Abstract
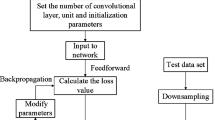
Remaining useful life prediction methods are extensively researched based on failure or suspension histories. However, for some applications, failure or suspension histories are hard to obtain due to high reliability requirement or expensive experiment cost. In addition, some systems’ work condition cannot be simulated. According to current research, remaining useful life prediction without failure or suspension histories is challenging. To solve this problem, an individual-based inference method is developed using recorded condition monitoring data to date. Features extracted from condition data are divided by adaptive time windows. The time window size is adjusted according to increasing rate. Features in two adjacent selected windows are regarded as the inputs and outputs to train an artificial neural network. Multi-step ahead rolling prediction is employed, predicted features are post-processed and regarded as inputs in the next prediction iteration. Rolling prediction is stopped until a prediction value exceeds failure threshold. The proposed method is validated by simulation bearing data and PHM-2012 Competition data. Results demonstrate that the proposed method is a promising intelligent prognostics approach.

























Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ab, S. I. (2002). The shock pulse method for determining condition of anti-friction bearings: SPM Technical Information. Sweden: SPM Instruments AB.
Aydın, I., Karaköse, M., & Ak, E. (2013). Combined intelligent methods based on wireless sensor networks for condition monitoring and fault diagnosis. Journal of Intelligent Manufacturing. doi:10.1007/s10845-013-0829-8.
Benkedjouh, T., Medjaher, K., Zerhouni, N., & Rechak, S. (2015). Health assessment and life prediction of cutting tools based on support vector regression. Journal of Intelligent Manufacturing, 26(2), 213–223.
Chen, C., Vachtsevanos, G., & Orchard, M. E. (2012). Machine remaining useful life prediction: An integrated adaptive neuro-fuzzy and high-order particle filtering approach. Mechanical Systems and Signal Processing, 28, 597–607.
Di Maio, F., Tsui, K. L., & Zio, E. (2012). Combining relevance vector machines and exponential regression for bearing residual life estimation. Mechanical Systems and Signal Processing, 31, 405–427.
Fink, O., Zio, E., & Weidmann, U. (2014). Predicting component reliability and level of degradation with complex-valued neural networks. Reliability Engineering and System Safety, 121, 198–206.
Heng, A., Zhang, S., Tan, A. C. C., & Mathew, J. (2009). Rotating machinery prognostics: State of the art, challenges and opportunities. Mechanical Systems and Signal Processing, 23(3), 724–739.
Hu, C., Youn, B. D., Wang, P., & Yoon, J. T. (2012). Ensemble of data-driven prognostic algorithms for robust prediction of remaining useful life. Reliability Engineering and System Safety, 103, 120–135.
Huang, R., Xi, L., Li, X., Richard Liu, C., Qiu, H., & Lee, J. (2007). Residual life predictions for ball bearings based on self-organizing map and back propagation neural network methods. Mechanical Systems and Signal Processing, 21(1), 193–207.
IEEE, PHM 2012 Data Challenge (2012). http://www.femto-st.fr/en/Research-departments/AS2M/Research-groups/PHM/IEEE-PHM-2012-Data-challenge.php.
Jardine, A. K. S., Lin, D., & Banjevic, D. (2006). A review on machinery diagnostics and prognostics implementing condition-based maintenance. Mechanical Systems and Signal Processing, 20(7), 1483–1510.
Lee, J., Wu, F., Zhao, W., Ghaffari, M., Liao, L., & Siegel, D. (2014). Prognostics and health management design for rotary machinery systems—Reviews, methodology and applications. Mechanical Systems and Signal Processing, 42(1–2), 314–334.
Li, C. J., & Lee, H. (2005). Gear fatigue crack prognosis using embedded model, gear dynamic model and fracture mechanics. Mechanical Systems and Signal Processing, 19(4), 836–846.
Liu, D., Deters, R., & Zhang, W. J. (2010). Architectural design for resilience. Enterprise Information Systems, 4(2), 137–152.
Lu, C., Tao, L., & Fan, H. (2014). An intelligent approach to machine component health prognostics by utilizing only truncated histories. Mechanical Systems and Signal Processing, 42(1–2), 300–313.
Marble, S., & Morton, B. P. (2006). Predicting the remaining life of propulsion system bearings. In Aerospace conference, IEEE, Big Sky, MT.
McFadden, P. D., & Smith, J. D. (1984). Model for the vibration produced by a single point defect in a rolling element bearing. Journal of Sound and Vibration, 96(1), 69–82.
