlane, D., Sarma, S., Chirn, J. L., Wong, C. Y., & Ashton, K. (2003). Auto-ID systems and intelligent manufacturing control. Engineering Applications of Artificial Intelligence, 16(4), 365–376.
Michalos, G., Makris, S., Papakostas, N., Mourtzis, D., & Chryssolouris, G. (2010). Automotive assembly technologies review: Challenges and outlook for a flexible and adaptive approach. CIRP Journal of Manufacturing Science and Technology, 2(2), 81–91.
Mitchell, H. B. (2007). An introduction. In MultiSensor data fusion (pp. 3–13). Berlin: Springer.
Monostori, L., & Prohaszka, J. (1993). A step towards intelligent manufacturing: Modelling and monitoring of manufacturing processes through artificial neural networks. CIRP Annals-Manufacturing Technology, 42(1), 485–488.
Nasr, E. S. A., & Kamrani, A. K. (2008). Intelligent design and manufacturing. In A. K. Kamrani & E. S. Abouel Nasr (Eds.), Collaborative engineering (pp. 103–125). New York: Springer. http://link.springer.com/chapter/10.1007/978-0-387-47321-5_6.
Nearchou, A. C., & Omirou, S. L. (2006). Differential evolution for sequencing and scheduling optimization. Journal of Heuristics, 12(6), 395–411.
Oztemel, E. (2010). Intelligent manufacturing systems. In L. Benyoucef & B. Grabot (Eds.), Artificial intelligence techniques for networked manufacturing enterprises management (pp. 1–41). London: Springer. http://link.springer.com/chapter/10.1007/978-0-387-47321-5_6.
Oztemel, E., & Tekez, E. K. (2009). A general framework of a reference model for intelligent integrated manufacturing systems (REMIMS). Engineering Applications of Artificial Intelligence, 22(6), 855–864.
Qu, T., Yang, H., Huang, G. Q., Zhang, Y., Luo, H., & Qin, W. (2012). A case of implementing RFID-based real-time shop-floor material management for household electrical appliance manufacturers. Journal of Intelligent Manufacturing, 23(6), 2343–2356.
Ruiz, N., Giret, A., Botti, V., & Feria, V. (2011). Agent-supported simulation environment for intelligent manufacturing and warehouse management systems. International Journal of Production Research, 49(5), 1469–1482.
Sabar, M., Montreuil, B., & Frayret, J.-M. (2012). An agent-based algorithm for personnel shift-scheduling and rescheduling in flexible assembly lines. Journal of Intelligent Manufacturing, 23(6), 2623–2634.
Saenz de Ugarte, B., Artiba, A., & Pellerin, R. (2009). Manufacturing execution system—a literature review. Production Planning and Control, 20(6), 525–539.
Silvestre, J., & Sempere, V. (2007). An architecture for flexible scheduling in Profibus networks. Computer Standards & Interfaces, 29(5), 546–560.
Sung, W. T., & Hsu, Y. C. (2011). Designing an industrial real-time measurement and monitoring system based on embedded system and ZigBee. Expert Systems with Applications, 38(4), 4522–4529.
Thiesse, F., Floerkemeier, C., Harrison, M., Michahelles, F., & Roduner, C. (2009). Technology, standards, and real-world deployments of the EPC network. IEEE Internet Computing, 13(2), 36–43.
Trappey, A. J., Lu, T.-H., & Fu, L.-D. (2009). Development of an intelligent agent system for collaborative mold production with RFID technology. Robotics and Computer-Integrated Manufacturing, 25(1), 42–56.
Tseng, M. C., & Lin, W. Y. (2001). Mining generalized association rules with multiple minimum supports. In Y. Kambayashi, W. Winiwarter & M. Arikawa (Eds.), Data warehousing and knowledge discovery (pp. 11–20). Berlin, Springer. http://link.springer.com/chapter/10.1007/3-540-44801-2_2.
Tu, M., Lin, J. H., Chen, R. S., Chen, K. Y., & Jwo, J. S. (2009). Agent-based control framework for mass customization manufacturing with UHF RFID technology. Ieee Systems Journal, 3(3), 343–359.
Wang, X. Z., & McGreavy, C. (1998). Automatic classification for mining process operational data. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 37(6), 2215–2222. doi:10.1021/ie970620h.
Youssef, S. M., & Salem, R. M. (2007). Automated barcode recognition for smart identification and inspection automation. Expert Systems with Applications, 33(4), 968–977.
Zayati, A., Biennier, F., Moalla, M., & Badr, Y. (2012). Towards lean service bus architecture for industrial integration infrastructure and pull manufacturing strategies. Journal of Intelligent Manufacturing, 23(1), 125–139.
Zhang, H. P., Gen, M. S., & Seo, Y. H. (2006). An effective coding approach for multiobjective integrated resource selection and operation sequences problem. Journal of Intelligent Manufacturing, 17(4), 385–397.
Zhang, Y., Huang, G. Q., Qu, T., & Ho, O. (2010). Agent-based workflow management for RFID-enabled real-time reconfigurable manufacturing. International Journal of Computer Integrated Manufacturing, 23(2), 101–112.
Zhang, Y., Jiang, P., Huang, G., Qu, T., Zhou, G., & Hong, J. (2012). RFID-enabled real-time manufacturing information tracking infrastructure for extended enterprises. Journal of Intelligent Manufacturing, 23(6), 2357–2366.
Zijm, W. (2000). Towards intelligent manufacturing planning and control systems. OR-Spektrum, 22(3), 313–345.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to acknowledge the financial support of the National Science Foundation of China (51375134) and National Basic Research Program of China (973 Program #2011CB013406).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, M., Ma, J., Lin, L. et al. Intelligent assembly system for mechanical products and key technology based on internet of things. J Intell Manuf 28, 271–299 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10845-014-0976-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10845-014-0976-6