Mehta, P., Werner, A., & Mears, L. (2015). Condition based maintenance-systems integration and intelligence using Bayesian classification and sensor fusion. Journal of Intelligent Manufacturing, 26, 331–346.
Mi, L., Tan, W., & Chen, R. (2013). Multi-steps degradation process prediction for bearing based on improved back propagation neural network. Proceedings of the Institution of Mechanical Engineers Part C: Journal of Mechanical Engineering Science, 227(7), 1544–1553.
Mosallam, A., Medjaher, K., & Zerhouni, N. (2014). Data-driven prognostic method based on Bayesian approaches for direct remaining useful life prediction. Journal of Intelligent Manufacturing. doi:10.1007/s10845-014-0933-4.
Ragab, A., Ouali, M., Yacout, S., & Osman, H. (2014). Remaining useful life prediction using prognostic methodology based on logical analysis of data and Kaplan-Meier estimation. Journal of Intelligent Manufacturing. doi:10.1007/s10845-014-0926-3.
Si, X., Wang, W., Hu, C., & Zhou, D. (2011). Remaining useful life estimation—A review on the statistical data driven approaches. European Journal of Operational Research, 213(1), 1–14.
Sikorska, J. Z., Hodkiewicz, M., & Ma, L. (2011). Prognostic modelling options for remaining useful life estimation by industry. Mechanical Systems and Signal Processing, 25(5), 1803–1836.
Tian, Z. (2012). An artificial neural network method for remaining useful life prediction of equipment subject to condition monitoring. Journal of Intelligent Manufacturing, 23(2), 227–237.
Tian, Z., Wong, L., & Safaei, N. (2010). A neural network approach for remaining useful life prediction utilizing both failure and suspension histories. Mechanical Systems and Signal Processing, 24(5), 1542–1555.
Tian, Z., & Zuo, M. J. (2010). Health condition prediction of gears using a recurrent neural network approach. IEEE Transactions on Reliability, 59(4), 700–705.
Tran, V. T., Yang, B., Oh, M., & Tan, A. C. C. (2008). Machine condition prognosis based on regression trees and one-step-ahead prediction. Mechanical Systems and Signal Processing, 22(5), 1179–1193.
Tran, V. T., Yang, B., & Tan, A. C. C. (2009). Multi-step ahead direct prediction for the machine condition prognosis using regression trees and neuro-fuzzy systems. Expert Systems with Applications, 36(5), 9378–9387.
Wang, D., Miao, Q., & Pecht, M. (2013). Prognostics of lithium-ion batteries based on relevance vectors and a conditional three-parameter capacity degradation model. Journal of Power Sources, 239, 253–264.
Wang, Y. F., & Kootsookos, P. J. (1998). Modeling of low shaft speed bearing faults for condition monitoring. Mechanical Systems and Signal Processing, 12(3), 415–426.
Wang, Y., Deng, C., Wu, J., & Xiong, Y. (2013). Failure time prediction for mechanical device based on the degradation sequence. Journal of Intelligent Manufacturing. doi:10.1007/s10845-013-0849-4.
Yang, C. K. (2011). Fatigue effect on task performance in haptic virtual environment for home-based rehabilitation. Master thesis, Department of Biomedical Engineering, University of Saskatchewan.
Zhang, W. J., & Lin, Y. (2010). On the principle of design of resilient systems—application to enterprise information systems. Enterprise Information Systems, 4(2), 99–110.
Zhang, W. J., & van Luttervelt, C. A. (2011). Toward a resilient manufacturing system. CIRP Annals-Manufacturing Technology, 60(1), 469–472.
Zhang, X., Kang, J., & Jin, T. (2014). Degradation modeling and maintenance decisions based on bayesian belief networks. IEEE Transactions on Reliability, 63(2), 620–633.
Zhang, Z., Wang, Y., & Wang, K. (2013). Fault diagnosis and prognosis using wavelet packet decomposition, Fourier transform and artificial neural network. Journal of Intelligent Manufacturing, 24, 1213–1227.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank great support from Key Project supported by National Science Foundation of China (51035008) and the Fundamental Research Funds for the State Key Laboratory of Mechanical Transmission, Chongqing University (SKLMT-ZZKT-2012 MS 02).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xiao, L., Chen, X., Zhang, X. et al. A novel approach for bearing remaining useful life estimation under neither failure nor suspension histories condition. J Intell Manuf 28, 1893–1914 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10845-015-1077-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10845-015-1077-x